Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps

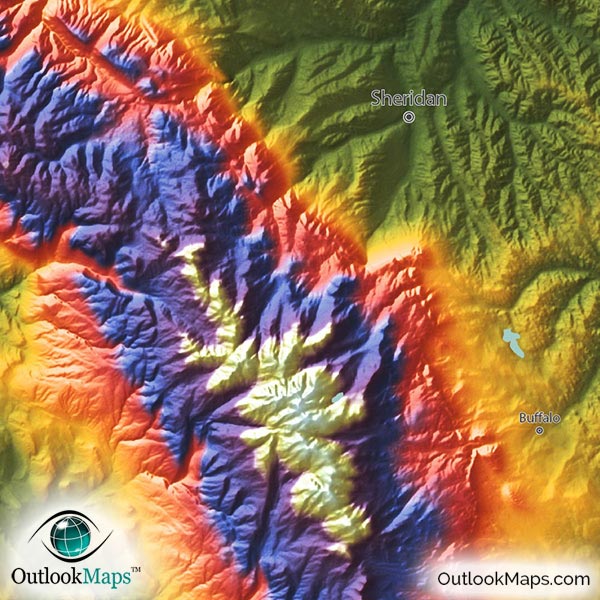
Topographic maps are essential tools for understanding and navigating the Earth’s surface. They provide a detailed representation of the terrain, capturing the shape and elevation of the land, which is crucial for various purposes, from hiking and camping to engineering and urban planning. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of topographic maps, explaining their significance and applications in a clear and informative manner.
Understanding the Language of the Land:
Topographic maps utilize a specific language to convey information about the terrain. This language is comprised of symbols, lines, and colors that represent different features and elevations.
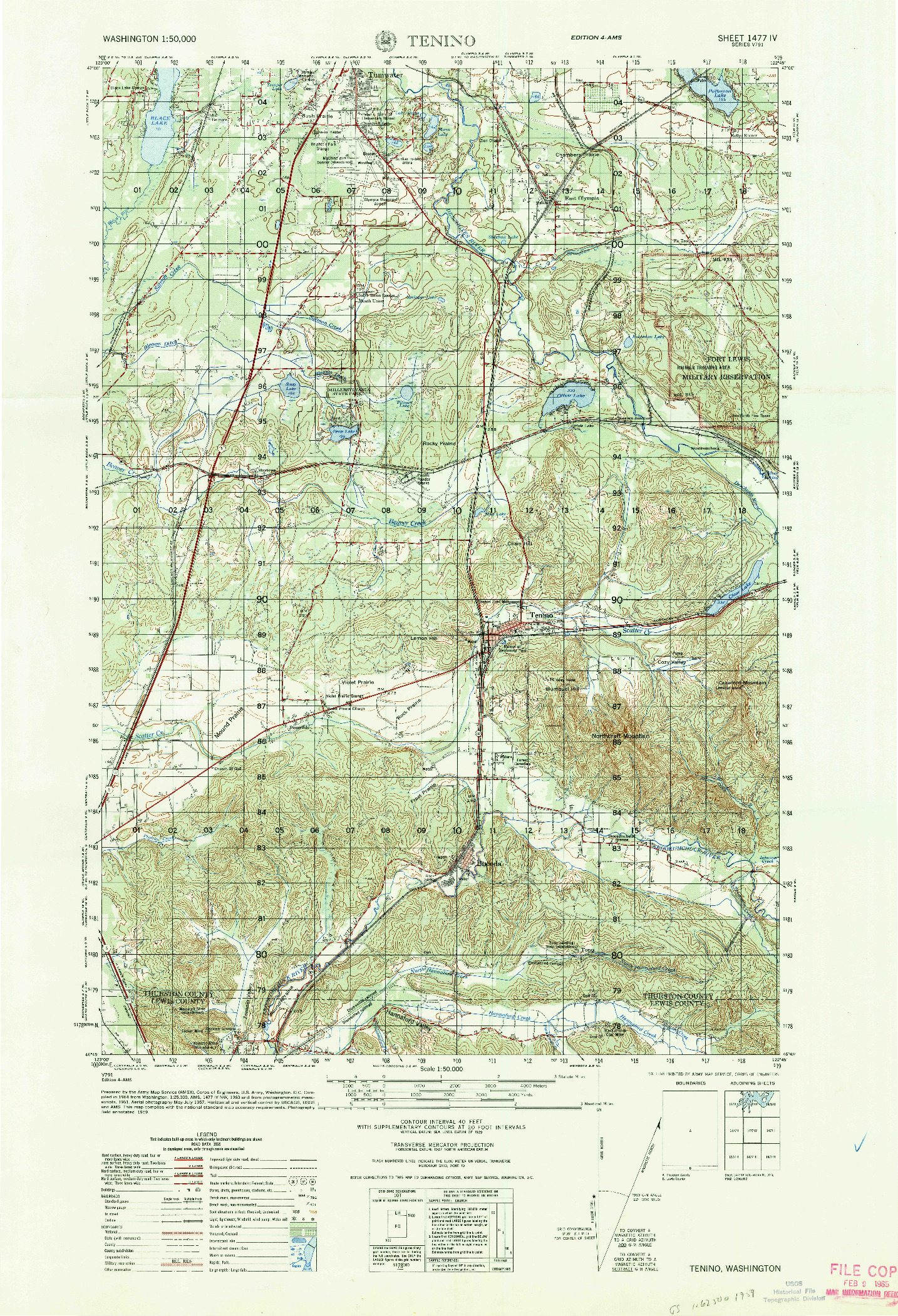
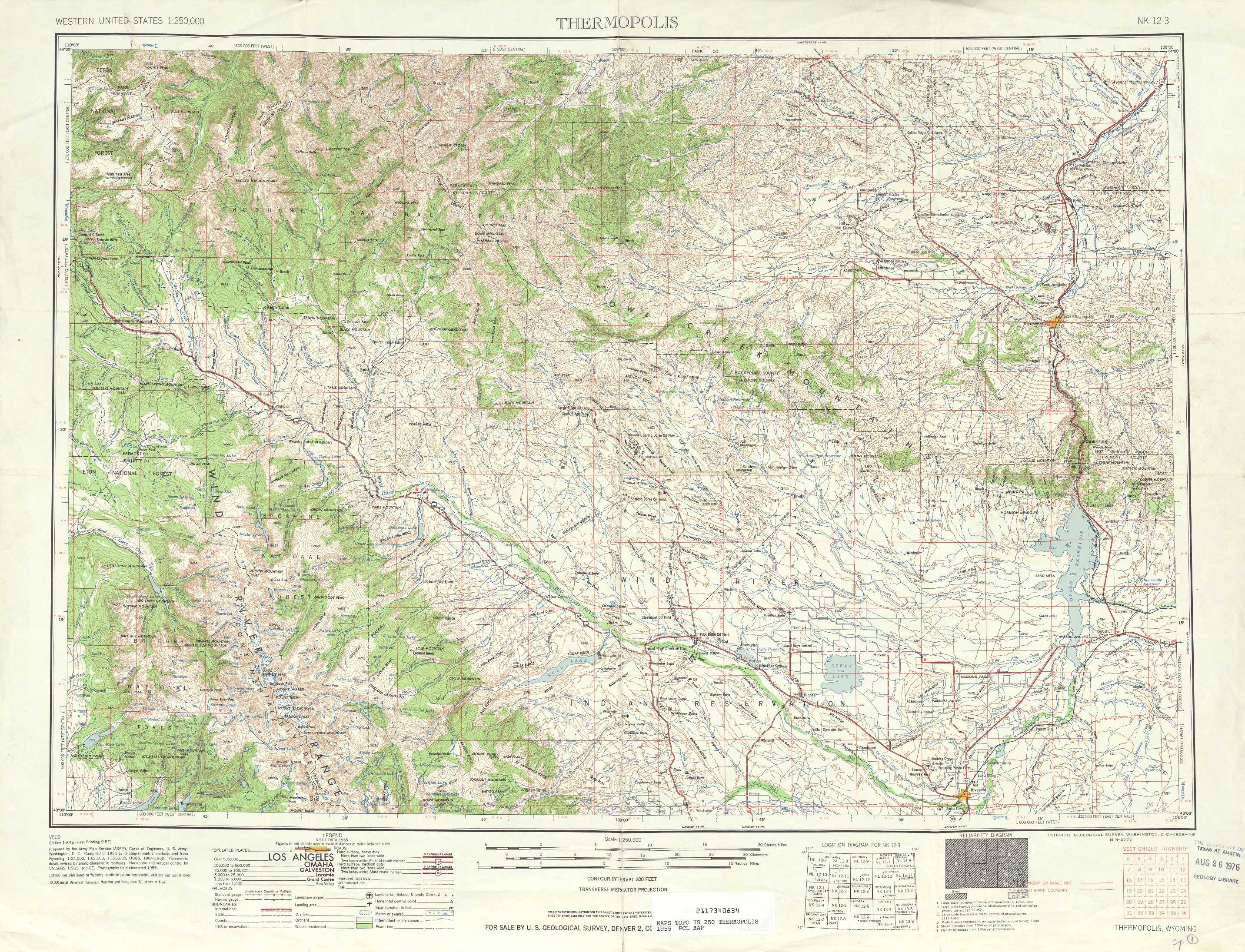
- Contour Lines: The most prominent feature of a topographic map is the use of contour lines. These lines connect points of equal elevation, forming a visual representation of the terrain’s shape. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart, the gentler the slope.
- Elevation: Each contour line represents a specific elevation, typically indicated by a numerical value. This allows users to determine the height of any point on the map.
- Spot Elevations: In addition to contour lines, spot elevations are often marked on maps to indicate the exact elevation of specific points, such as mountain peaks or valleys.
- Symbols: A wide range of symbols is used to represent various features, such as roads, rivers, buildings, forests, and even cultural landmarks. These symbols provide context and detail, enhancing the map’s utility.
- Color: Color plays a significant role in topographic maps. Different colors are used to distinguish between land cover types, such as forests, grasslands, and water bodies. This color-coding helps users quickly identify and interpret the landscape.
Applications of Topographic Maps:
Topographic maps are indispensable tools for a wide range of activities, including:
- Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, campers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely heavily on topographic maps to navigate trails, identify potential hazards, and plan their routes. The maps’ detailed elevation information allows users to assess the difficulty of trails and anticipate changes in terrain.
- Engineering and Construction: Engineers and construction professionals utilize topographic maps to plan and design infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and buildings. The maps provide precise information about the land’s topography, which is crucial for ensuring the stability and functionality of these projects.
- Urban Planning and Development: Urban planners use topographic maps to understand the existing landscape and plan for future development. The maps help identify areas suitable for housing, commercial development, or infrastructure projects, while considering the terrain’s limitations and opportunities.
- Environmental Management: Topographic maps are vital for environmental studies and management. They provide data on watersheds, soil types, and vegetation patterns, which are essential for understanding and managing environmental resources.
- Military Operations: Topographic maps are crucial for military planning and operations. They provide detailed information about terrain features, which is essential for troop movement, reconnaissance, and target identification.
The Evolution of Topographic Maps:
Topographic maps have evolved significantly over time, with advancements in technology and data acquisition methods leading to greater accuracy and detail.
- Traditional Mapping: Traditionally, topographic maps were created through manual surveys and aerial photography. This process involved meticulous field measurements and the interpretation of aerial images to create detailed representations of the terrain.
- Digital Mapping: With the advent of digital technologies, topographic mapping has become more efficient and precise. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing techniques allow for the collection and processing of large amounts of data, resulting in highly accurate and detailed maps.
- 3D Mapping: Recent advancements in technology have led to the development of 3D topographic maps. These maps provide a more immersive and realistic representation of the terrain, enhancing their utility for various applications.
Benefits of Using Topographic Maps:
Utilizing topographic maps offers numerous benefits:
- Improved Decision Making: The detailed information provided by topographic maps allows users to make informed decisions about their activities, whether it’s planning a hiking trip or designing a construction project.
- Enhanced Safety: By understanding the terrain’s features and potential hazards, topographic maps contribute to increased safety in outdoor activities and construction projects.
- Effective Planning: Topographic maps provide essential data for planning and executing a wide range of projects, from infrastructure development to environmental management.
- Resource Management: By understanding the distribution and characteristics of natural resources, topographic maps facilitate effective resource management.
- Increased Awareness: Topographic maps foster a deeper understanding and appreciation of the Earth’s surface, promoting responsible interaction with the environment.
FAQs about Topographic Maps:
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A: A topographic map differs from a regular map by focusing on the terrain’s elevation and shape. While a regular map primarily shows locations and political boundaries, a topographic map provides detailed information about the land’s contours, slopes, and features.
Q: How can I learn to read a topographic map?
A: Numerous resources are available to help you learn to read topographic maps. Online tutorials, books, and workshops offer comprehensive guidance on interpreting contour lines, symbols, and other map elements.
Q: What are the limitations of topographic maps?
A: Topographic maps are representations of the real world and are subject to limitations. They may not capture all the details of the terrain, and their accuracy can be affected by factors such as the map’s scale and the age of the data used.
Q: How are topographic maps used in everyday life?
A: Topographic maps are used in various aspects of everyday life, from navigation apps on smartphones to planning outdoor activities and understanding environmental issues.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps:
- Choose the Right Scale: Select a map with an appropriate scale for your intended use. A larger scale map provides more detail but covers a smaller area.
- Understand the Legend: Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend, which explains the symbols and colors used to represent different features.
- Identify Contour Lines: Pay close attention to contour lines to understand the terrain’s shape and elevation changes.
- Use a Compass and Altimeter: A compass and altimeter are essential tools for navigating with topographic maps, ensuring accurate direction and elevation measurements.
- Practice Reading Maps: Regularly practice reading topographic maps to enhance your skills and gain a deeper understanding of the information they convey.
Conclusion:
Topographic maps are indispensable tools for understanding and interacting with the Earth’s surface. They provide a comprehensive representation of the terrain, capturing its shape, elevation, and features, which is crucial for a wide range of activities, from outdoor recreation to engineering and environmental management. As technology advances, topographic maps continue to evolve, offering greater accuracy, detail, and accessibility. By understanding the language of topographic maps and utilizing their benefits, we can navigate the landscape, plan for the future, and make informed decisions about our interaction with the environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!