Unveiling the Power of Visual Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Visual Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Visual Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Visual Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Maps
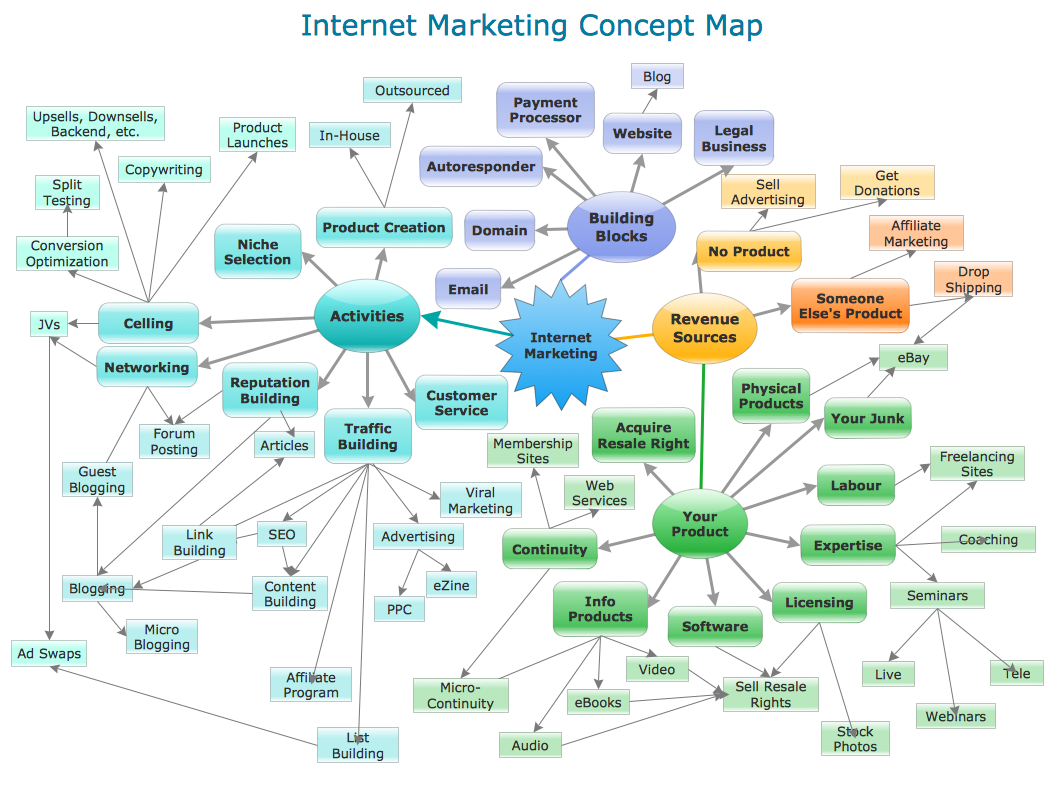
In the realm of education and knowledge acquisition, visual aids have long been recognized as powerful tools for enhancing comprehension and retention. Among these, concept maps stand out as a versatile and effective visual representation of knowledge, offering a structured framework for understanding complex ideas and their interconnected relationships. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of concept maps, exploring their fundamental principles, diverse applications, and the multifaceted benefits they provide.
Defining the Concept Map: A Visual Network of Knowledge
A concept map, at its core, is a graphical representation of knowledge that uses nodes and connecting lines to illustrate the relationships between concepts. Nodes, typically represented by boxes or circles, encapsulate key ideas, terms, or elements within a specific topic. Connecting lines, often accompanied by linking phrases or verbs, establish the nature of the relationship between these nodes. This visual network provides a structured and intuitive framework for organizing information, fostering deeper understanding, and promoting active learning.
Key Components of a Concept Map:
-
Concepts: These are the fundamental building blocks of a concept map, representing individual ideas, terms, or entities. They are typically enclosed within nodes, which can be arranged in various shapes and sizes depending on the complexity of the concept.
-
Connecting Lines: These lines visually connect the nodes, signifying the relationships between concepts. The direction of the line can indicate the nature of the relationship, such as hierarchical, causal, or associative.
-
Linking Phrases: These are brief descriptions that accompany the connecting lines, clarifying the specific relationship between the connected concepts. They provide context and detail, enhancing the clarity and understanding of the map.
Building a Concept Map: A Step-by-Step Approach:
-
Identify the Central Concept: Begin by defining the core topic or idea that the concept map will focus on. This central concept serves as the starting point for the visual representation.
-
Brainstorm Related Concepts: Engage in a brainstorming session to identify concepts that are directly or indirectly related to the central concept. This step involves exploring the topic from different perspectives, generating a comprehensive list of relevant ideas.
-
Establish Hierarchies and Relationships: Organize the concepts into a hierarchical structure based on their level of importance and relationships. This involves identifying main concepts, sub-concepts, and supporting ideas.
-
Connect Concepts with Lines and Linking Phrases: Use connecting lines to visually represent the relationships between the concepts. Accompany these lines with linking phrases that clearly explain the nature of the relationship.
-
Refine and Evaluate: Once the initial structure is established, refine the map by adding details, adjusting connections, and ensuring clarity and coherence. Regularly evaluate the map for effectiveness and make necessary revisions.
Applications of Concept Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
The versatility of concept maps extends beyond the classroom, finding applications in diverse fields and contexts:
-
Education: Concept maps are widely used in education to facilitate learning, enhance comprehension, and promote active recall of information. They help students visualize complex concepts, understand relationships between ideas, and organize their thoughts effectively.
-
Research: Researchers employ concept maps to visualize research questions, organize literature reviews, and develop theoretical frameworks. They provide a clear and concise representation of research ideas, facilitating the identification of gaps and potential areas for further investigation.
-
Business: Concept maps are valuable tools for brainstorming, problem-solving, and decision-making in business settings. They help teams to identify key factors, analyze relationships between variables, and develop comprehensive solutions.
-
Personal Development: Concept maps can be used for personal goal setting, project planning, and personal knowledge organization. They provide a visual framework for breaking down complex tasks, identifying dependencies, and tracking progress towards goals.
Benefits of Concept Maps: Unlocking Cognitive Potential
The use of concept maps yields a multitude of benefits, fostering effective learning, critical thinking, and knowledge retention:
-
Enhanced Comprehension: By visually representing complex ideas and their relationships, concept maps promote deeper understanding and facilitate the integration of new knowledge with existing knowledge structures.
-
Active Learning: The process of creating a concept map encourages active engagement with the material, requiring learners to critically analyze, synthesize, and organize information. This active learning approach leads to greater retention and understanding.
-
Improved Memory and Recall: Visual representations like concept maps facilitate better memory and recall of information. The visual cues and connections help learners retrieve information more effectively, enhancing long-term retention.
-
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: Concept maps encourage critical thinking by prompting learners to analyze relationships between concepts, identify patterns, and draw inferences. This process enhances problem-solving abilities and fosters a deeper understanding of complex issues.
-
Communication and Collaboration: Concept maps provide a shared visual language for communication and collaboration. They facilitate clear and concise communication of ideas, fostering shared understanding and collaboration among individuals or teams.
FAQs about Concept Maps:
1. What are the limitations of concept maps?
While concept maps offer numerous benefits, they also have limitations:
-
Subjectivity: The creation of a concept map can be subjective, influenced by individual perspectives and prior knowledge. This can lead to variations in the representation of concepts and relationships.
-
Complexity: Complex topics with numerous interconnected concepts can result in intricate and challenging concept maps, potentially hindering clarity and comprehension.
-
Time and Effort: Creating a comprehensive and effective concept map can require significant time and effort, especially for complex topics.
2. How can I improve my concept map skills?
Developing effective concept map skills involves practice, experimentation, and a focus on clarity and coherence:
-
Start with Simple Topics: Begin by creating concept maps for simple topics to build confidence and understanding of the basic principles.
-
Use Different Visual Styles: Experiment with various node shapes, connecting lines, and colors to find a visual style that suits your preferences and the topic.
-
Seek Feedback: Share your concept maps with others and solicit feedback to identify areas for improvement and enhance clarity.
-
Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to developing your concept map skills, enabling you to create effective and informative representations of knowledge.
3. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a concept map?
-
Overcrowding: Avoid cramming too many concepts into a single map, as this can make it difficult to understand.
-
Unclear Connections: Ensure that the connecting lines and linking phrases clearly explain the relationships between concepts.
-
Lack of Hierarchy: Establish a clear hierarchy of concepts, identifying main ideas, sub-concepts, and supporting details.
-
Ignoring Visual Aesthetics: Pay attention to the visual presentation of the concept map, ensuring clarity, readability, and aesthetic appeal.
Tips for Creating Effective Concept Maps:
-
Keep it Simple: Start with a limited number of concepts and focus on establishing clear relationships.
-
Use Meaningful Linking Phrases: Choose linking phrases that accurately reflect the nature of the relationship between concepts.
-
Consider the Audience: Tailor the complexity and detail of the concept map to the knowledge and understanding of the intended audience.
-
Utilize Technology: There are numerous software programs and online tools available for creating concept maps, offering features for collaboration and visual customization.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Learning
Concept maps, as a powerful visual learning tool, provide a structured framework for organizing knowledge, enhancing comprehension, and promoting active learning. By visually representing relationships between concepts, they facilitate deeper understanding, improve memory and recall, and foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. As educators, researchers, and individuals continue to explore the vast realms of knowledge, concept maps remain a valuable tool for navigating complexity, fostering clarity, and unlocking the full potential of visual learning.
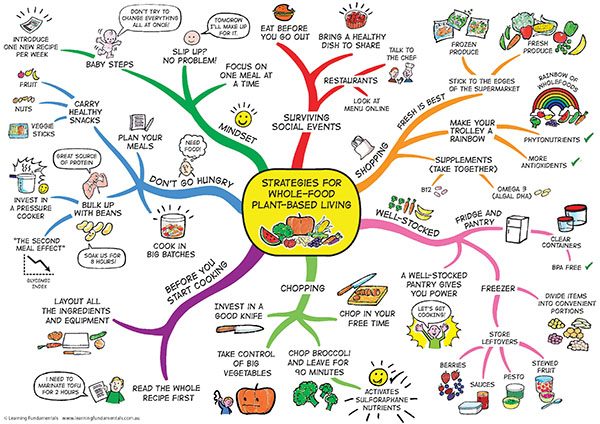
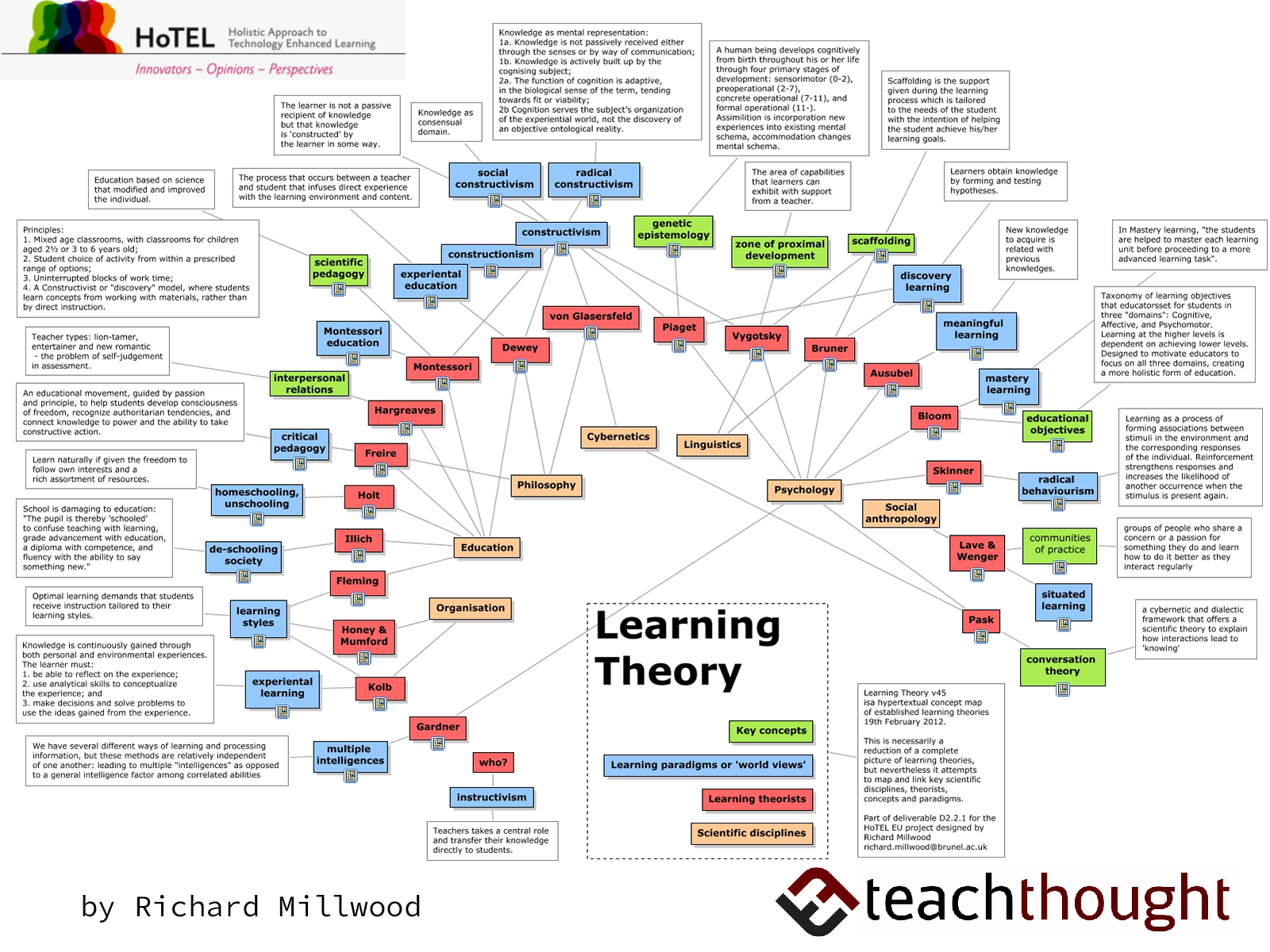



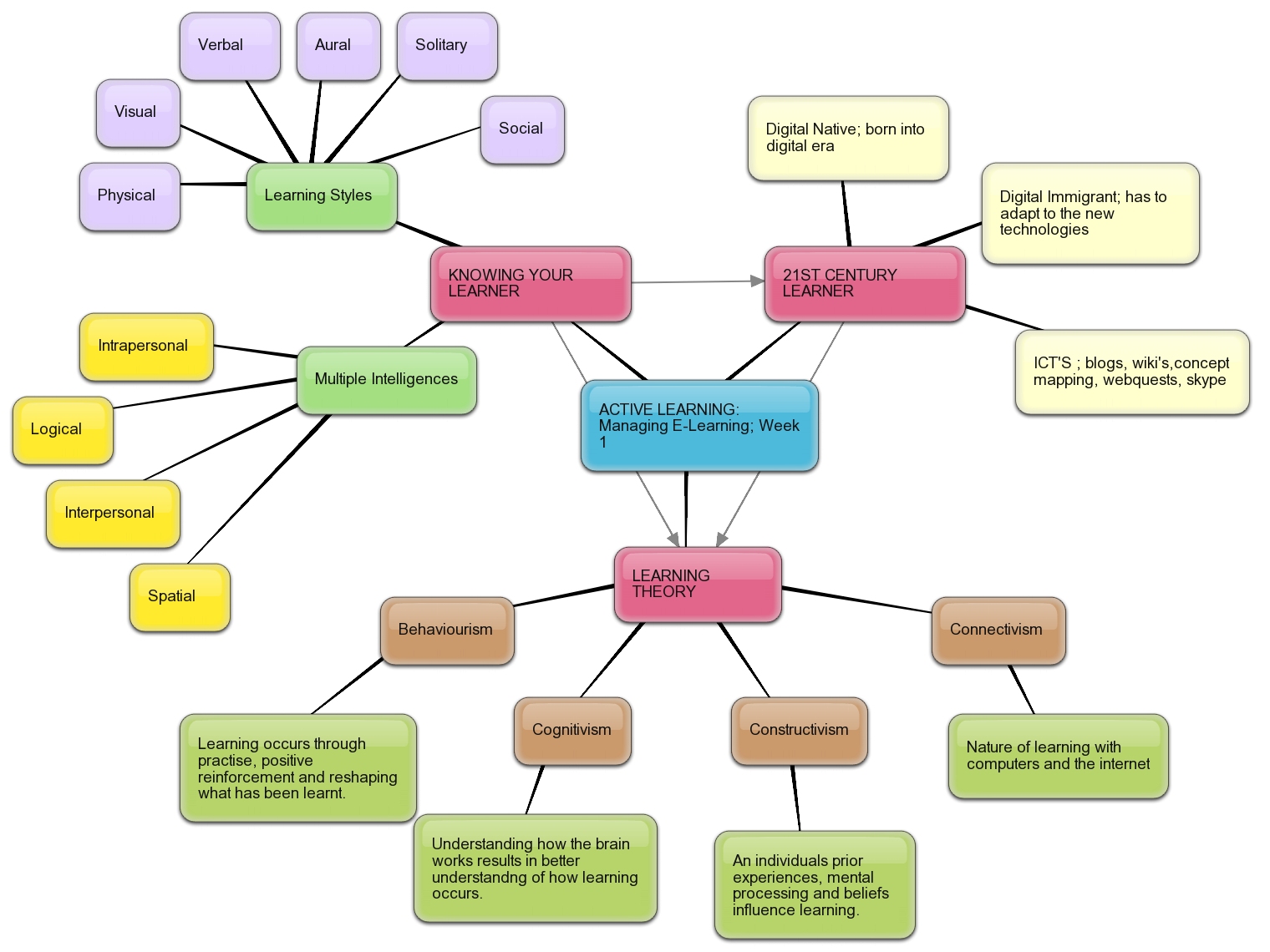

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Visual Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!