Uncovering California’s Golden Past: A Guide to the State’s Historic Gold Mines
Related Articles: Uncovering California’s Golden Past: A Guide to the State’s Historic Gold Mines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Uncovering California’s Golden Past: A Guide to the State’s Historic Gold Mines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Uncovering California’s Golden Past: A Guide to the State’s Historic Gold Mines
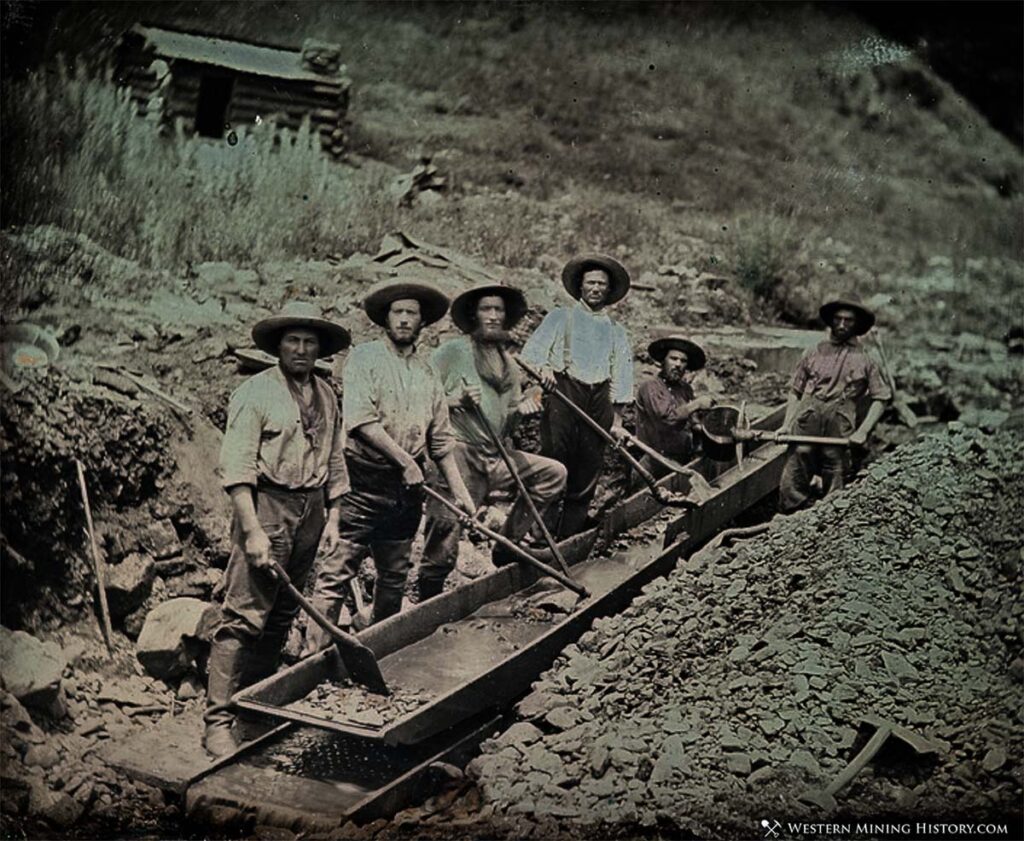

California’s history is inextricably linked to gold. The discovery of gold in 1848 sparked the California Gold Rush, a period of intense migration and economic transformation that fundamentally reshaped the state and the nation. While the era of large-scale gold mining has largely passed, the legacy of these operations remains etched in the landscape, offering a glimpse into a bygone era.
This comprehensive guide explores the rich history of gold mining in California, providing a detailed overview of the state’s significant gold mines, their historical context, and their lasting impact.
A Map of California’s Golden History
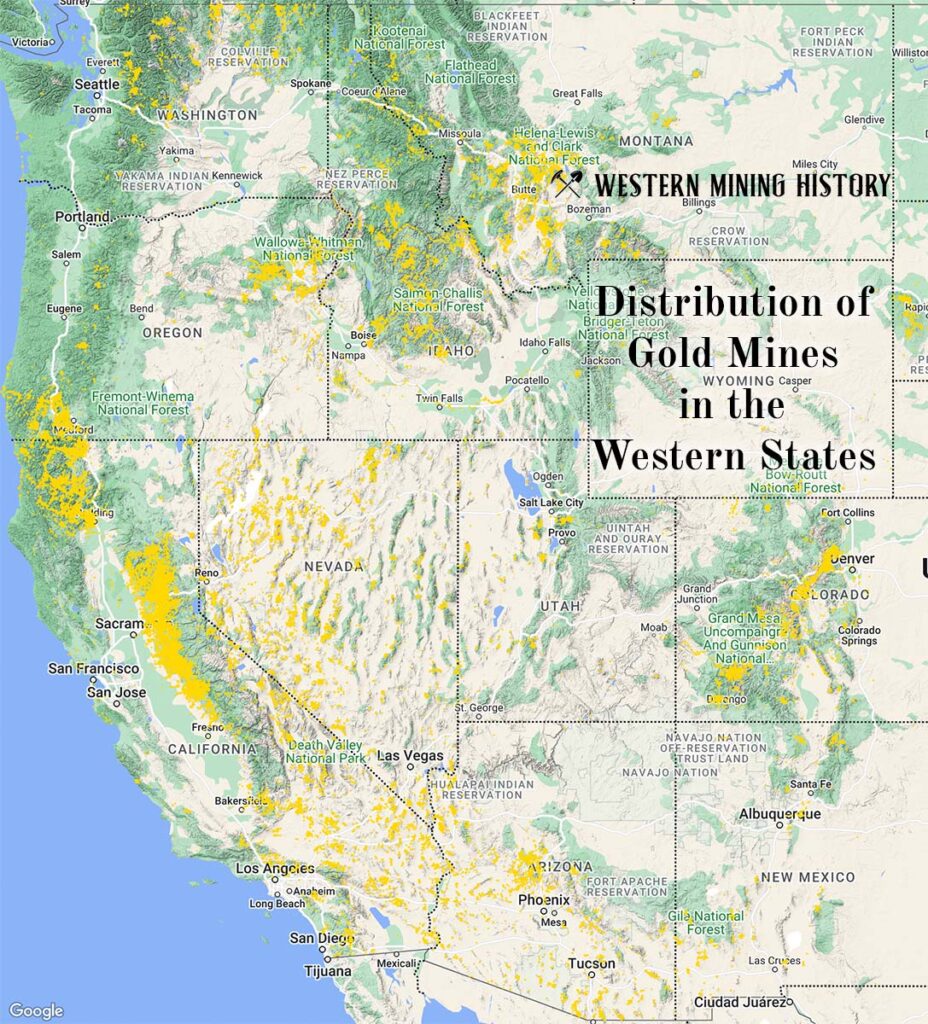
Understanding the distribution of gold mines across California requires a visual framework. While a comprehensive map encompassing every single gold mine would be unwieldy, several key regions stand out for their historical significance and the abundance of gold deposits they yielded.
-
The Mother Lode: Stretching for over 120 miles from Mariposa County to Calaveras County, the Mother Lode is arguably the most famous gold mining region in California. Its name aptly reflects its immense significance, as it produced a substantial portion of the state’s gold during the Gold Rush. Notable mines in this region include the renowned "Big Trees" mine in Calaveras County, known for its enormous quartz veins, and the "Rawhide" mine in Tuolumne County, which produced significant amounts of gold in the late 19th century.
-
The Sierra Nevada: This majestic mountain range, home to towering peaks and deep canyons, is another prominent gold mining region. The rugged terrain proved challenging but ultimately rewarding, as numerous gold deposits were discovered in its foothills and valleys. The "Bodie" mine in Mono County, once a bustling mining town, is a notable example, known for its prolific gold production and its eerie ghost town legacy.
-
The Klamath Mountains: This rugged mountain range in Northern California holds significant gold deposits, attracting prospectors and miners for over a century. The "Red Dog" mine in Siskiyou County, known for its extensive open-pit operation, is a testament to the region’s enduring mining history.
-
The Coast Ranges: While less prominent than the Sierra Nevada or the Mother Lode, the Coast Ranges also yielded gold, particularly in the counties of San Benito, Monterey, and Santa Cruz. The "New Idria" mine in San Benito County, notable for its mercury production alongside gold, exemplifies the diverse mineral wealth of this region.
Beyond the Golden Rush: A Legacy of Mining
The California Gold Rush had a profound and enduring impact on the state’s development. While the initial boom subsided, gold mining continued, albeit on a smaller scale, in various parts of the state. This ongoing activity shaped communities, fueled economic growth, and left behind a lasting imprint on the landscape.
-
Technological Advancements: The gold rush era witnessed significant advancements in mining technology, from the introduction of hydraulic mining, which utilized powerful water jets to dislodge gold-bearing gravel, to the development of more efficient extraction methods. These innovations not only increased gold production but also shaped the physical landscape, leaving behind distinctive mining scars and tailings piles.
-
Economic and Social Impacts: Gold mining contributed significantly to California’s economic growth, attracting investment, fueling infrastructure development, and creating new industries. However, it also led to social and environmental consequences, including the displacement of Native American populations, the rise of boomtowns, and the depletion of natural resources.
-
Preservation and Heritage: Today, many former gold mines stand as silent reminders of California’s past. Some have been preserved as historical sites, allowing visitors to experience the remnants of a bygone era. Others have been transformed into parks, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities. The preservation of these sites is essential for understanding California’s history and appreciating the legacy of its gold-mining past.
Navigating the Path to Gold: A Guide for Explorers
For those seeking to explore California’s gold mining history, several resources and tips can enhance their journey.
-
Historical Societies and Museums: Numerous historical societies and museums across California are dedicated to preserving and interpreting the state’s gold mining heritage. Visiting these institutions can provide invaluable insights into the history, technology, and social impact of gold mining. The California State Mining and Mineral Museum in Mariposa, for example, offers a comprehensive collection of artifacts and exhibits showcasing the state’s mining history.
-
Ghost Towns and Mining Sites: Many former mining towns, now deserted and often referred to as ghost towns, stand as poignant reminders of California’s gold rush era. Exploring these sites, such as Bodie in Mono County or Columbia in Tuolumne County, can offer a tangible connection to the past, allowing visitors to imagine the bustling life that once thrived in these communities.
-
Hiking Trails and Scenic Byways: Numerous hiking trails and scenic byways traverse former gold mining regions, offering opportunities to witness the remnants of mining operations and experience the natural beauty of these areas. The "Mother Lode Scenic Byway" in the Sierra Nevada foothills, for example, winds through historic mining towns and offers breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape.
-
Online Resources and Maps: Several online resources, including historical maps, geological surveys, and archival records, provide valuable information about California’s gold mines. The California Geological Survey’s website, for example, offers detailed maps and reports on mineral resources, including gold deposits.
FAQs about California’s Gold Mines
Q: Are there still gold mines operating in California today?
A: While large-scale gold mining has largely ceased in California, small-scale operations and recreational gold panning continue in some areas. However, most of the state’s gold production today comes from byproducts of other mining operations, such as copper or silver mines.
Q: What are the environmental impacts of gold mining?
A: Gold mining has historically had significant environmental impacts, including deforestation, erosion, water pollution, and the release of heavy metals. Modern mining practices have incorporated environmental mitigation measures, but the legacy of past mining activities continues to pose challenges for environmental restoration.
Q: What are the best places to find gold in California today?
A: While finding significant gold deposits is unlikely, recreational gold panning is a popular activity in many areas. Designated panning areas, such as those managed by state parks or private companies, offer a safe and enjoyable experience.
Q: Can I legally pan for gold in California?
A: Yes, recreational gold panning is generally permitted on public lands, but it’s essential to obtain the necessary permits and follow regulations. Some areas may have restrictions or require specific licenses.
Conclusion
The legacy of gold mining in California is multifaceted, encompassing technological advancements, economic growth, social transformations, and environmental impacts. While the era of large-scale gold mining has largely passed, the state’s gold mining history remains an integral part of its identity. By understanding the significance of these operations, exploring their remnants, and appreciating the enduring impact they have had on the landscape and society, we gain a deeper understanding of California’s past and its enduring connection to its golden heritage.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Uncovering California’s Golden Past: A Guide to the State’s Historic Gold Mines. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!