Navigating the Lifeline: An Exploration of Iraq’s River Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Lifeline: An Exploration of Iraq’s River Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Lifeline: An Exploration of Iraq’s River Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Lifeline: An Exploration of Iraq’s River Network

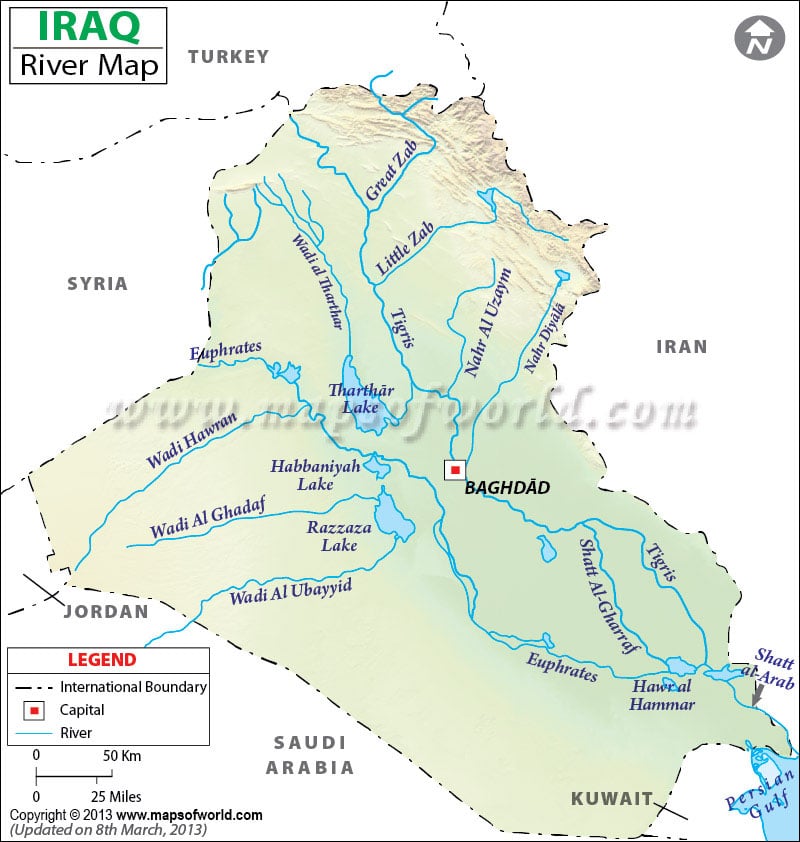
Iraq, a nation cradled in the heart of the Middle East, boasts a rich tapestry of history and culture interwoven with a vital network of rivers. These waterways, flowing like arteries through the land, have profoundly shaped the country’s landscape, economy, and very existence. Understanding the intricate geography of Iraq’s rivers is crucial for appreciating its past, present, and future.
The Tigris and Euphrates: The Twin Pillars of Civilization
The Tigris and Euphrates rivers, renowned as the "cradle of civilization," form the bedrock of Iraq’s hydrological system. Originating in the Taurus Mountains of Turkey, these mighty rivers traverse vast distances before converging in the Shatt al-Arab, a shared waterway with Iran, eventually emptying into the Persian Gulf.
The Tigris:
- Course: The Tigris, the eastern of the two, flows through southeastern Turkey, northern Syria, and ultimately through Iraq, where it carves its way through the country’s heartland.
- Significance: The Tigris has long been a vital source of water for agriculture, supporting the fertile plains of Mesopotamia. It also plays a crucial role in transportation, connecting major cities like Mosul, Tikrit, and Baghdad.
- Notable Tributaries: The Tigris receives several tributaries along its journey, including the Greater Zab, the Lesser Zab, and the Diyala River. These tributaries significantly contribute to the river’s volume and water resources.
The Euphrates:
- Course: The Euphrates, the western of the two, originates in Turkey, passes through Syria, and then traverses a vast distance through Iraq, where it flows alongside the Tigris before joining it at the Shatt al-Arab.
- Significance: The Euphrates, like the Tigris, has been a cornerstone of civilization in the region, providing irrigation for agriculture and supporting a rich ecosystem. It also served as a major trade route connecting Mesopotamia to other parts of the ancient world.
- Notable Tributaries: The Euphrates receives tributaries like the Balikh River and the Khabur River, which contribute to its water flow and ecological diversity.
The Shatt al-Arab:
- Formation: The Shatt al-Arab is formed by the confluence of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, marking a crucial junction for both water flow and political significance.
- Significance: This shared waterway serves as a vital artery for maritime trade, connecting Iraq to the Persian Gulf and the wider world. It also carries significant ecological value, supporting a rich diversity of marine life.
Other Notable Rivers:
Beyond the Tigris and Euphrates, several other rivers contribute to Iraq’s water resources:
- The Karun River: This major river originates in Iran and flows into the Shatt al-Arab, playing a significant role in the shared waterway’s water flow.
- The Diyala River: A tributary of the Tigris, the Diyala River flows through the eastern part of Iraq, providing irrigation and supporting a vibrant ecosystem.
- The Wadi Al-Hasa: This seasonal river flows through the western desert of Iraq, contributing to the country’s water resources during the rainy season.
The Significance of Iraq’s River Network:
- Water Security: Iraq’s rivers are the lifeblood of the nation, providing water for agriculture, drinking, and industrial use. The country’s water security is inextricably linked to the health and flow of these waterways.
- Agriculture and Food Security: The fertile plains along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers have historically supported a thriving agricultural sector, producing a wide range of crops that contribute to Iraq’s food security.
- Transportation and Trade: The rivers have long served as vital arteries for transportation, connecting cities and facilitating trade both within Iraq and with neighboring countries.
- Ecological Importance: The rivers support a rich and diverse ecosystem, providing habitats for a wide range of flora and fauna, including endangered species.
- Cultural and Historical Significance: The rivers have played a pivotal role in shaping Iraq’s cultural heritage and history, serving as centers of civilization, trade, and artistic expression.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite their immense importance, Iraq’s rivers face significant challenges:
- Water Scarcity: The increasing demand for water resources, coupled with climate change and upstream water management practices in neighboring countries, poses a growing threat to water security in Iraq.
- Pollution: Industrial activities, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge contribute to pollution levels in the rivers, impacting water quality and threatening aquatic life.
- Dam Construction: Dams constructed upstream in Turkey and Syria have significantly altered the flow of the Tigris and Euphrates, impacting water availability downstream in Iraq.
- Political Disputes: Water rights and the management of shared water resources are often subject to political disputes between Iraq and its neighbors.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for collaboration and innovation:
- Water Management: Implementing sustainable water management strategies, including efficient irrigation systems and water conservation measures, is crucial for ensuring water security in the long term.
- Environmental Protection: Investing in infrastructure to reduce pollution and protect the ecological integrity of the rivers is vital for safeguarding biodiversity and water quality.
- Regional Cooperation: Fostering cooperation with neighboring countries on water management issues is essential for ensuring equitable access to water resources and mitigating the impacts of upstream water management practices.
FAQs About Iraq’s Rivers:
1. What is the most important river in Iraq?
Both the Tigris and Euphrates rivers are of paramount importance to Iraq, as they provide the country with its most significant water resources.
2. How do the Tigris and Euphrates rivers affect the landscape of Iraq?
The Tigris and Euphrates have shaped the landscape of Iraq, creating fertile plains and alluvial valleys that have supported agriculture and civilization for millennia.
3. What are the main challenges facing Iraq’s rivers?
The main challenges facing Iraq’s rivers include water scarcity, pollution, dam construction, and political disputes over water resources.
4. What are the potential solutions to these challenges?
Potential solutions include sustainable water management practices, environmental protection measures, regional cooperation, and investment in infrastructure to improve water quality and availability.
5. How do the rivers contribute to Iraq’s economy?
The rivers contribute to Iraq’s economy through agriculture, transportation, and tourism. They support a thriving agricultural sector, provide transportation routes, and attract tourists interested in the country’s rich cultural heritage.
Tips for Understanding Iraq’s Rivers:
- Consult Maps: Use maps and online resources to visualize the course of Iraq’s major rivers and their tributaries.
- Read Historical Accounts: Explore historical texts and accounts to gain insights into the role of rivers in Iraq’s history and civilization.
- Follow Current Events: Stay informed about current events related to water management, environmental issues, and political disputes concerning Iraq’s rivers.
- Support Sustainable Practices: Encourage and support sustainable water management practices and environmental protection efforts to ensure the long-term health of Iraq’s rivers.
Conclusion:
Iraq’s river network, a vital lifeline for the nation, holds immense significance for its economy, culture, and very existence. Understanding the complex interplay of these waterways, their challenges, and potential solutions is crucial for navigating the country’s future. By fostering sustainable practices, promoting regional cooperation, and embracing innovation, Iraq can ensure the continued flow of these precious rivers and safeguard its future prosperity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Lifeline: An Exploration of Iraq’s River Network. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!