Understanding the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Maps
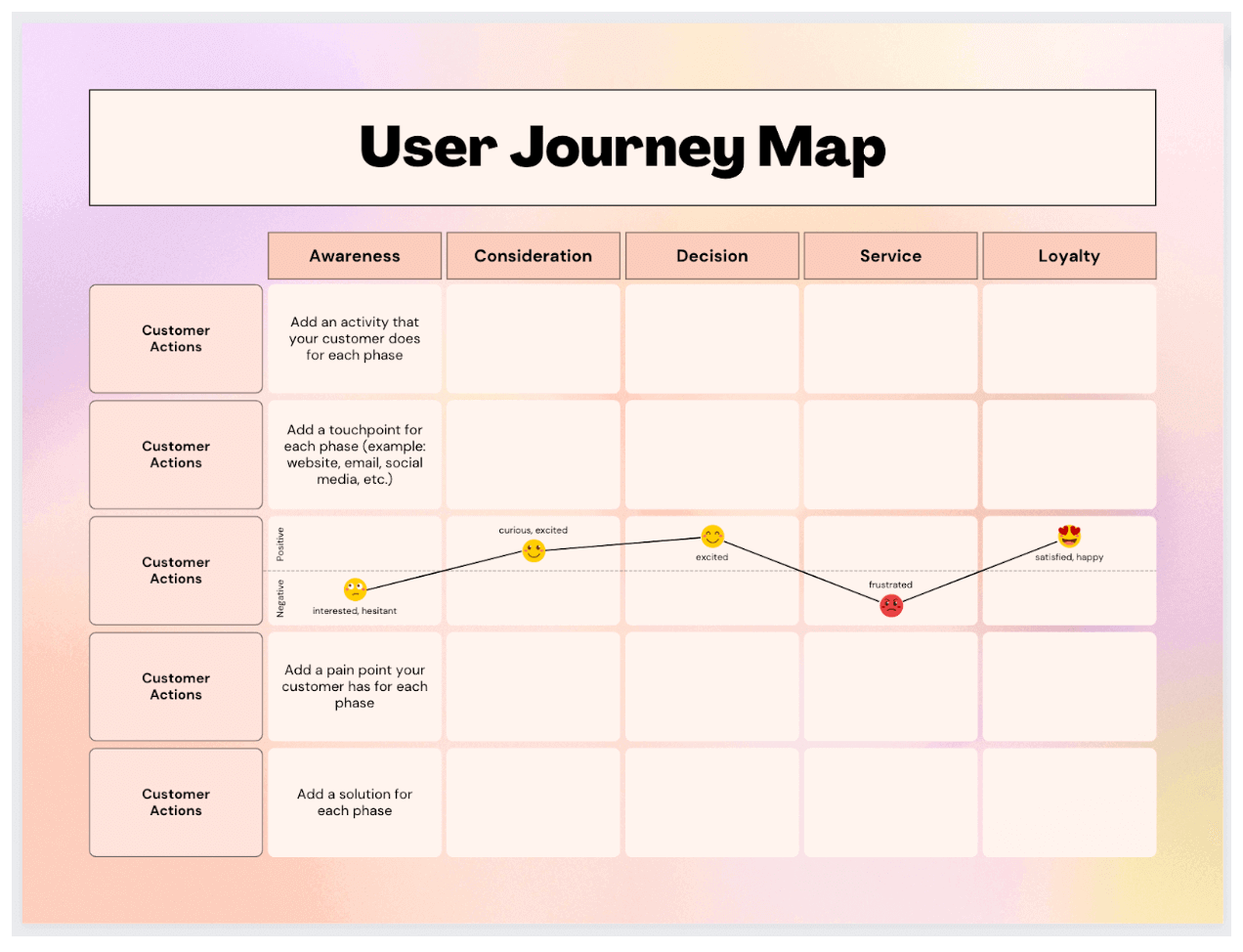
In the dynamic landscape of digital marketing, understanding the user journey is paramount to achieving success. This journey, encompassing every interaction a user has with a product, service, or brand, is complex and multifaceted. To navigate this complexity, marketers and designers rely on a powerful tool known as a user map.
What is a User Map?
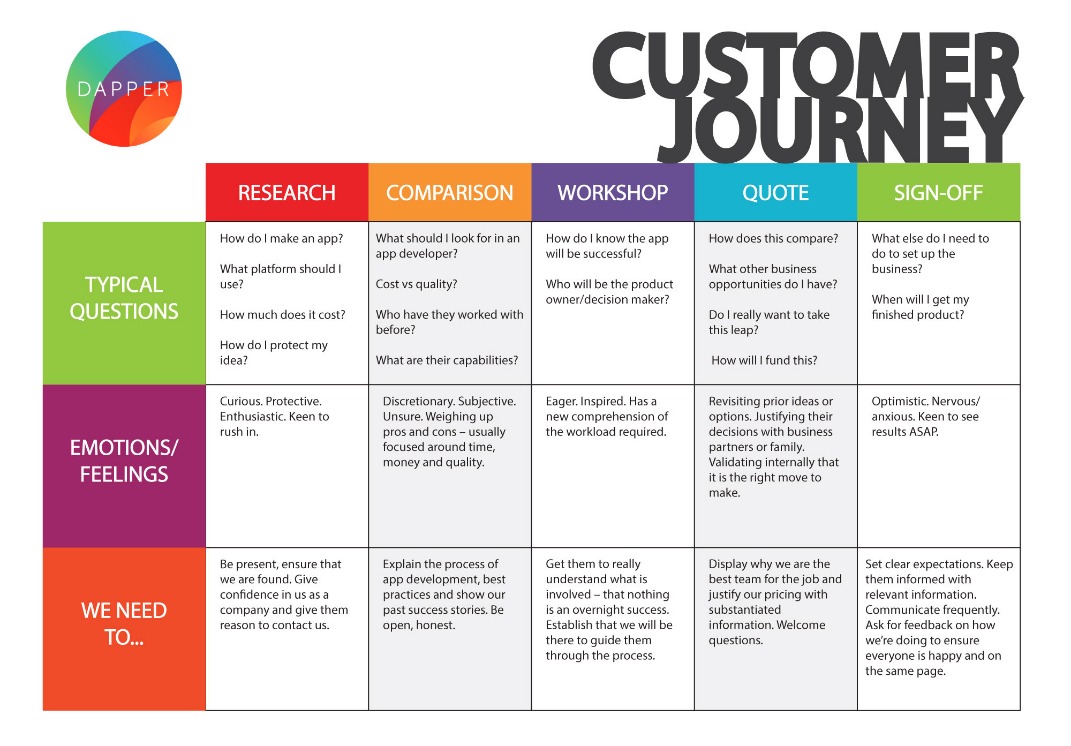
A user map, also known as a customer journey map, is a visual representation of the stages a user goes through during their interaction with a product, service, or brand. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the user’s experience, capturing their motivations, pain points, touchpoints, and emotions at each stage.
The Anatomy of a User Map:
A typical user map comprises the following key elements:
- User Persona: This element defines the target user, outlining their demographics, psychographics, goals, and motivations.
- Touchpoints: These are all the interactions a user has with the product, service, or brand. Touchpoints can be online (website, social media, email) or offline (physical store, customer service calls).
- Emotions: User maps highlight the emotions experienced by users at each touchpoint. This could range from excitement and anticipation to frustration and disappointment.
- Actions: Each touchpoint is associated with specific user actions, such as browsing a website, making a purchase, or contacting customer support.
- Pain Points: These are the challenges or frustrations users encounter during their journey. Identifying pain points is crucial for improving the user experience.
- Opportunities: User maps also reveal opportunities for improvement, such as streamlining processes, enhancing communication, or introducing new features.
Types of User Maps:
User maps can be categorized into different types based on their scope and focus:
- Customer Journey Map: This type focuses on the overall journey of a customer from awareness to purchase and beyond.
- Service Blueprint: This map delves deeper into the internal processes involved in delivering a specific service.
- Experience Map: This type focuses on the user’s emotional experience at each touchpoint.
Benefits of Using User Maps:
User maps offer a multitude of benefits for businesses seeking to optimize their user experience and drive growth:
- Enhanced User Understanding: By visualizing the user journey, businesses gain a deeper understanding of their target audience’s needs, motivations, and pain points.
- Improved User Experience: Identifying and addressing user pain points leads to a smoother and more enjoyable user experience.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: By providing a positive and seamless experience, businesses can foster customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Optimized Marketing Efforts: User maps help businesses tailor their marketing messages and campaigns to resonate with users at each stage of their journey.
- Improved Product Development: By understanding user needs and expectations, businesses can develop products and services that are more relevant and valuable.
- Enhanced Customer Service: User maps can help identify areas where customer service can be improved, leading to greater customer satisfaction.
Creating a User Map: A Step-by-Step Guide:
Creating a user map requires a systematic approach:
- Define Your Target Audience: Identify the specific user persona you are targeting with your product or service.
- Map the User Journey: Outline the key stages of the user journey, from awareness to purchase and beyond.
- Identify Touchpoints: List all the interactions a user has with your product, service, or brand at each stage.
- Determine User Emotions: Consider the emotions users experience at each touchpoint, both positive and negative.
- Identify Pain Points: Pinpoint the challenges or frustrations users encounter during their journey.
- Explore Opportunities for Improvement: Brainstorm ways to address pain points and enhance the user experience.
- Visualize the Map: Create a clear and concise visual representation of the user map, using diagrams, flowcharts, or other appropriate tools.
FAQs About User Maps:
Q: Who should use user maps?
A: User maps are valuable tools for anyone involved in the user experience, including:
- Marketing and Sales Teams
- Product Development Teams
- Customer Service Representatives
- UX/UI Designers
- Business Analysts
Q: How often should user maps be updated?
A: User maps should be reviewed and updated regularly, ideally on a quarterly or semi-annual basis. Changes in market trends, user behavior, and product features can necessitate updates.
Q: What are some common user map tools?
A: There are numerous software tools available for creating user maps, including:
- Miro: A collaborative online whiteboard tool
- Lucidchart: A diagramming and flowcharting tool
- Canva: A design platform with user map templates
- XMind: A mind mapping and brainstorming tool
- Google Docs: A versatile document editor for creating simple user maps
Q: How can user maps be used for marketing?
A: User maps can be used to:
- Target the right audience: Identify the user persona and their specific needs and interests.
- Develop effective content: Create content that addresses user pain points and resonates with their emotions.
- Optimize marketing channels: Allocate marketing resources to channels where users are most engaged.
- Personalize customer communications: Tailor messaging and offers to individual user preferences.
Tips for Creating Effective User Maps:
- Focus on the user: Always keep the user at the center of your map and prioritize their needs.
- Use a consistent format: Maintain a consistent structure and visual style throughout the map for clarity.
- Include relevant details: Provide enough information to understand the user’s journey and pain points.
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid jargon and use simple language that is easy to understand.
- Test and iterate: Regularly review and update your user map based on feedback and insights.
Conclusion:
User maps are essential tools for businesses seeking to optimize their user experience and drive growth. By understanding the user journey, identifying pain points, and exploring opportunities for improvement, businesses can create products, services, and marketing campaigns that resonate with their target audience and foster customer loyalty. By embracing the power of user maps, businesses can unlock the full potential of their digital presence and achieve lasting success in the competitive digital landscape.
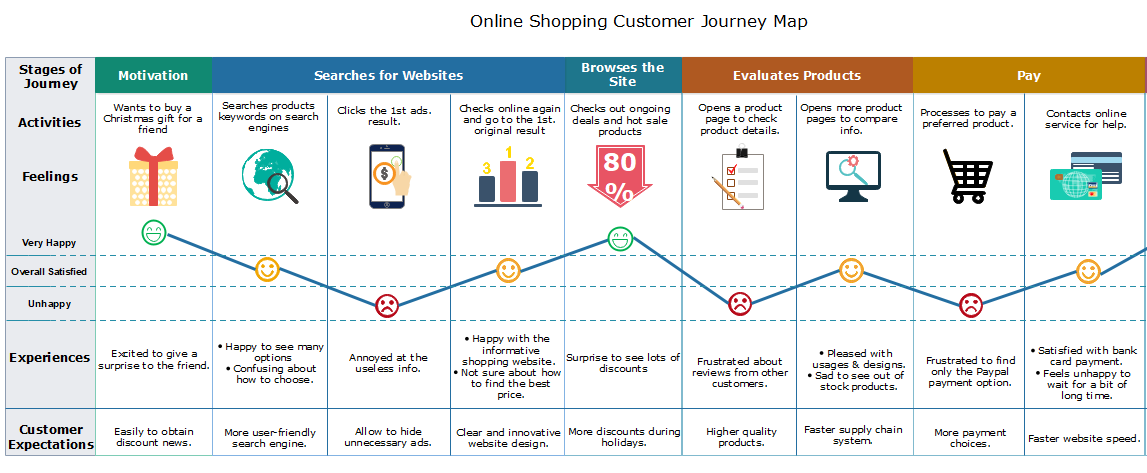

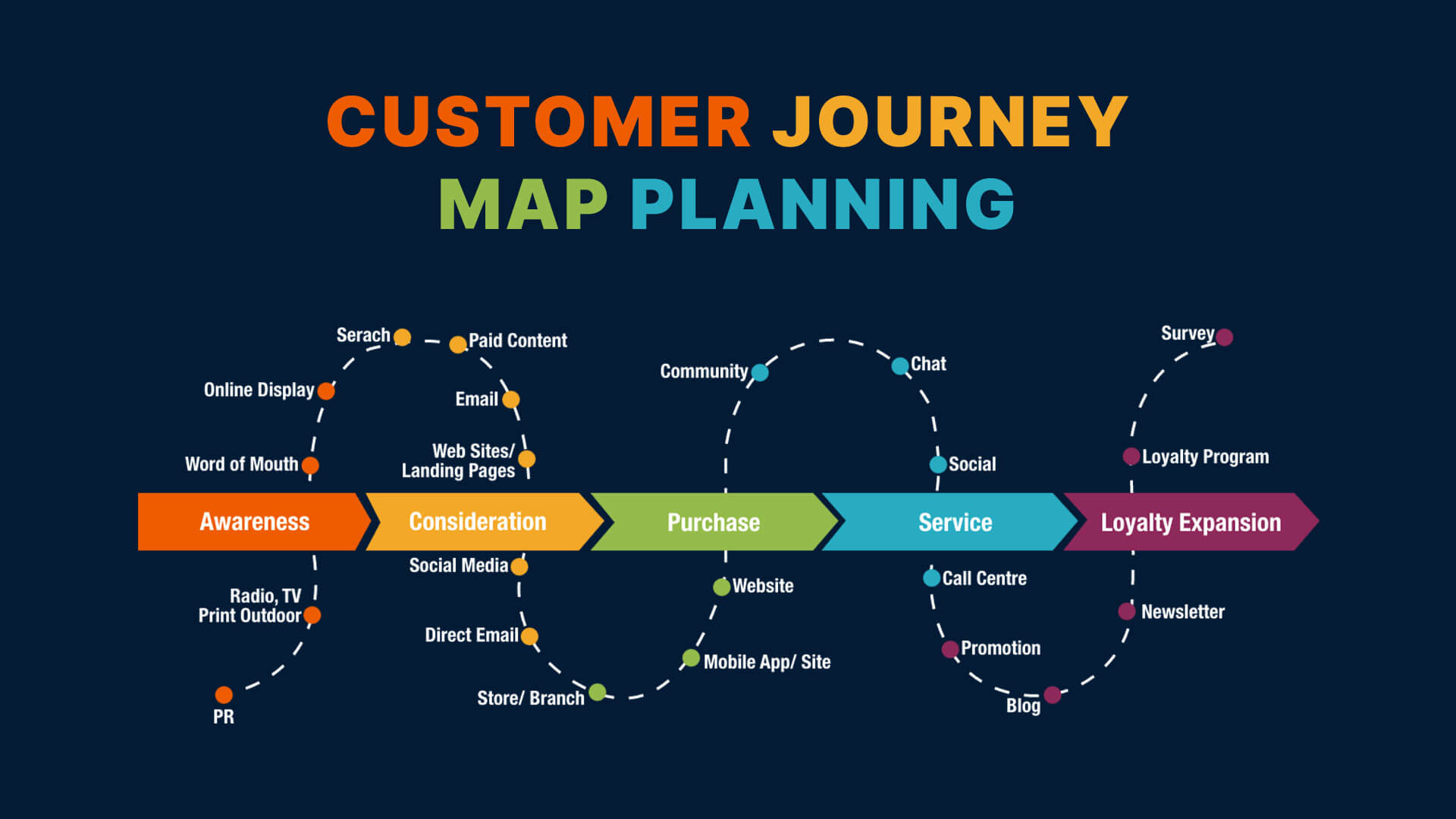
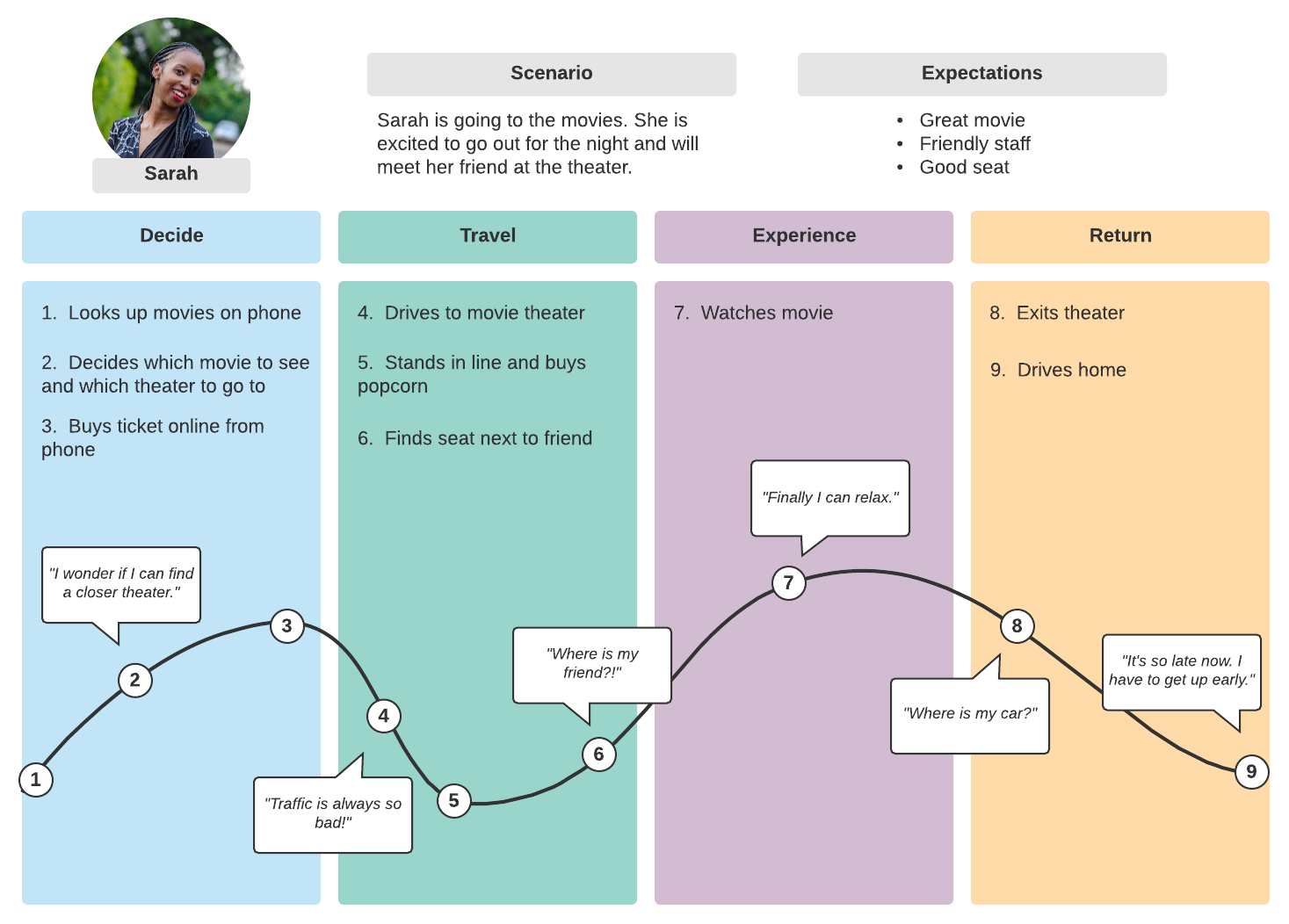



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!