Navigating Venezuela: A Geographical Exploration of a Nation in South America
Related Articles: Navigating Venezuela: A Geographical Exploration of a Nation in South America
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Venezuela: A Geographical Exploration of a Nation in South America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Venezuela: A Geographical Exploration of a Nation in South America

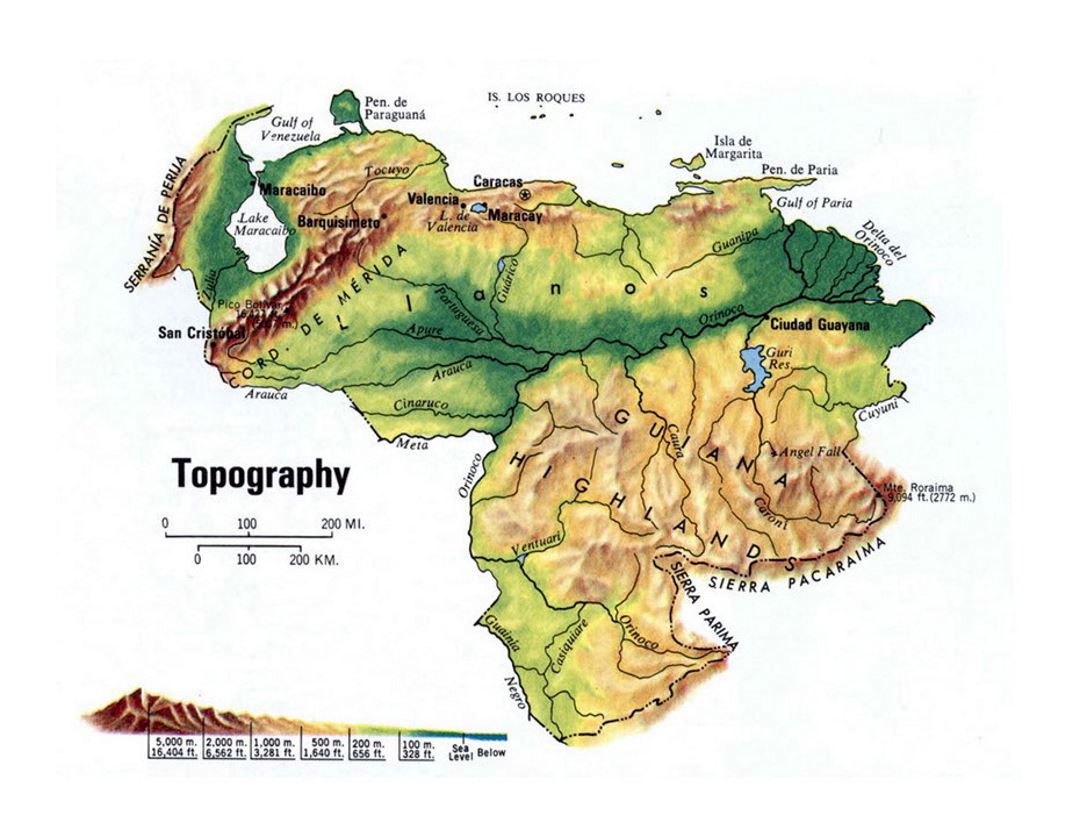
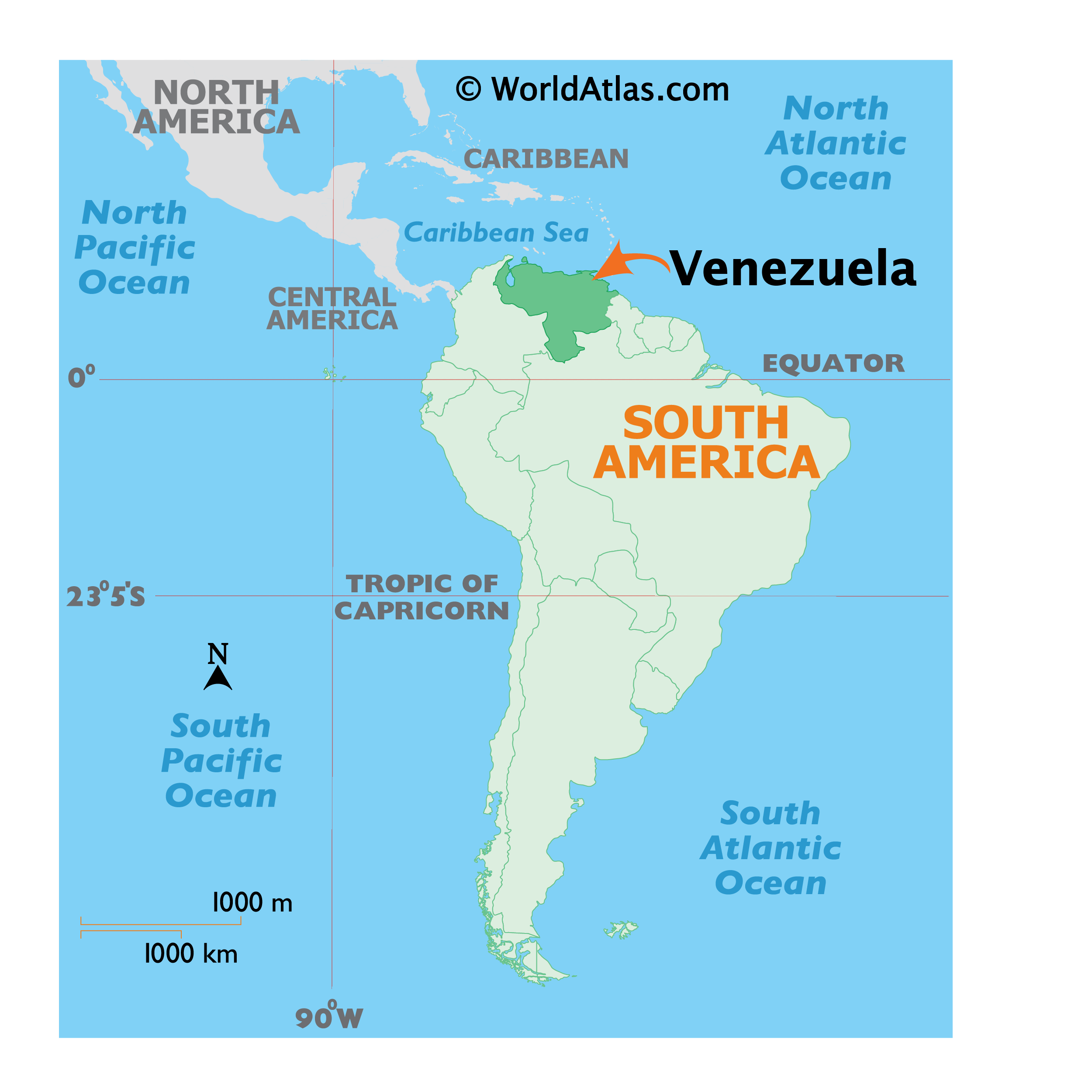
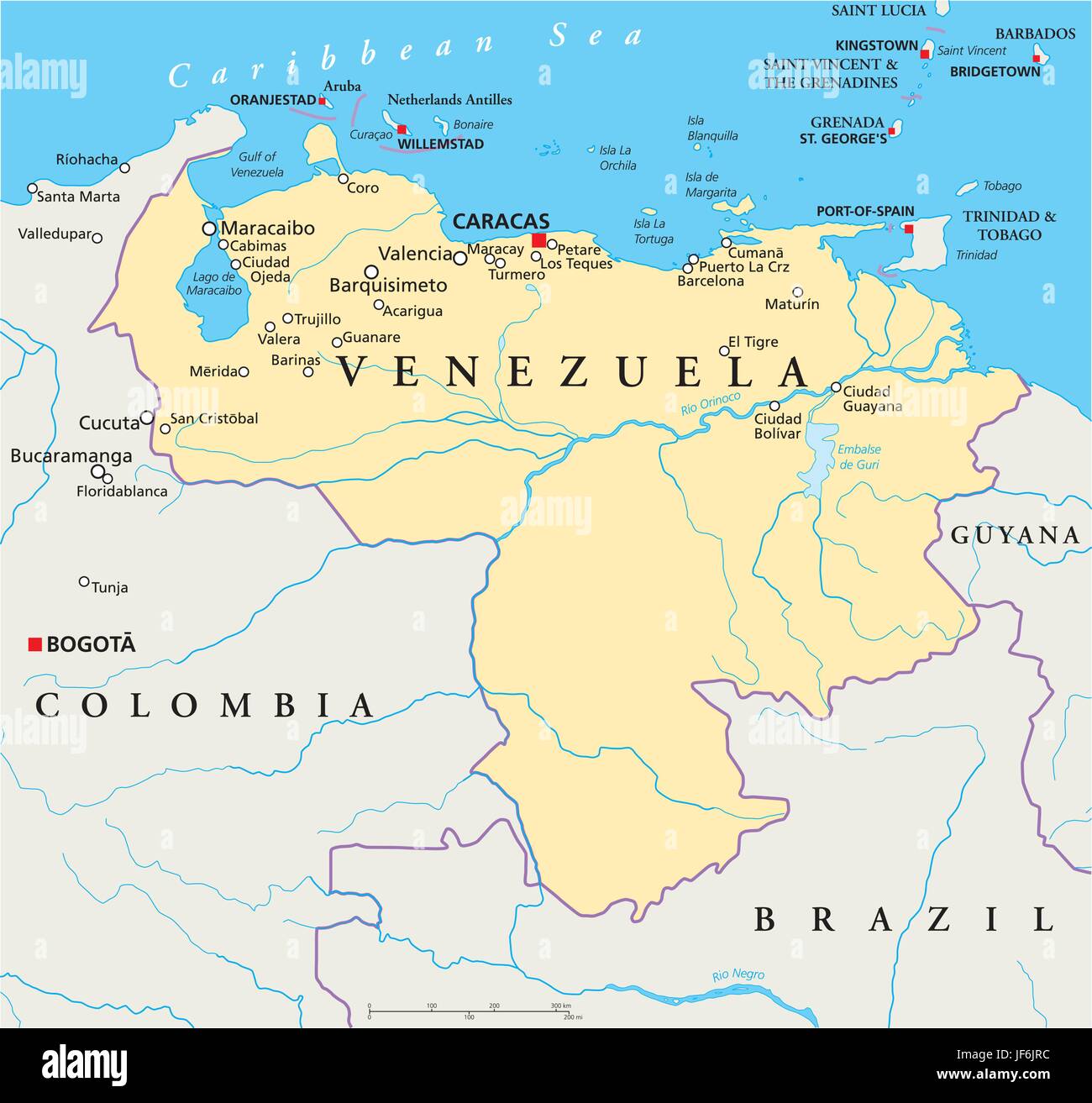
Venezuela, a country nestled in the northernmost region of South America, is a land of striking contrasts. From the towering peaks of the Andes Mountains to the vast plains of the Llanos, and from the lush rainforests of the Amazon to the pristine beaches of the Caribbean, Venezuela boasts a diverse and captivating landscape. Understanding the country’s geography, as revealed through its map, is crucial for appreciating its natural beauty, cultural richness, and historical significance.
A Geographical Overview: Unveiling Venezuela’s Landscape
Venezuela’s geographical position, straddling the northern edge of South America, has shaped its history, culture, and economy. The country shares borders with Colombia to the west, Brazil to the south, and Guyana to the east. Its northern coastline stretches along the Caribbean Sea, providing access to key shipping routes and fostering a maritime culture.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Andes Mountains: The Venezuelan Andes, a branch of the vast Andean mountain range, run through the western part of the country. These mountains are home to diverse ecosystems, including cloud forests, páramos (high-altitude grasslands), and snow-capped peaks. They are also rich in mineral resources, including gold, copper, and iron ore.
- The Llanos: The Llanos, vast savannas that cover much of central Venezuela, are characterized by flat, grassy plains, punctuated by occasional rivers and streams. This region is ideal for cattle ranching and agriculture, particularly the cultivation of rice, corn, and soybeans.
- The Amazon Rainforest: The Amazon basin extends into southeastern Venezuela, encompassing a significant portion of the country’s territory. This region is home to a staggering array of biodiversity, including countless species of plants, animals, and indigenous communities.
- The Caribbean Coast: Venezuela’s northern coastline, stretching along the Caribbean Sea, boasts stunning beaches, coral reefs, and numerous islands. This region is a major tourist destination, drawing visitors from around the world to enjoy its pristine waters and vibrant culture.
- The Orinoco River Basin: The Orinoco River, one of the largest rivers in South America, flows through the country’s interior, creating a fertile basin that supports a rich ecosystem and various indigenous communities. The Orinoco Delta, where the river meets the Atlantic Ocean, is a unique and ecologically important area.
The Importance of Venezuela’s Geography:
- Natural Resources: Venezuela’s diverse geography has endowed it with abundant natural resources, including oil, gas, gold, iron ore, and diamonds. These resources have played a significant role in the country’s economic development, although their extraction has also had a significant impact on the environment.
- Biodiversity: Venezuela is home to a remarkable diversity of flora and fauna, thanks to its varied ecosystems. The country is a global hotspot for biodiversity, with a significant portion of its territory covered by protected areas and national parks.
- Climate and Agriculture: Venezuela’s climate varies considerably across the country, ranging from tropical in the lowlands to temperate in the highlands. This diversity allows for the cultivation of a wide range of crops, including coffee, cacao, bananas, and sugar cane.
- Transportation and Trade: Venezuela’s geographical position, with its access to both the Caribbean Sea and the Orinoco River, has made it a key hub for transportation and trade in the region. The country’s ports and waterways facilitate the movement of goods and people, connecting it to other countries in South America and the wider world.
- Cultural Diversity: Venezuela’s diverse geography has fostered a rich and varied culture, shaped by the interactions of indigenous peoples, European colonists, and African slaves. The country’s different regions have developed unique traditions, languages, and customs, reflecting the influences of their diverse landscapes and histories.
Navigating Venezuela: A Guide to Understanding the Map
To fully appreciate the complexities of Venezuela’s geography, it is essential to engage with its map. By studying the map, one can gain insights into:
- The Country’s Boundaries: Understanding the borders that define Venezuela’s territory provides a starting point for exploring its geographical context. Recognizing its neighbors, Colombia, Brazil, and Guyana, allows for a broader understanding of regional relationships and interactions.
- Major Cities and Towns: Identifying the locations of major cities and towns, such as Caracas, Maracaibo, Valencia, and Ciudad Guayana, provides a framework for understanding population distribution, economic activity, and cultural centers.
- Key Geographical Features: Recognizing the Andes Mountains, the Llanos, the Amazon Rainforest, the Caribbean Coast, and the Orinoco River Basin helps to grasp the diversity of landscapes and ecosystems that shape Venezuela.
- Transportation Networks: Examining roads, railways, and waterways reveals the country’s infrastructure, highlighting major transportation routes and connecting points. This understanding is crucial for comprehending the flow of goods, people, and information within Venezuela.
- Natural Resources: Identifying areas rich in oil, gas, gold, iron ore, and other natural resources allows for a better understanding of the country’s economic potential and the impact of resource extraction on the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Venezuela’s Geography:
Q: What is the highest point in Venezuela?
A: The highest point in Venezuela is Pico Bolívar, located in the Andes Mountains, reaching an elevation of 4,981 meters (16,342 feet).
Q: What is the largest city in Venezuela?
A: The largest city in Venezuela is Caracas, the country’s capital, with a population of over 2 million.
Q: What is the main language spoken in Venezuela?
A: The official language of Venezuela is Spanish. However, there are numerous indigenous languages spoken in different regions of the country.
Q: What is the climate like in Venezuela?
A: Venezuela has a diverse climate, ranging from tropical in the lowlands to temperate in the highlands. The country experiences a wet season from May to October and a dry season from November to April.
Q: What are some of the major industries in Venezuela?
A: Venezuela’s economy is heavily reliant on oil and gas production. Other major industries include agriculture, mining, and tourism.
Tips for Using a Map of Venezuela:
- Use a detailed and up-to-date map: Ensure that the map you are using is comprehensive and accurate, providing detailed information about the country’s geography and infrastructure.
- Focus on key features: Pay attention to major cities, rivers, mountains, and other prominent geographical features.
- Explore different scales: Use maps at different scales to gain a broader understanding of the country’s overall geography and then zoom in on specific regions of interest.
- Combine maps with other resources: Use maps in conjunction with other resources, such as photographs, satellite imagery, and online tools, to gain a more comprehensive view of Venezuela’s landscape.
Conclusion:
Understanding the geography of Venezuela through its map is crucial for appreciating the country’s natural beauty, cultural richness, and historical significance. The map reveals the country’s diverse landscape, from towering mountains to vast plains, and highlights the importance of its natural resources, biodiversity, and transportation networks. By engaging with the map, one can gain a deeper understanding of Venezuela’s unique geographical context, which has shaped its history, culture, and economy.
/Christopher-Columbus-58b9ca2c5f9b58af5ca6b758.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Venezuela: A Geographical Exploration of a Nation in South America. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!