Unveiling the World: A Journey Through the Map of Ibn Battuta
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Journey Through the Map of Ibn Battuta
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Journey Through the Map of Ibn Battuta. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: A Journey Through the Map of Ibn Battuta

Ibn Battuta, the 14th-century Moroccan traveler, remains a legendary figure in the annals of exploration. His extensive journeys, spanning over three decades and covering vast swathes of the known world, are documented in his seminal work, "Rihla" (The Journey). This captivating narrative not only recounts his personal experiences but also provides invaluable insights into the socio-cultural landscape of the 14th century.
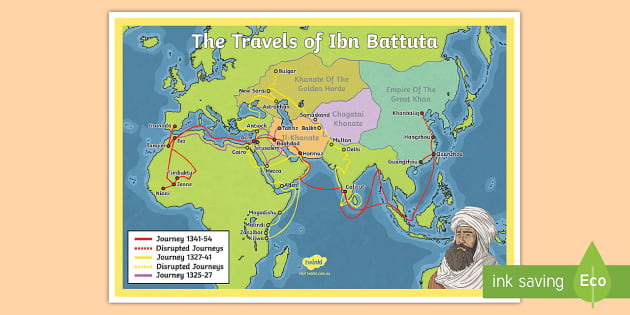
A Map of Unparalleled Scope:
While the "Rihla" itself is a treasure trove of information, its geographical scope is best visualized through a map. Ibn Battuta’s travels, encompassing over 120,000 kilometers, crisscrossed continents, traversing the Arabian Peninsula, Africa, the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, and even reaching China. This remarkable feat of exploration, undertaken during a time when travel was arduous and fraught with danger, makes his journey all the more impressive.
Decoding the Map:
A map depicting Ibn Battuta’s travels reveals a complex tapestry of trade routes, religious centers, and cultural interactions. It showcases the interconnectedness of the world in the 14th century, highlighting the flow of goods, ideas, and people across vast distances.
Key Locations and Their Significance:
1. Tangier, Morocco: The starting point of Ibn Battuta’s epic journey. Tangier served as a vital port city, connecting North Africa with the rest of the Mediterranean world.
2. Mecca, Saudi Arabia: A crucial destination for any Muslim traveler, Mecca held immense religious significance. Ibn Battuta’s pilgrimage to Mecca marked the beginning of his extended travels.
3. Cairo, Egypt: A bustling center of learning, trade, and culture, Cairo was a pivotal stop for Ibn Battuta. He spent several years in the city, immersing himself in its vibrant intellectual and social life.
4. The Indian Subcontinent: Ibn Battuta spent over a decade in the Indian subcontinent, traveling extensively across its diverse regions. He encountered various cultures, religions, and customs, documenting them meticulously in his "Rihla."
5. Southeast Asia: Ibn Battuta’s journey extended to Southeast Asia, reaching as far as the Maldive Islands and China. He observed the unique cultures and trade practices of these regions, offering valuable insights into the interconnectedness of the ancient world.
Beyond the Physical Journey:
While the map vividly portrays the physical journey, it also offers a glimpse into the intellectual and cultural landscape of the 14th century. Ibn Battuta’s observations on political structures, social customs, religious practices, and economic activities provide a rich understanding of the world he traversed.
Benefits of Studying Ibn Battuta’s Map:
- Historical Understanding: The map offers a unique perspective on the interconnectedness of the world in the 14th century, revealing the flow of goods, ideas, and people across vast distances.
- Cultural Insights: Ibn Battuta’s observations on diverse cultures, religions, and customs provide invaluable insights into the social fabric of the ancient world.
- Geographical Knowledge: The map serves as a valuable resource for understanding the geographical landscape of the 14th century, highlighting key trade routes, religious centers, and cultural hubs.
- Inspiration for Exploration: Ibn Battuta’s journey serves as a powerful reminder of the human spirit’s capacity for exploration and discovery, inspiring future generations to embrace the unknown.
FAQs about Ibn Battuta’s Travels Map:
1. What is the purpose of mapping Ibn Battuta’s travels?
Mapping Ibn Battuta’s travels serves multiple purposes:
- To visually represent the vast scope and extent of his journey.
- To understand the geographical context of his observations and experiences.
- To analyze the interconnectedness of the world in the 14th century.
2. How accurate is the map of Ibn Battuta’s travels?
The accuracy of the map is dependent on the available historical data and the interpretation of Ibn Battuta’s descriptions. While some locations can be pinpointed with precision, others remain subject to debate and scholarly interpretation.
3. What are the challenges in creating a map of Ibn Battuta’s travels?
Creating an accurate map of Ibn Battuta’s travels presents several challenges:
- Lack of Precise Coordinates: Ibn Battuta’s descriptions often rely on relative distances and landmarks, making it difficult to pinpoint exact locations.
- Changing Geography: The geographical landscape has undergone significant changes since the 14th century, making it challenging to accurately represent the locations described by Ibn Battuta.
- Interpreting Descriptions: Ibn Battuta’s writing style and the cultural context of his time require careful interpretation to understand the locations and events he describes.
4. What are the key resources for understanding Ibn Battuta’s travels?
The primary resource for understanding Ibn Battuta’s travels is his own account, "Rihla." Scholars have also produced numerous studies and interpretations of his journey, offering valuable insights into his travels and the world he traversed.
5. How does Ibn Battuta’s map compare to other historical maps?
Ibn Battuta’s map stands out for its scope and detail, encompassing a wider geographical area than many other historical maps of the period. It provides a unique perspective on the interconnectedness of the world in the 14th century, highlighting the flow of goods, ideas, and people across continents.
Tips for Studying Ibn Battuta’s Travels Map:
- Focus on Key Locations: Identify the major cities and regions visited by Ibn Battuta and understand their significance in the context of his journey.
- Analyze Trade Routes: Examine the trade routes depicted on the map and understand their role in connecting different regions and cultures.
- Explore Cultural Exchanges: Identify the cultural exchanges and interactions that took place along Ibn Battuta’s route, highlighting the flow of goods, ideas, and people.
- Consider Historical Context: Understand the political, social, and economic context of the 14th century to better interpret Ibn Battuta’s observations and experiences.
Conclusion:
Ibn Battuta’s travels map is a testament to the human spirit’s capacity for exploration and discovery. It reveals the interconnectedness of the world in the 14th century, highlighting the flow of goods, ideas, and people across vast distances. Beyond its geographical significance, the map offers valuable insights into the cultural, social, and religious landscape of the ancient world, providing a rich understanding of the past and inspiring future generations to embrace the unknown. Studying Ibn Battuta’s travels map allows us to embark on a journey through time, uncovering the intricate tapestry of human history and the enduring legacy of a remarkable traveler.





![The Travels of Ibn Battuta [2268 X 2195] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/jUMyu2jOMxKwN2cGmMyopyendfmG3CxZQ1b0kwX3_-g.jpg?auto=webpu0026s=3225cc2cc0040067619568b63d91f2c7052d694b)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Journey Through the Map of Ibn Battuta. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!