Visualizing Data: The Power of Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map
Related Articles: Visualizing Data: The Power of Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Data: The Power of Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Visualizing Data: The Power of Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Visualizing Data: The Power of Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map
- 3.1 The Significance of Visualizing Location Data
- 3.2 Tools and Techniques for Plotting Multiple Locations
- 3.3 Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
- 3.4 Applications of Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map
- 3.5 FAQs about Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map
- 3.6 Tips for Plotting Multiple Locations Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Visualizing Data: The Power of Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map
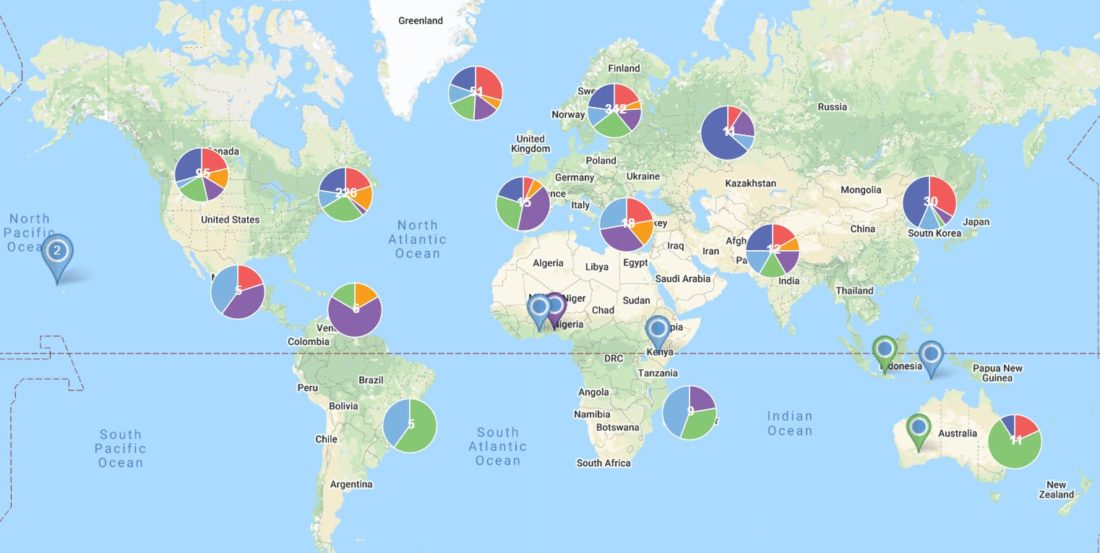
In a world increasingly reliant on data, the ability to visualize information effectively is paramount. Maps, long used for navigation, have evolved into powerful tools for data representation, offering a unique advantage: spatial context. Plotting multiple locations on a map transforms raw data into a compelling narrative, revealing patterns, relationships, and insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
The Significance of Visualizing Location Data
The ability to plot multiple locations on a map transcends simple visualization. It empowers us to:
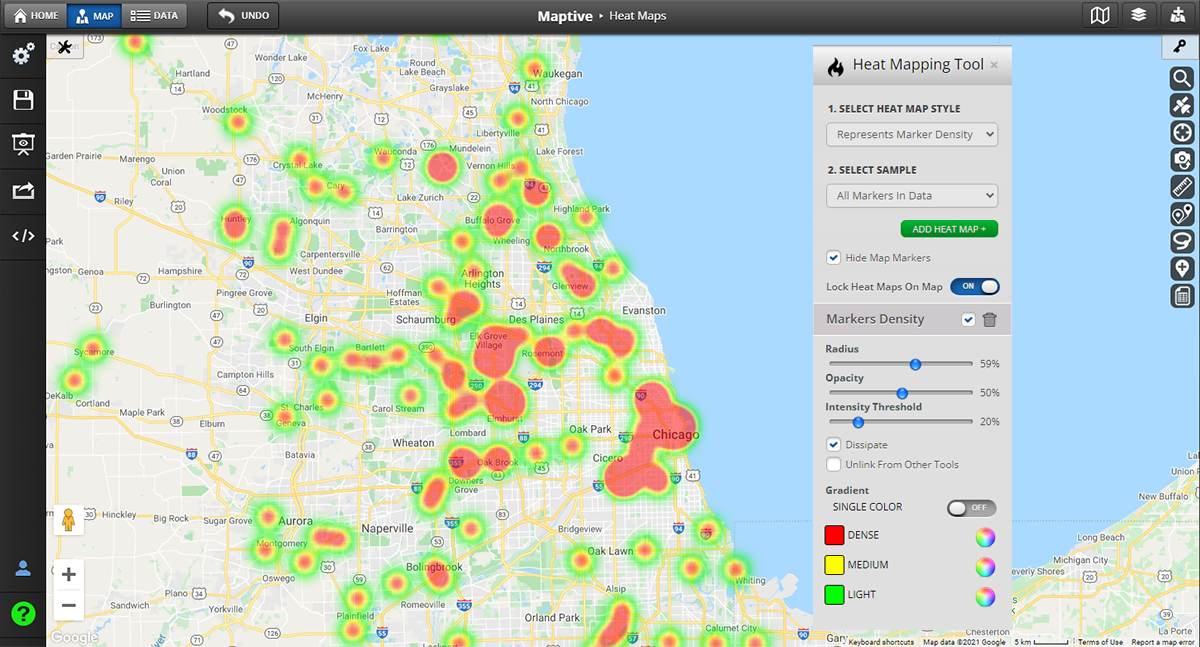
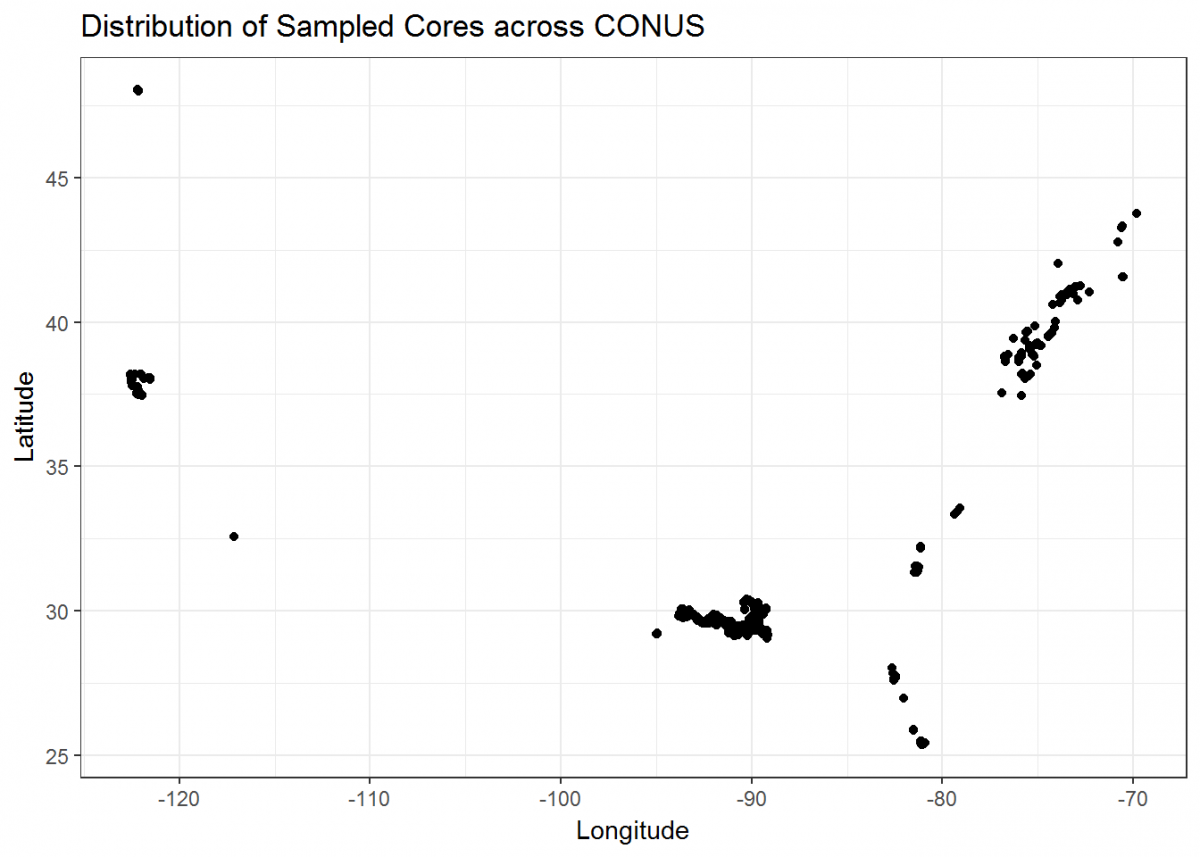
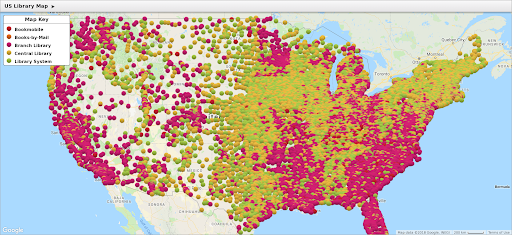
- Understand Spatial Distribution: Visualizing the geographic spread of data points reveals clusters, outliers, and regional trends. This is invaluable for understanding population density, disease outbreaks, market penetration, or environmental hazards.
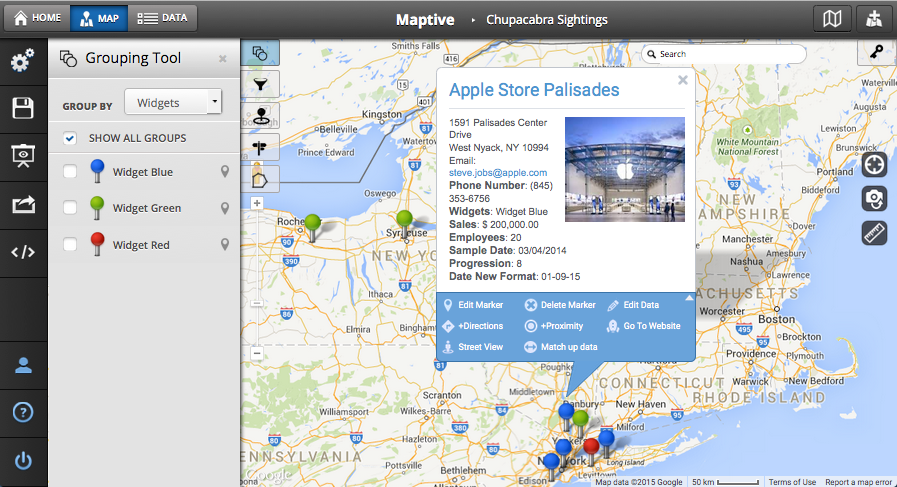
- Analyze Relationships: By plotting multiple locations, we can identify connections and correlations. For example, mapping crime hotspots against socioeconomic factors can reveal potential underlying causes.
- Communicate Effectively: Maps provide a readily understandable visual language. They effectively convey complex data to diverse audiences, making information more accessible and engaging.
- Support Decision-Making: Informed decisions require a clear understanding of spatial relationships. By visualizing data on a map, stakeholders can gain a holistic view of the situation, leading to more strategic and effective interventions.
Tools and Techniques for Plotting Multiple Locations
Numerous tools and techniques exist for plotting multiple locations on a map, each with its own strengths and applications.
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS):
GIS software is the gold standard for advanced spatial analysis. These powerful platforms offer a wide range of capabilities, including:
- Data Management: GIS allows for the efficient storage, management, and manipulation of geographically referenced data.
- Map Creation: GIS provides sophisticated tools for creating custom maps with various layers, symbology, and projections.
- Spatial Analysis: GIS offers advanced analytical functions, such as proximity analysis, spatial autocorrelation, and network analysis, to uncover deeper insights.
- Data Visualization: GIS enables the creation of interactive maps, 3D visualizations, and dynamic dashboards for effective data communication.
2. Online Mapping Platforms:
User-friendly online mapping platforms like Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap provide accessible tools for basic mapping tasks. These platforms offer:
- Easy Location Identification: Simple search functions allow for quick location identification.
- Marker Placement: Users can easily drop markers on the map to represent specific locations.
- Basic Data Visualization: Some platforms allow for basic data visualization through color-coding markers or adding simple charts.
- Sharing and Collaboration: Maps can be shared and embedded in websites or documents, facilitating collaboration and communication.
3. Programming Libraries and APIs:
For more customized and programmatic mapping solutions, programming libraries and APIs offer greater flexibility. Popular options include:
- Leaflet: A lightweight JavaScript library for creating interactive maps.
- Mapbox: A platform providing customizable basemaps and APIs for building advanced map applications.
- OpenStreetMap: A collaborative project offering open-source data and APIs for creating maps.
4. Spreadsheet Software:
Even spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel can be used for basic location plotting.
- Geocoding: Excel offers tools for converting addresses into latitude and longitude coordinates, enabling location plotting.
- Data Visualization: Excel can create simple maps and charts to visualize location data.
5. Data Visualization Tools:
Specialized data visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI offer powerful capabilities for creating interactive maps and dashboards. These platforms excel in:
- Data Integration: Seamless integration with various data sources.
- Visual Storytelling: Tools for creating engaging narratives through interactive maps and visualizations.
- Dashboard Creation: Building dashboards that combine maps with other data visualizations for comprehensive insights.
Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
The choice of tool for plotting multiple locations depends on the specific requirements of the task. Consider the following factors:
- Data Complexity: For complex data analysis and sophisticated visualizations, GIS software is ideal.
- User Skill Level: Online mapping platforms are user-friendly for basic mapping tasks, while programming libraries require technical expertise.
- Customization Needs: Programming libraries and APIs offer the greatest flexibility for customizing maps and functionality.
- Budget: Online mapping platforms are often free, while GIS software and specialized data visualization tools can incur costs.
Applications of Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map
The applications of plotting multiple locations on a map are vast and diverse, spanning various fields:
1. Business:
- Market Research: Mapping customer locations, competitor locations, and market potential to identify growth opportunities.
- Sales and Distribution: Optimizing delivery routes and territories for efficient logistics.
- Site Selection: Identifying suitable locations for new stores, offices, or manufacturing facilities.
2. Government:
- Emergency Response: Mapping emergency locations, evacuation routes, and resource distribution during disasters.
- Urban Planning: Visualizing population density, infrastructure, and public services for effective city planning.
- Environmental Monitoring: Mapping pollution levels, deforestation patterns, and wildlife habitats for environmental protection.
3. Healthcare:
- Disease Surveillance: Tracking the spread of diseases and identifying hotspots for targeted interventions.
- Healthcare Access: Mapping healthcare facilities and their accessibility to ensure equitable healthcare distribution.
- Public Health Campaigns: Targeting public health campaigns based on population demographics and geographic distribution.
4. Education:
- Geography Education: Visualizing geographic features, cultural landscapes, and historical events.
- Environmental Studies: Mapping biodiversity hotspots, climate change impacts, and conservation efforts.
- Social Studies: Mapping population movements, migration patterns, and social inequalities.
5. Research and Development:
- Scientific Data Visualization: Mapping research data, experimental results, and geographic phenomena.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation: Extracting insights from spatial data for research and decision-making.
- Modeling and Simulation: Creating virtual environments for testing hypotheses and simulating real-world scenarios.
FAQs about Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map
1. What are the benefits of plotting multiple locations on a map?
Visualizing data on a map provides a powerful way to understand spatial relationships, reveal patterns and trends, communicate information effectively, and support informed decision-making.
2. What types of data can be plotted on a map?
Various data types can be plotted on a map, including location data (addresses, coordinates), demographic data (population density, age distribution), environmental data (pollution levels, weather patterns), and socioeconomic data (income, education levels).
3. What are some common applications of plotting multiple locations on a map?
Mapping multiple locations has applications in various fields, including business, government, healthcare, education, and research. It is used for market research, emergency response, disease surveillance, urban planning, environmental monitoring, and many other purposes.
4. What are some popular tools for plotting multiple locations on a map?
Popular tools include GIS software (ArcGIS, QGIS), online mapping platforms (Google Maps, Bing Maps), programming libraries (Leaflet, Mapbox), spreadsheet software (Microsoft Excel), and data visualization tools (Tableau, Power BI).
5. How can I learn to plot multiple locations on a map?
Numerous resources are available online and in educational institutions. Online tutorials, documentation, and courses offer guidance on using various mapping tools and techniques.
Tips for Plotting Multiple Locations Effectively
- Define Your Objective: Clearly identify the purpose of your map and the insights you aim to convey.
- Choose the Right Data: Select relevant and accurate data that aligns with your objectives.
- Select Appropriate Tools: Choose tools that best suit your data complexity, skill level, and customization needs.
- Design for Clarity: Use clear and concise map elements, such as markers, colors, and labels, to ensure readability.
- Tell a Story: Use map features and data visualization techniques to create a compelling narrative and communicate your insights effectively.
- Consider Accessibility: Design maps that are accessible to all users, including those with visual impairments.
Conclusion
Plotting multiple locations on a map transforms data into compelling visuals, revealing spatial patterns, relationships, and insights. By leveraging the power of maps, we can gain a deeper understanding of the world around us, make informed decisions, and communicate information effectively. With the right tools and techniques, mapping multiple locations becomes a powerful tool for exploring data, uncovering hidden trends, and driving informed action.
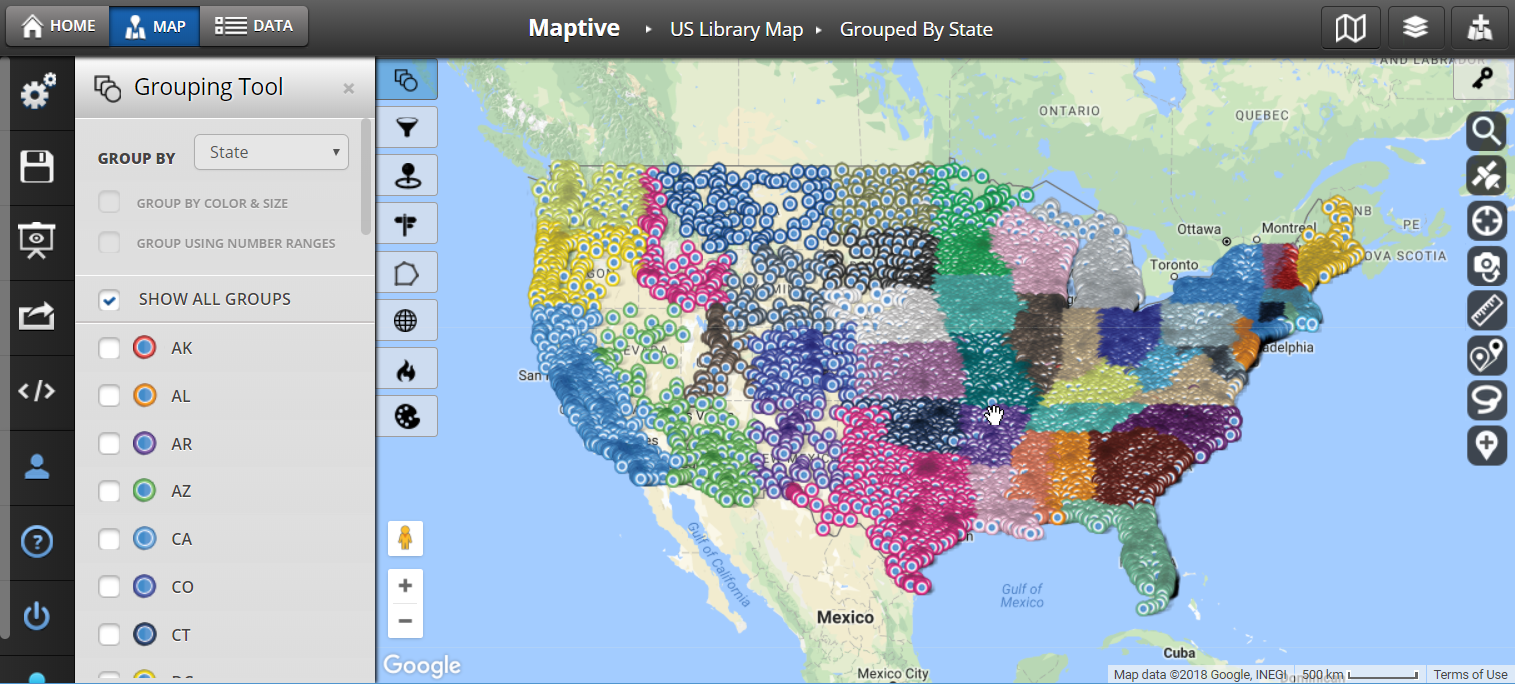
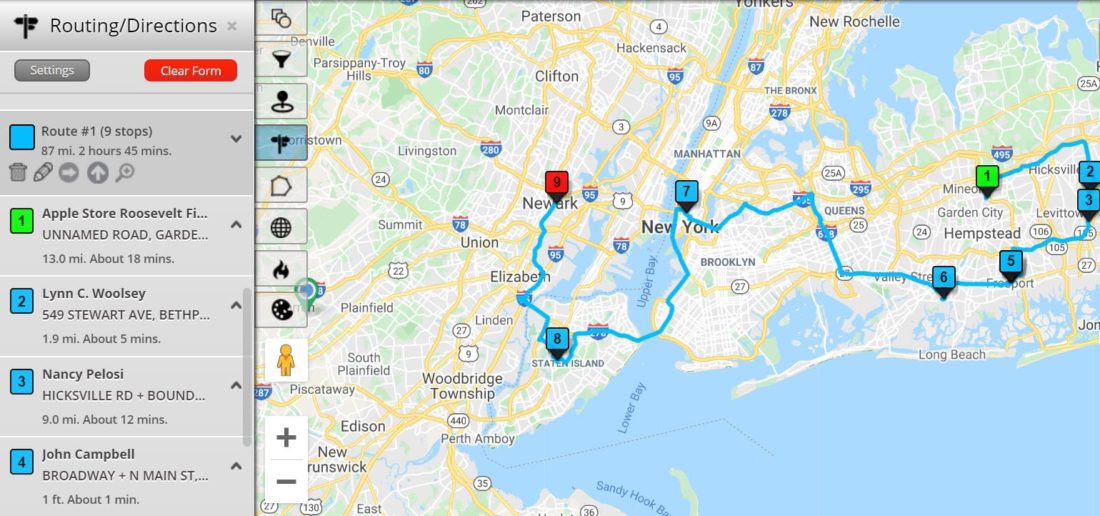
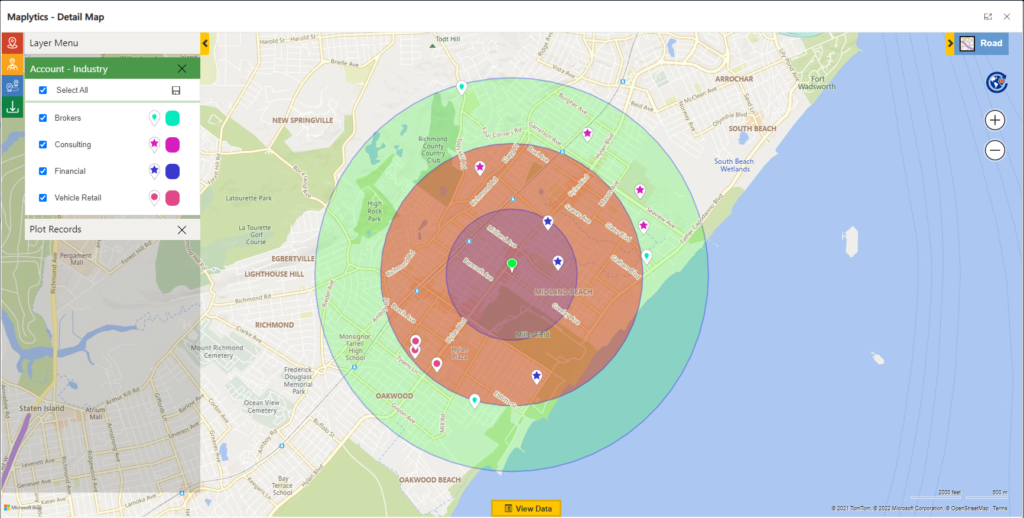
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Data: The Power of Plotting Multiple Locations on a Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!