Unveiling the Significance of Saddle Points in Geographic Analysis
Related Articles: Unveiling the Significance of Saddle Points in Geographic Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Significance of Saddle Points in Geographic Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Significance of Saddle Points in Geographic Analysis

Saddle points, often referred to as "passes" or "col," are critical features in geographic analysis, playing a vital role in understanding the landscape’s structure, influencing weather patterns, and impacting human activity. These points, characterized by their unique topographic configuration, represent crucial nodes in the spatial distribution of elevation and contribute to the overall understanding of a region’s physical environment.
Defining the Saddle Point
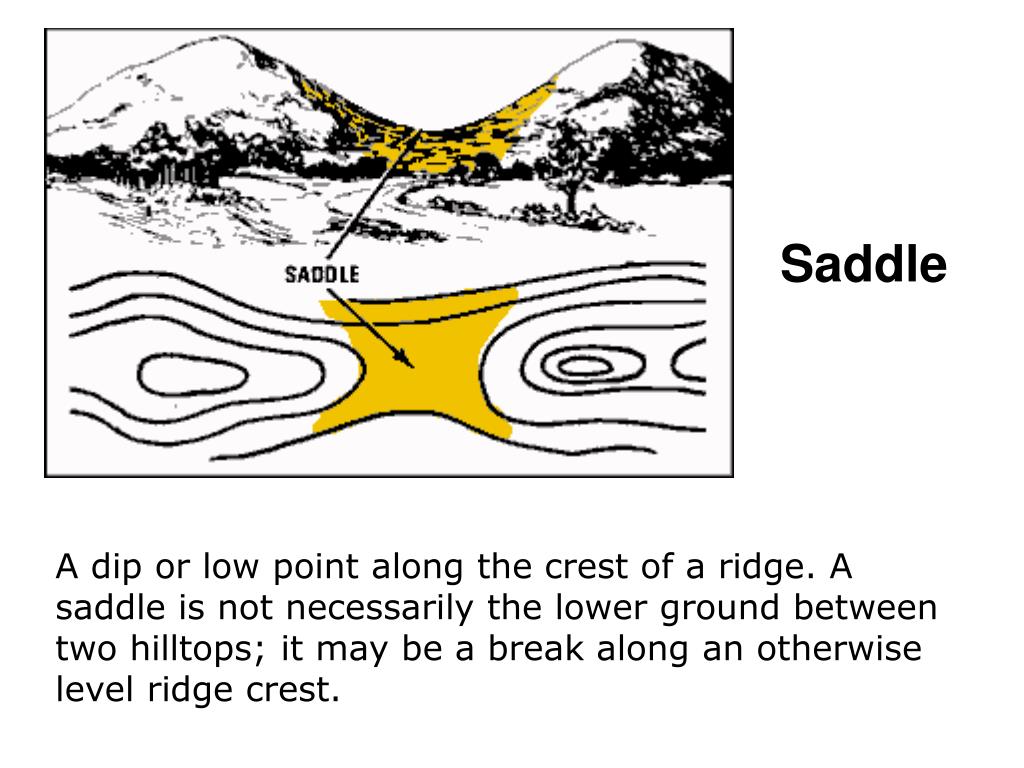
A saddle point is a location on a topographic surface where the elevation is lower than the surrounding terrain in two directions, but higher in the remaining directions. This creates a distinct depression or "saddle" shape in the landscape, resembling a mountain pass or a valley connecting two higher peaks. Visually, it can be imagined as the point where two hillsides meet, forming a dip or a trough.
Formation and Characteristics
Saddle points are formed through various geological processes, including tectonic uplift, erosion, and deposition. Tectonic forces can create folds and faults, leading to the formation of depressions or valleys that become saddle points. Erosion by wind, water, or glaciers can carve out valleys and passes, further shaping the landscape and creating saddle points.
Key characteristics of saddle points include:
- Lower elevation: The elevation at a saddle point is lower than the surrounding terrain in two directions, creating a depression.
- Higher elevation in other directions: The elevation at the saddle point is higher than the surrounding terrain in the remaining directions, forming a ridge or a divide.
- Connecting two higher points: Saddle points typically connect two higher elevation points, such as mountain peaks or ridges, forming a passageway or a route.
- Impact on water flow: Saddle points often act as drainage divides, directing water flow in different directions.
Significance in Geographic Analysis
The importance of saddle points in geographic analysis stems from their role in:
- Understanding landscape structure: Saddle points provide valuable insights into the topography and landform development of a region. They reveal the interconnectedness of different elevation zones and help map out the overall structure of the landscape.
- Analyzing drainage patterns: Saddle points act as drainage divides, influencing the direction of water flow and shaping the drainage network of a region. They play a crucial role in understanding water resources, erosion patterns, and the formation of river systems.
- Identifying potential pathways: Saddle points, particularly mountain passes, often serve as natural routes for transportation, migration, and trade. They provide access to different regions and facilitate movement across topographic barriers.
- Studying climate and weather patterns: Saddle points influence air flow and precipitation patterns. They can create microclimates and impact the distribution of vegetation and wildlife in a region.
- Modeling and simulation: Saddle points are incorporated into various geographic models and simulations, such as hydrological models, climate models, and landscape evolution models. They provide crucial data for understanding the dynamic interactions within the physical environment.
Applications of Saddle Point Analysis
The understanding of saddle points has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Geomorphology: Saddle points are essential for studying landform evolution, understanding erosion processes, and mapping drainage patterns.
- Hydrology: Saddle points play a key role in hydrological modeling, predicting water flow, and assessing water resource availability.
- Climate Science: Saddle points are crucial for studying climate change impacts, analyzing air flow patterns, and understanding regional climate variations.
- Transportation and Infrastructure: Saddle points are considered in transportation planning, identifying potential routes for roads, railways, and pipelines.
- Urban Planning: Saddle points can be used to assess the suitability of land for urban development, considering factors like drainage, accessibility, and microclimates.
- Environmental Management: Understanding saddle points is crucial for environmental management, assessing the impact of human activities on the landscape, and promoting sustainable development.
Illustrative Examples
- Mountain Passes: The Khyber Pass in Pakistan, the Brenner Pass in the Alps, and the St. Gotthard Pass in Switzerland are prominent examples of mountain passes that serve as critical transportation routes and have played significant roles in history.
- Drainage Divides: The Continental Divide of North America, separating the water flow to the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, is a prominent example of a drainage divide formed by a series of saddle points.
- Weather Patterns: The windward and leeward sides of mountain ranges, often separated by saddle points, experience distinct weather patterns due to the influence of elevation and air flow.
FAQs about Saddle Points
1. What is the difference between a saddle point and a valley?
A valley is a depression in the landscape formed by erosion or tectonic activity, typically with a continuous downward slope. A saddle point, while also a depression, is characterized by a lower elevation in two directions but higher in the remaining directions, creating a "saddle" shape.
2. How are saddle points identified?
Saddle points can be identified using topographic maps, satellite imagery, and digital elevation models. They are typically characterized by contour lines that converge and form a "U" shape, indicating a dip in the elevation.
3. What is the importance of saddle points in transportation?
Saddle points, particularly mountain passes, often serve as natural routes for transportation, providing access to different regions and facilitating movement across topographic barriers. They have played a significant role in historical trade routes and continue to be important for modern transportation infrastructure.
4. Can saddle points be created by human activities?
While saddle points are primarily formed by natural processes, human activities, such as mining or construction, can create artificial saddle points or modify existing ones. These human-induced changes can have significant impacts on the surrounding landscape and water flow.
5. How do saddle points affect climate?
Saddle points can influence climate by affecting air flow and precipitation patterns. They can create microclimates and impact the distribution of vegetation and wildlife in a region.
Tips for Analyzing Saddle Points
- Use topographic maps: Topographic maps are essential for identifying and analyzing saddle points. Look for contour lines that converge and form a "U" shape, indicating a dip in the elevation.
- Consider the surrounding terrain: Analyze the elevation and slope of the surrounding terrain to understand the context of the saddle point and its role in the landscape.
- Examine drainage patterns: Observe the direction of water flow and the drainage network to understand the influence of the saddle point on the water cycle.
- Study historical data: Explore historical maps, records, and accounts to understand the significance of saddle points in transportation, trade, and human activity.
- Utilize digital tools: Digital elevation models, GIS software, and other tools can be used to analyze saddle points, create visualizations, and conduct simulations.
Conclusion
Saddle points, often overlooked in the broader landscape, hold significant importance in geographic analysis. Their unique topographic configuration impacts various aspects of the physical environment, influencing drainage patterns, facilitating transportation, and shaping climate. Understanding saddle points is crucial for comprehending the interconnectedness of the landscape, informing sustainable development practices, and navigating the complexities of the natural world. As we continue to explore and analyze these critical features, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of interactions that shape our planet.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Significance of Saddle Points in Geographic Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!