Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of America
Related Articles: Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of America
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of America
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of America
- 3.1 Demystifying Topographic Maps: A Visual Language of Elevation
- 3.2 Navigating the Landscape: Applications of Topographic Maps
- 3.3 Exploring the Topography of America: A Regional Overview
- 3.4 Navigating the Digital Age: Online Topographic Maps and Resources
- 3.5 FAQs about Topographic Maps of America
- 3.6 Tips for Using Topographic Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: Understanding America’s Topographic Landscape
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of America
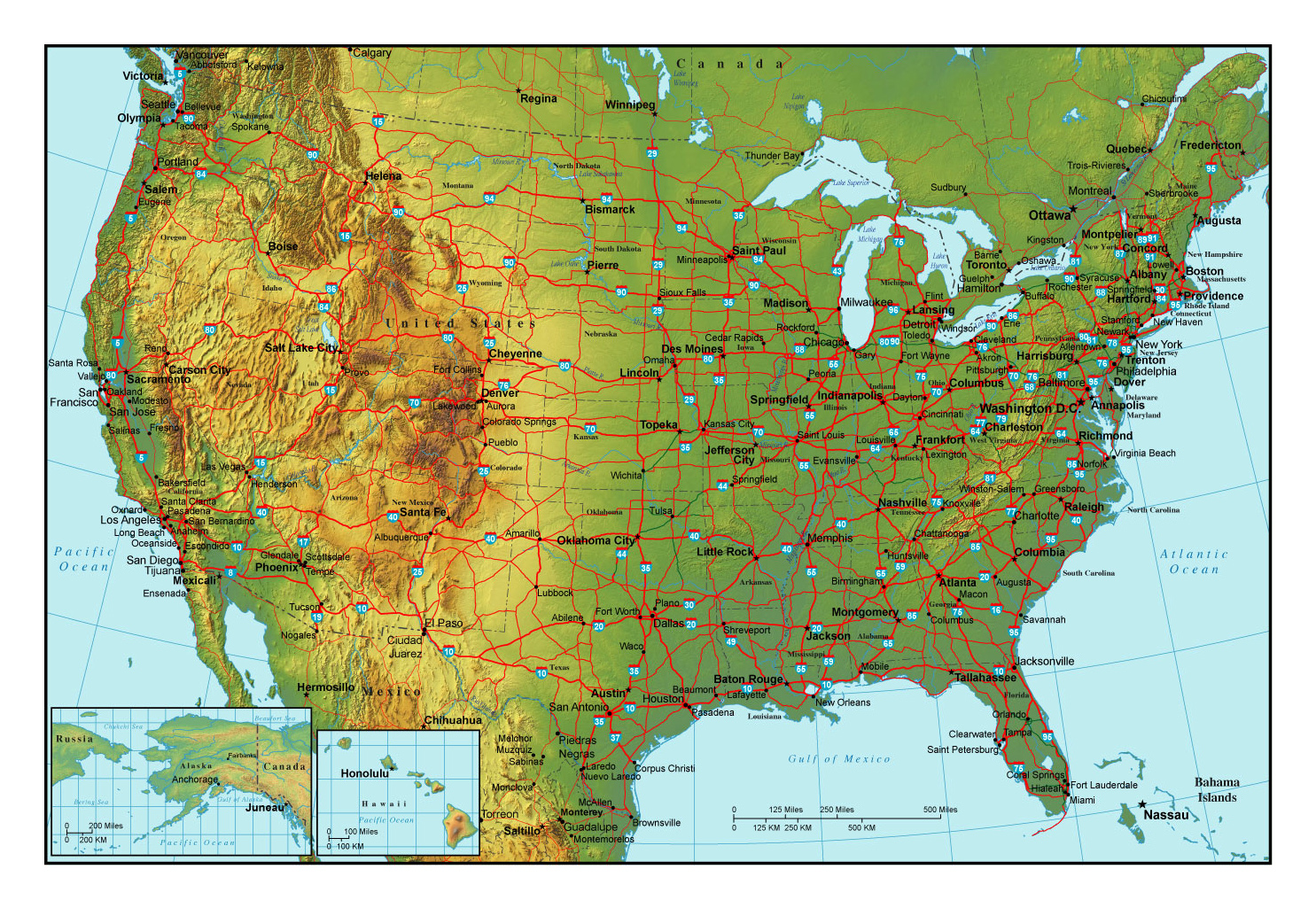
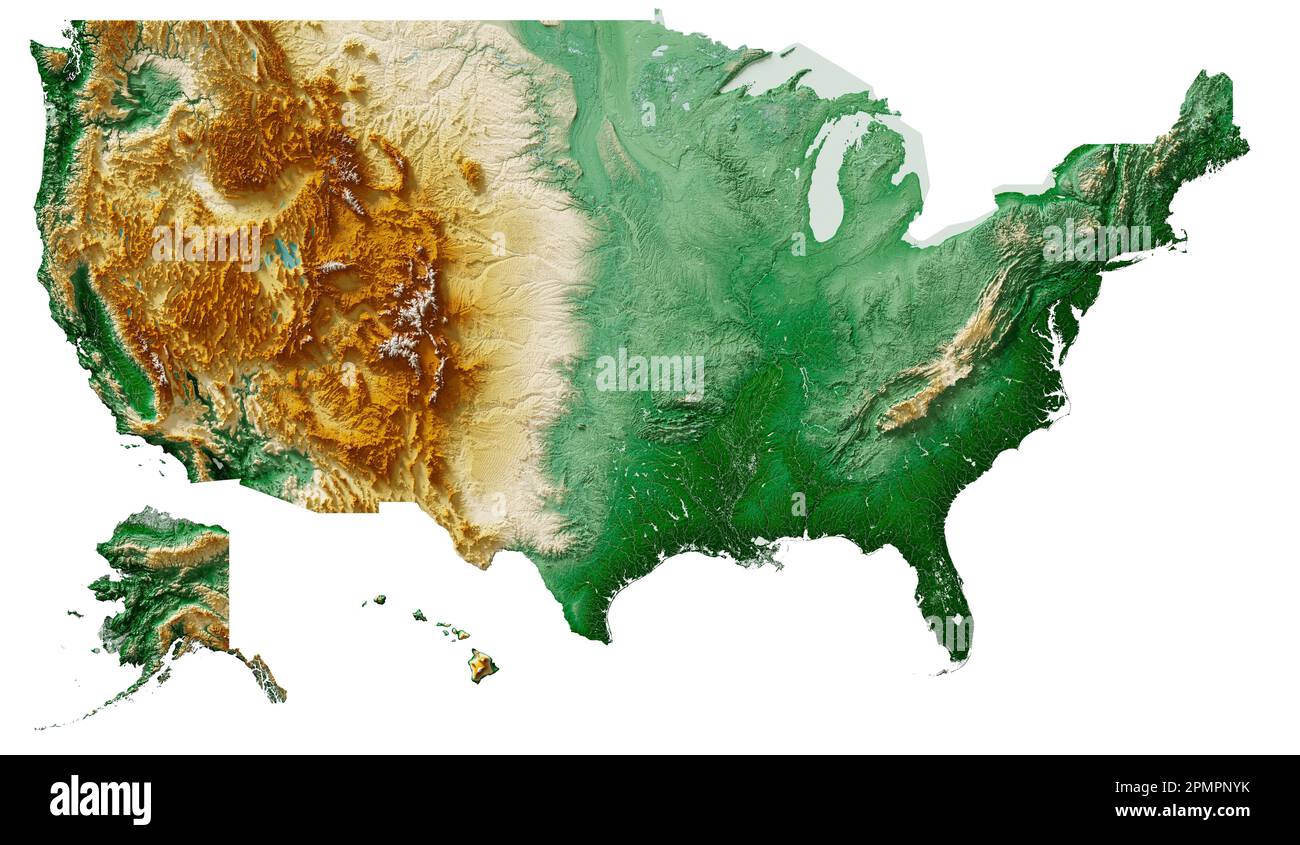
The United States, a vast and diverse nation, boasts a landscape sculpted by millennia of geological forces. From the towering peaks of the Rocky Mountains to the gentle rolling hills of the Appalachians, from the arid deserts of the Southwest to the verdant forests of the Pacific Northwest, the nation’s topography is a tapestry woven with contrasts. Understanding this complex terrain is crucial for a multitude of purposes, from navigation and resource management to urban planning and environmental conservation. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of topographic maps, exploring their significance and applications in unraveling the geographical tapestry of America.
Demystifying Topographic Maps: A Visual Language of Elevation
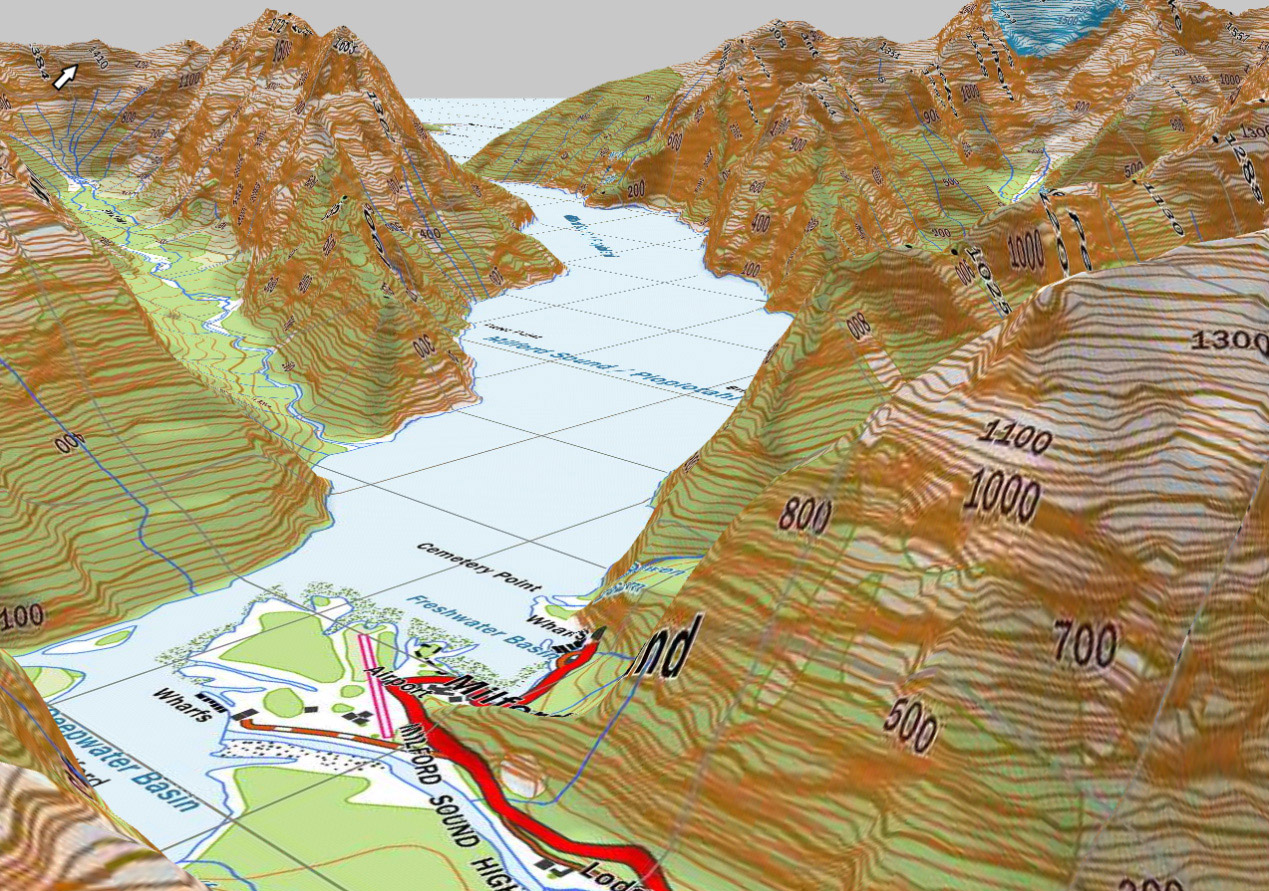
A topographic map, often referred to as a "topo," is a specialized cartographic representation that depicts the earth’s surface with a primary focus on elevation. Unlike standard maps that primarily showcase political boundaries and geographical features, topographic maps utilize contour lines to illustrate the terrain’s ups and downs. These contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation, provide a visual representation of the landscape’s shape, allowing users to discern hills, valleys, plateaus, and other topographic features.
Understanding the Language of Contour Lines:
- Contour Interval: The vertical distance between successive contour lines. This interval remains constant throughout the map, providing a consistent scale for elevation measurements.
- Contour Lines: Continuous lines that connect points of equal elevation. Closer contour lines indicate steeper slopes, while widely spaced lines suggest gentler inclines.
- Index Contours: Thicker contour lines that are typically labeled with their elevation value, aiding in quick identification of specific elevation points.
- Depressions: Closed contour lines with hachures (short lines perpendicular to the contours) indicate depressions or enclosed areas with lower elevation than surrounding terrain.
Navigating the Landscape: Applications of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps are invaluable tools for a wide range of activities, serving as essential guides for professionals and enthusiasts alike. Their applications encompass:
1. Navigation and Outdoor Recreation:
- Hiking and Backpacking: Topo maps provide critical information for navigating trails, identifying potential hazards (such as steep cliffs or water crossings), and planning routes.
- Camping and Wilderness Exploration: They assist in selecting suitable campsites, assessing water sources, and understanding the overall terrain for safe and enjoyable outdoor experiences.
- Rock Climbing and Mountaineering: Topo maps are essential for identifying climbing routes, assessing the difficulty of ascents, and understanding the terrain for safe climbing practices.
2. Engineering and Construction:
- Road and Bridge Construction: Topo maps provide critical data for site selection, determining the feasibility of construction projects, and planning infrastructure development.
- Pipeline and Utility Installation: They assist in identifying potential obstacles, planning optimal routes, and minimizing environmental impact during construction.
- Flood Control and Drainage: Topo maps help in understanding drainage patterns, identifying flood-prone areas, and developing effective flood control measures.
3. Environmental Management and Conservation:
- Wildlife Habitat Mapping: Topo maps aid in identifying critical habitat areas for endangered species, understanding wildlife movement patterns, and implementing conservation strategies.
- Water Resource Management: They provide information on watersheds, stream gradients, and groundwater resources, assisting in sustainable water management practices.
- Land Use Planning: Topo maps facilitate informed decision-making regarding land use, ensuring sustainable development and minimizing environmental impacts.
4. Urban Planning and Development:
- Site Selection and Development: Topo maps help in identifying suitable locations for residential, commercial, and industrial development, considering factors like slope, drainage, and accessibility.
- Infrastructure Planning: They assist in planning the development of roads, utilities, and other infrastructure, ensuring efficient and sustainable urban growth.
- Disaster Preparedness: Topo maps aid in identifying areas at risk from natural disasters like floods, earthquakes, and landslides, enabling effective disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
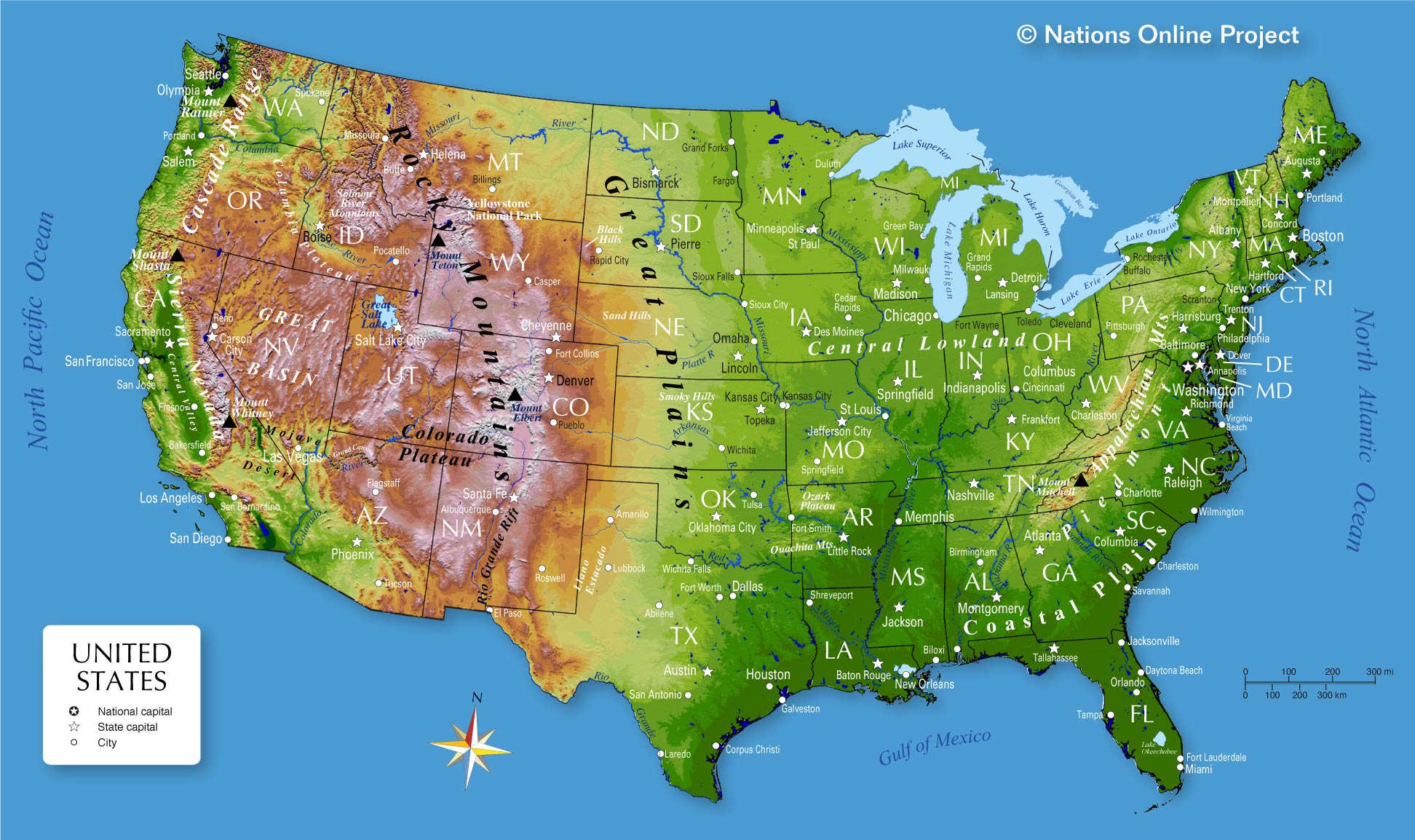
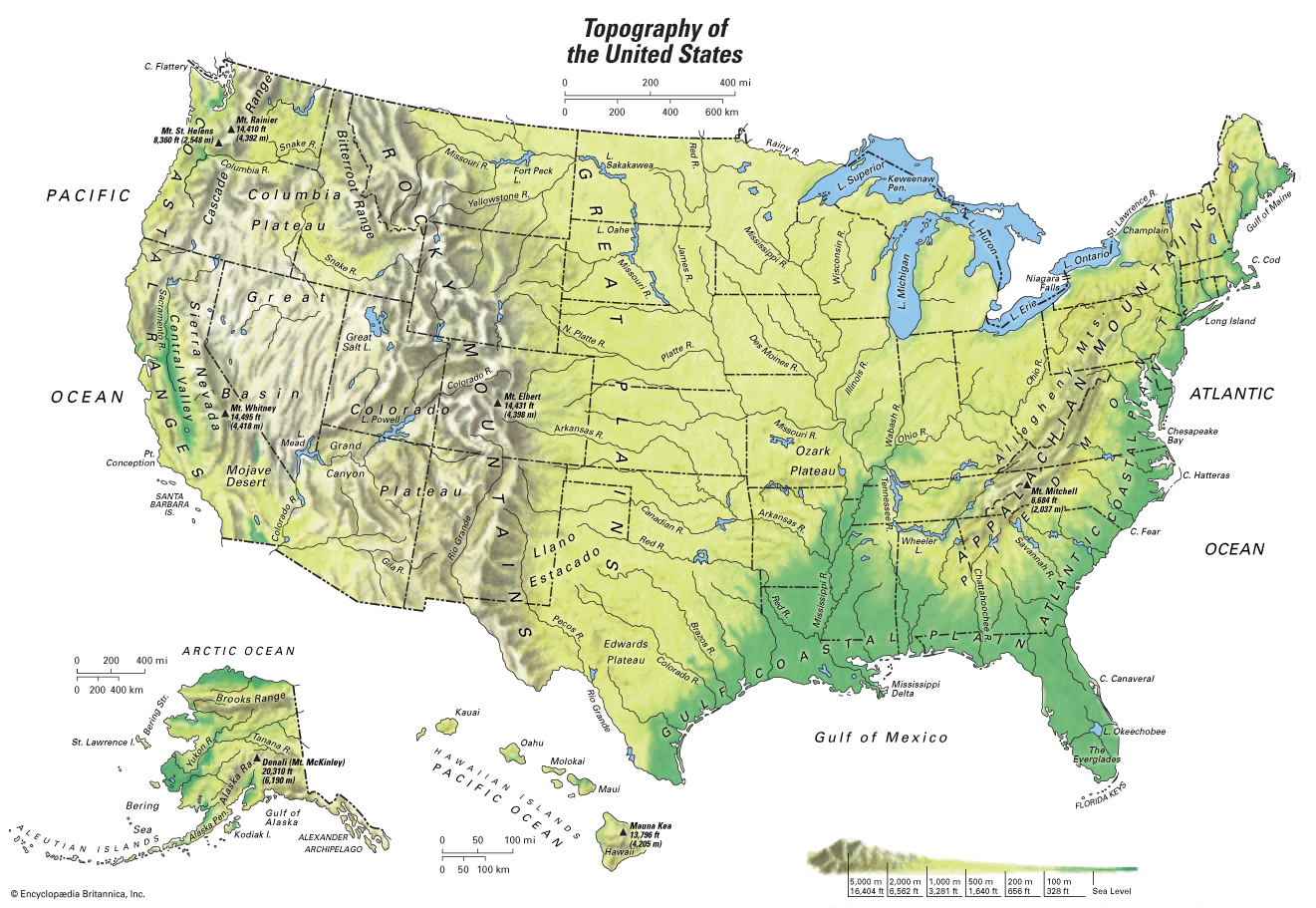
Exploring the Topography of America: A Regional Overview
The topographic map of America reveals a diverse and fascinating landscape, shaped by geological processes over millions of years. A regional overview highlights some of the most prominent features:
1. The Rocky Mountains: This vast mountain range stretches over 3,000 miles from Canada to Mexico, forming the continental divide and shaping the western landscape. Characterized by towering peaks, deep canyons, and rugged terrain, the Rockies are a haven for outdoor enthusiasts and a testament to the power of tectonic forces.
2. The Appalachian Mountains: Extending from Newfoundland to Alabama, the Appalachians are older and less dramatic than the Rockies. They are marked by rolling hills, fertile valleys, and a rich history of coal mining and timber production.
3. The Great Plains: This vast expanse of flat grasslands stretches from the Rocky Mountains to the Mississippi River, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting a diverse ecosystem.
4. The Mississippi River Basin: The heartland of America, the Mississippi River Basin encompasses a vast network of rivers and tributaries, draining a significant portion of the continent. It plays a vital role in transportation, agriculture, and the overall ecosystem.
5. The Coastal Plains: Stretching along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts, the Coastal Plains are characterized by flat, low-lying terrain and a variety of ecosystems, including coastal forests, wetlands, and sandy beaches.
6. The Great Basin: This arid region in the western United States is characterized by high mountains, desert valleys, and salt flats. It is home to unique plant and animal life adapted to the harsh desert environment.
7. The Pacific Coast: The Pacific Coast is a diverse landscape ranging from rugged mountains to sandy beaches. It is home to a variety of ecosystems, including redwood forests, coastal deserts, and the volcanic Cascade Range.
Navigating the Digital Age: Online Topographic Maps and Resources
The advancement of technology has revolutionized the way we access and utilize topographic maps. Online platforms and digital resources provide a wealth of information and interactive tools for exploring and understanding the terrain of America.
1. Online Mapping Platforms:
- Google Maps: While not solely focused on topography, Google Maps offers a terrain layer that provides a basic visual representation of elevation.
- USGS TopoView: The United States Geological Survey (USGS) offers a free online service that provides access to a vast library of topographic maps covering the entire country.
- CalTopo: This platform provides a highly detailed and interactive topographic map experience, with features like custom basemaps, route planning, and elevation profiles.
2. Digital Mapping Software:
- ArcGIS: A powerful geographic information system (GIS) software used by professionals for advanced mapping and analysis.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software that offers a range of tools for working with topographic data.
3. Mobile Apps:
- Gaia GPS: A comprehensive navigation app for outdoor enthusiasts, offering offline maps, route planning, and elevation data.
- AllTrails: A popular app for finding and navigating hiking trails, providing detailed information on elevation gain, trail conditions, and user reviews.
FAQs about Topographic Maps of America
1. What is the best way to read a topographic map?
The key to reading a topographic map is understanding contour lines. Start by identifying the contour interval, which tells you the elevation difference between each line. Closely spaced lines indicate steeper slopes, while widely spaced lines represent gentler terrain. Look for index contours, which are thicker lines labeled with their elevation value, to quickly identify specific elevation points.
2. Where can I find topographic maps for a specific location?
The USGS TopoView website offers a comprehensive collection of topographic maps for the entire United States. You can search by location, map scale, or other criteria to find the map you need. Many online mapping platforms and mobile apps also offer access to topographic data.
3. How do I use a topographic map for navigation?
Use a compass to orient yourself on the map and match it to your surroundings. Identify landmarks and features on the map, such as trails, streams, or hills, and correlate them to what you see in the real world. Use the contour lines to understand the terrain and plan your route accordingly.
4. Are there any online resources for learning more about topographic maps?
Yes, there are many online resources available for learning more about topographic maps. The USGS website offers educational materials and tutorials on map reading and interpretation. Online mapping platforms and software also provide documentation and support resources.
5. How do topographic maps contribute to environmental conservation?
Topographic maps provide valuable information for understanding watersheds, identifying critical habitat areas, and planning conservation strategies. They help in assessing potential impacts of development projects, managing water resources, and protecting sensitive ecosystems.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps Effectively
1. Choose the Right Scale: Select a map with a scale appropriate for your needs. A larger scale map (smaller ratio) provides more detail for smaller areas, while a smaller scale map (larger ratio) covers a wider region.
2. Familiarize Yourself with the Map Legend: Understand the symbols and conventions used on the map to identify features such as roads, trails, water bodies, and elevation points.
3. Use a Compass and GPS: For accurate navigation, use a compass to orient yourself on the map and a GPS device to track your location.
4. Plan Your Route Carefully: Study the contour lines to understand the terrain and plan your route accordingly, avoiding steep slopes, hazardous areas, and potential obstacles.
5. Be Prepared for Changing Conditions: Weather and environmental conditions can affect terrain, so be prepared for unexpected challenges and always carry appropriate gear and supplies.
Conclusion: Understanding America’s Topographic Landscape
The topographic map of America, with its intricate network of contour lines, reveals a landscape rich in diversity and complexity. By understanding the language of elevation, we can navigate the terrain, plan our adventures, and appreciate the remarkable beauty of the nation’s natural wonders. From the towering peaks of the Rockies to the gentle slopes of the Appalachians, from the arid deserts of the Southwest to the lush forests of the Pacific Northwest, the topographic map serves as a vital tool for exploration, conservation, and sustainable development. As we continue to explore and understand the intricate tapestry of America’s terrain, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationship between human activity and the natural world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Topographic Map of America. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!