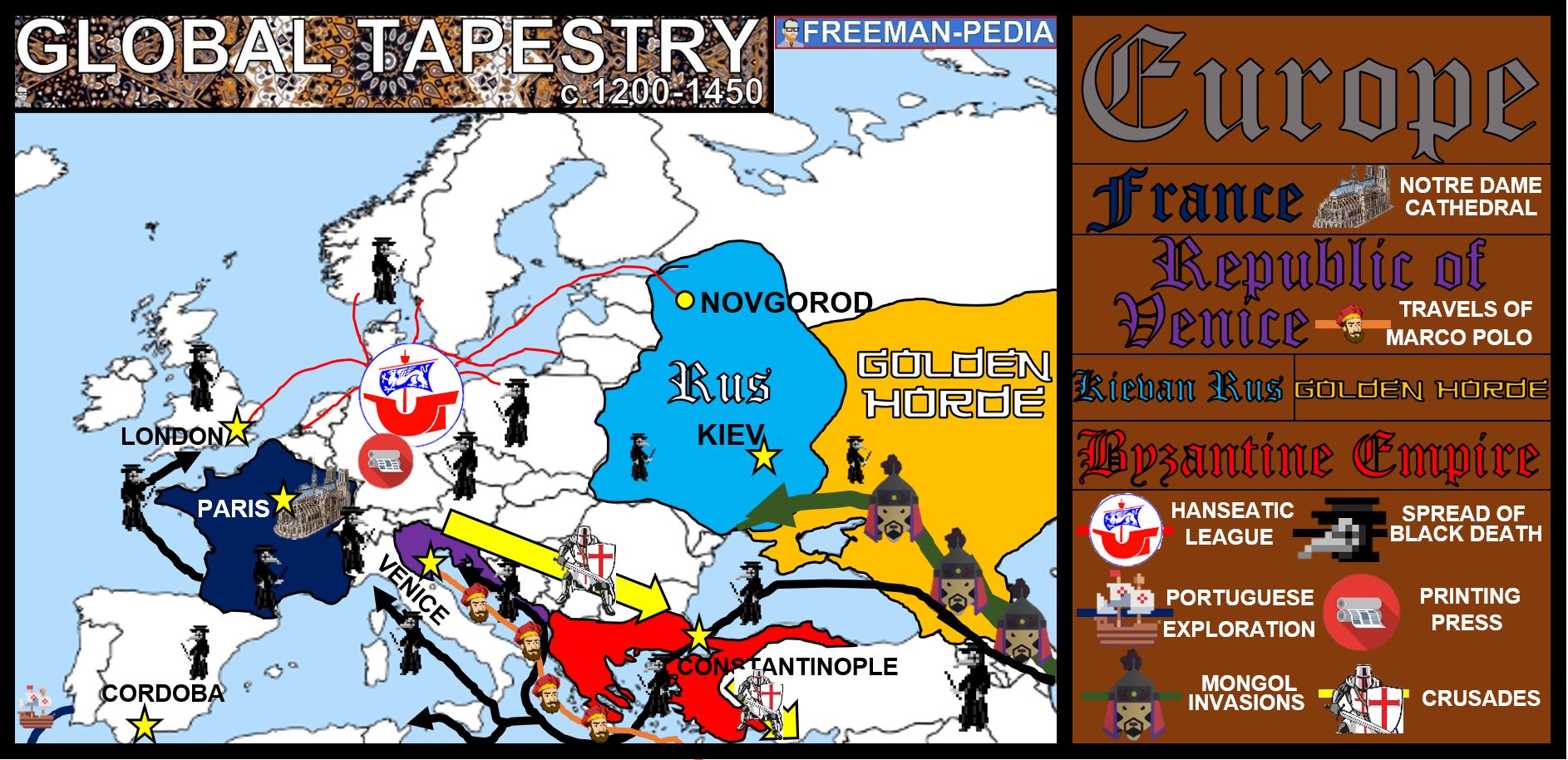
Unraveling the Geographic Tapestry: Exploring Europe’s Latitude and its Significance
Related Articles: Unraveling the Geographic Tapestry: Exploring Europe’s Latitude and its Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Geographic Tapestry: Exploring Europe’s Latitude and its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Geographic Tapestry: Exploring Europe’s Latitude and its Significance
Europe, a continent rich in history, culture, and diverse landscapes, is geographically defined by its unique position on the globe. Its latitude, the angular distance north or south of the equator, plays a crucial role in shaping its climate, ecosystems, and cultural evolution. Understanding Europe’s latitude provides a fundamental framework for comprehending its multifaceted character.
Latitude’s Impact on Europe’s Climate
Europe’s latitude spans a significant range, extending from the Arctic Circle in the north to the Mediterranean Sea in the south. This latitudinal variation directly influences the continent’s climate, creating diverse weather patterns and distinct biomes.
- Northern Europe: Situated at higher latitudes, northern Europe experiences long, cold winters and short, cool summers. The region is characterized by boreal forests, tundra, and icy landscapes.
- Central Europe: Located at mid-latitudes, central Europe enjoys a temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The region is dominated by deciduous forests and fertile agricultural lands.
- Southern Europe: Situated at lower latitudes, southern Europe benefits from a Mediterranean climate with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The region is known for its olive groves, vineyards, and coastal landscapes.
Latitude’s Influence on Europe’s Ecosystems
The latitudinal gradient across Europe has a profound impact on its ecosystems, shaping the distribution of plant and animal life.
- Arctic and Subarctic Regions: These regions, located at high latitudes, are characterized by low biodiversity and harsh conditions. The dominant vegetation is tundra, with hardy plants adapted to cold temperatures and short growing seasons.
- Temperate Forests: Found in central Europe, these forests are rich in biodiversity and support a wide variety of plant and animal species. The deciduous trees, adapted to seasonal changes, provide a diverse habitat for a multitude of organisms.
- Mediterranean Biome: This biome, found in southern Europe, is characterized by drought-resistant vegetation like olive trees, vineyards, and scrubland. The warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters create a unique environment for specialized plant and animal life.
Latitude’s Role in Europe’s Cultural Evolution
Latitude has played a significant role in shaping Europe’s cultural development, influencing its history, architecture, and traditions.
- Northern Europe: The harsh climate and long winters have influenced the development of strong communities, communal living, and a reliance on indoor activities. The region is known for its rich folklore and storytelling traditions.
- Central Europe: The temperate climate and fertile lands have fostered a strong agricultural tradition, leading to the development of vibrant city-states and trade networks. The region is renowned for its architecture, art, and music.
- Southern Europe: The warm climate and abundant sunshine have encouraged outdoor living, a relaxed lifestyle, and a strong connection to the land. The region is famous for its culinary traditions, vibrant festivals, and artistic heritage.
Understanding Europe’s Latitude: A Key to Exploration
By comprehending the influence of latitude on Europe’s climate, ecosystems, and culture, we gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s diversity and complexity. This knowledge serves as a valuable tool for travelers, historians, scientists, and anyone seeking to understand the intricate tapestry of Europe’s identity.
FAQs
Q: What is the range of latitude in Europe?
A: Europe’s latitude spans approximately 36° to 71° North.
Q: How does latitude affect Europe’s climate?
A: Latitude influences the amount of solar radiation received, resulting in distinct climate zones across Europe, from the cold Arctic north to the warm Mediterranean south.
Q: What are the main ecosystems found in Europe?
A: Europe’s ecosystems vary significantly based on latitude, encompassing Arctic tundra, boreal forests, temperate forests, and Mediterranean biomes.
Q: How has latitude influenced European culture?
A: Latitude has shaped European culture through its impact on climate, agriculture, and lifestyle, leading to diverse traditions, architecture, and artistic expressions.
Tips for Exploring Europe’s Latitudinal Diversity
- Travel to different regions: Experience the diverse climates and ecosystems by visiting northern Europe, central Europe, and southern Europe.
- Research the local culture: Learn about the unique traditions, customs, and history shaped by the region’s latitude.
- Engage with local communities: Interact with people living in different parts of Europe to gain insights into their lives and perspectives.
Conclusion
Europe’s latitude serves as a fundamental geographic element shaping its climate, ecosystems, and cultural evolution. By understanding the influence of latitude, we gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s multifaceted character, its rich history, and its diverse landscapes. The exploration of Europe’s latitudinal diversity offers a unique opportunity to discover the interconnectedness of geography, climate, and culture, revealing the intricate tapestry of this remarkable continent.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Geographic Tapestry: Exploring Europe’s Latitude and its Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!