Navigating the Landscape of American Agriculture: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of American Agriculture: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of American Agriculture: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of American Agriculture: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map

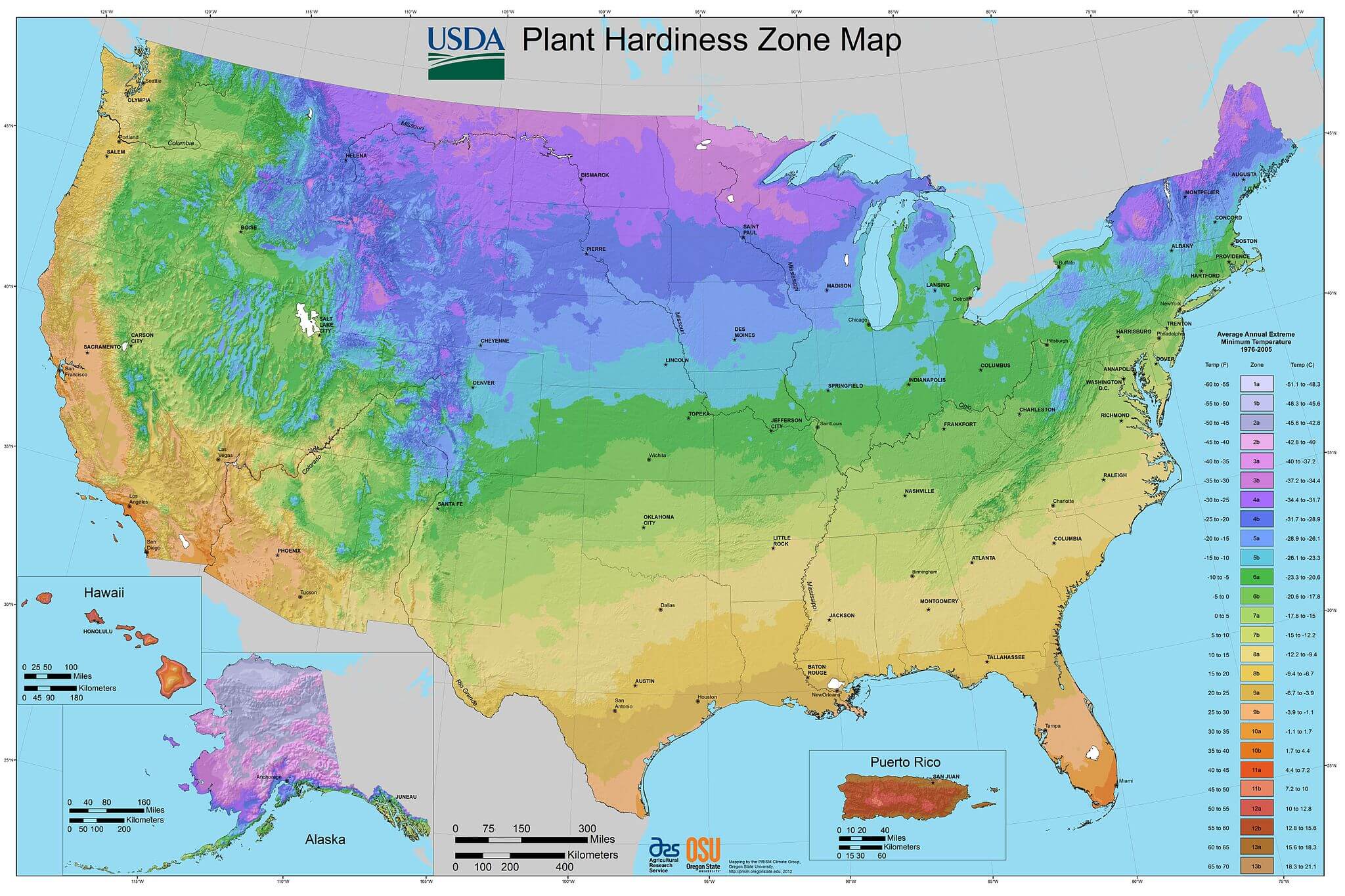
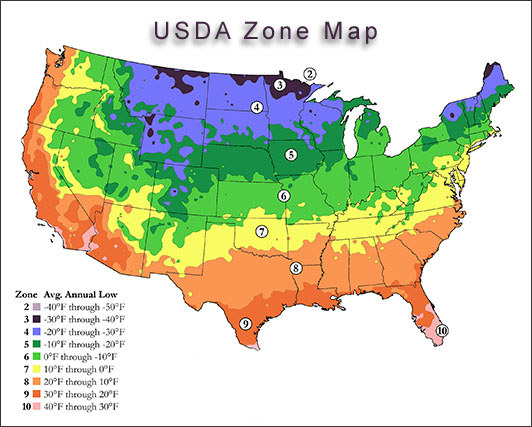
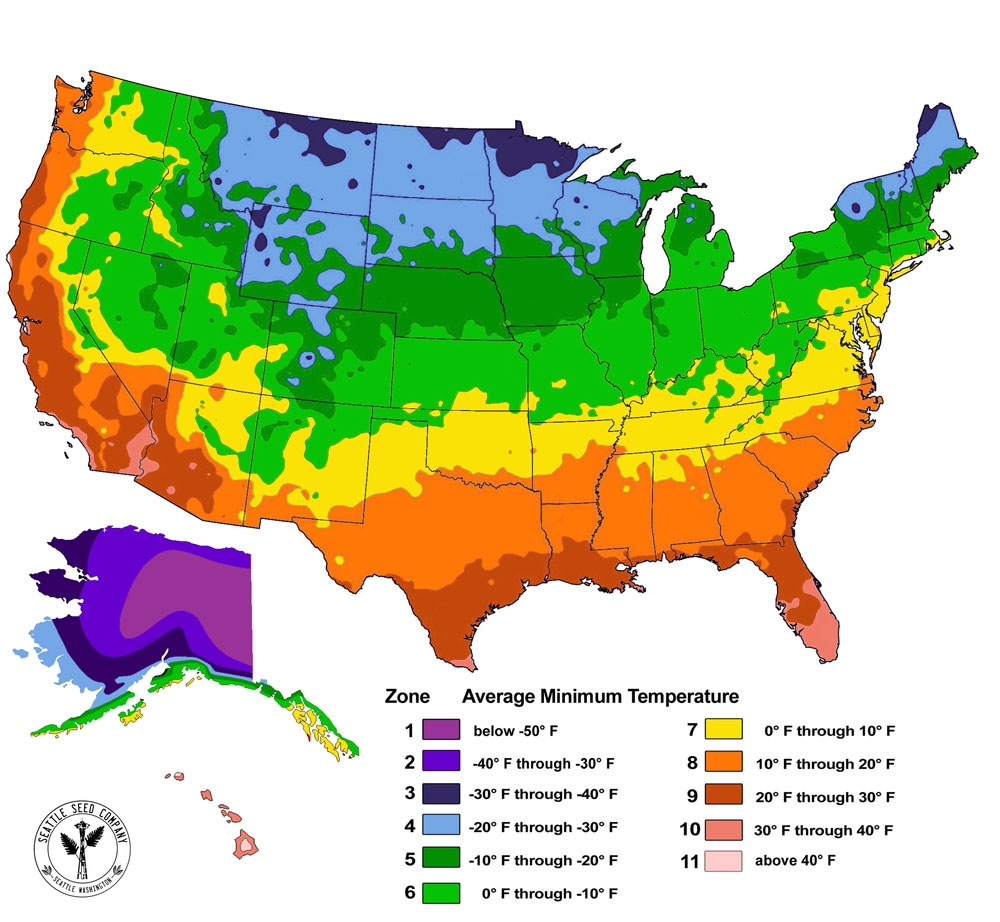
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Plant Hardiness Zone Map is an indispensable tool for gardeners, farmers, and anyone involved in agriculture across the country. This map, updated every decade, provides valuable information about the average minimum winter temperatures in different regions, allowing individuals to select plants that thrive in their specific climate. Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map empowers informed decision-making, fostering successful plant growth and contributing to the sustainability of agricultural practices.
Decoding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Comprehensive Overview
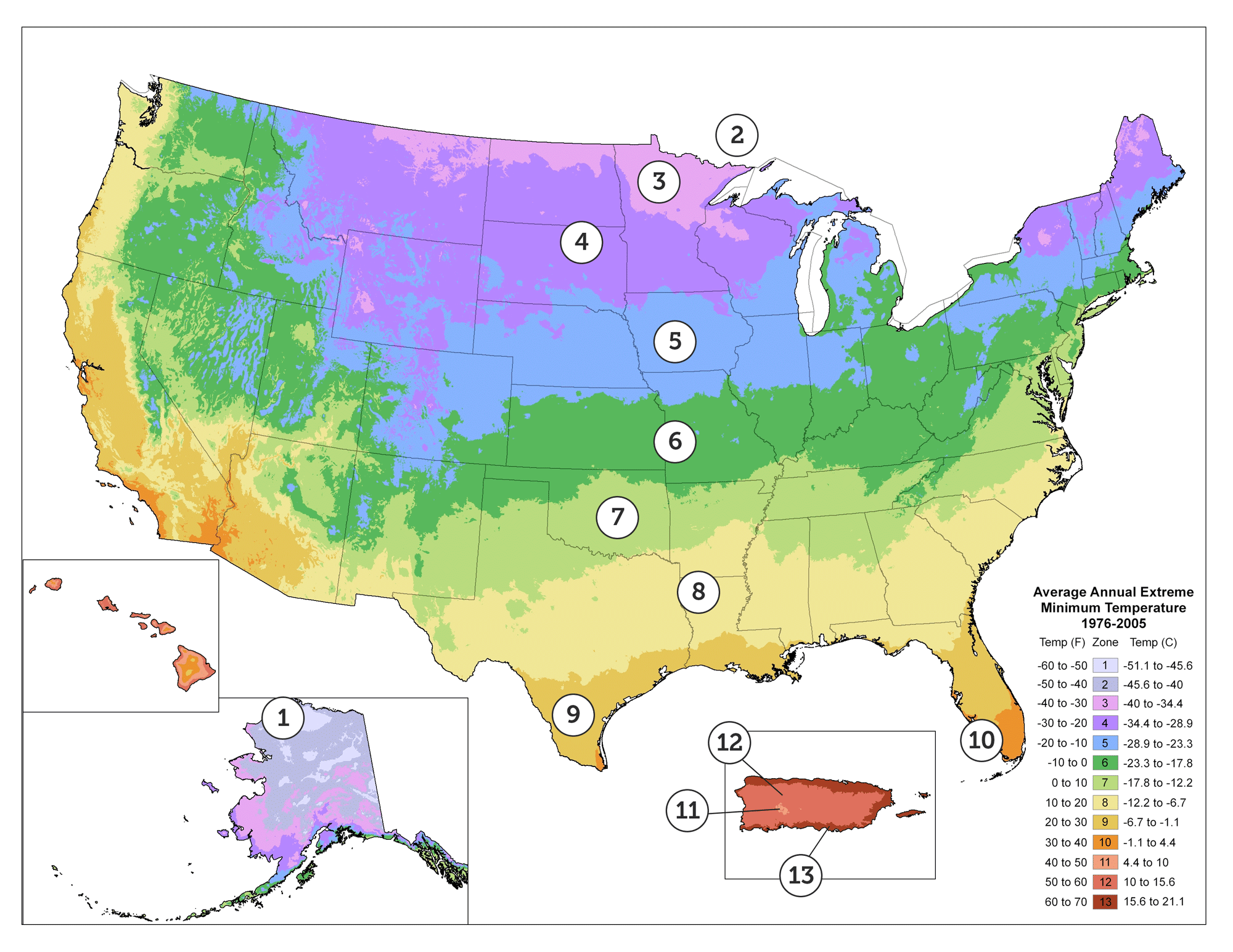
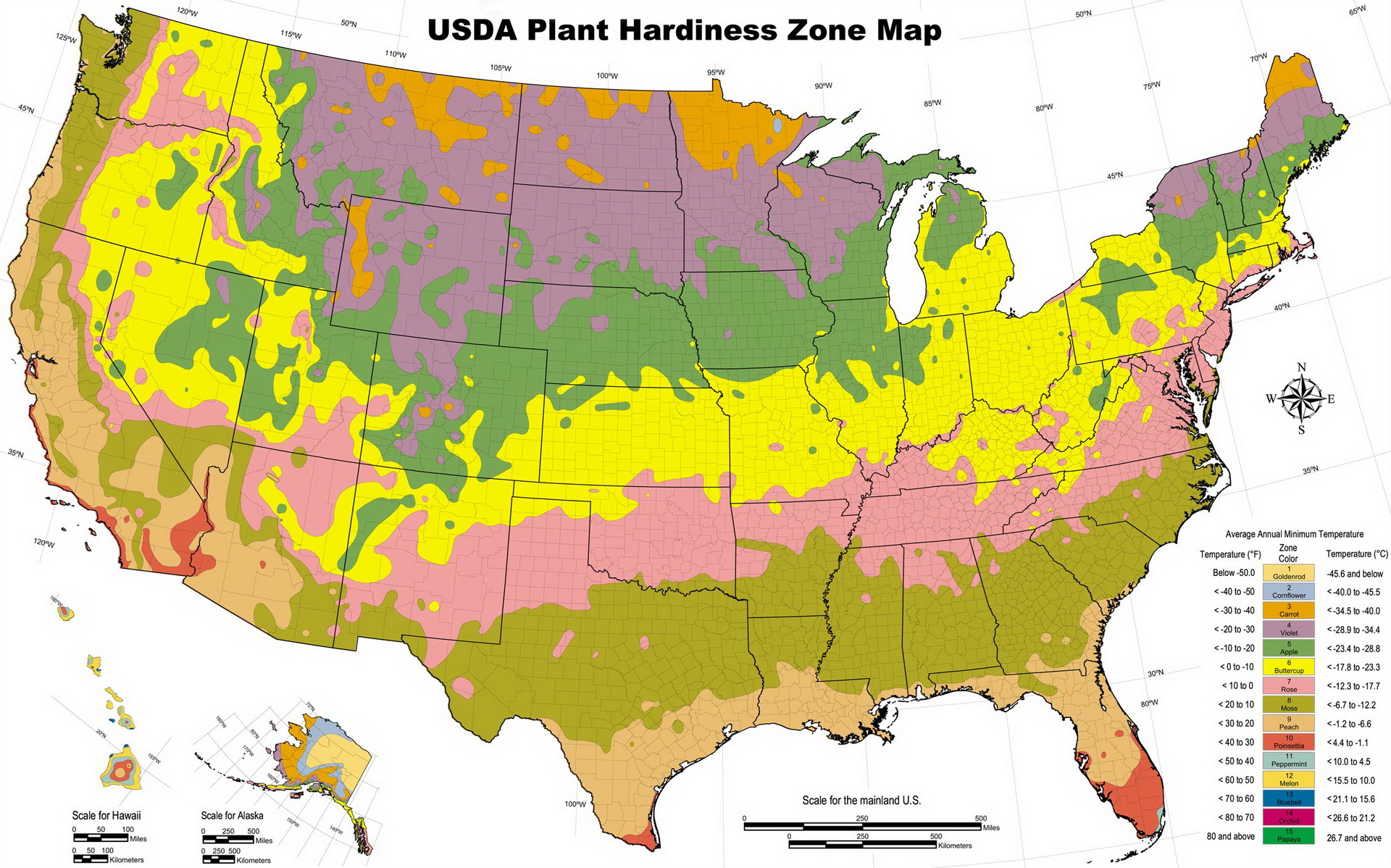
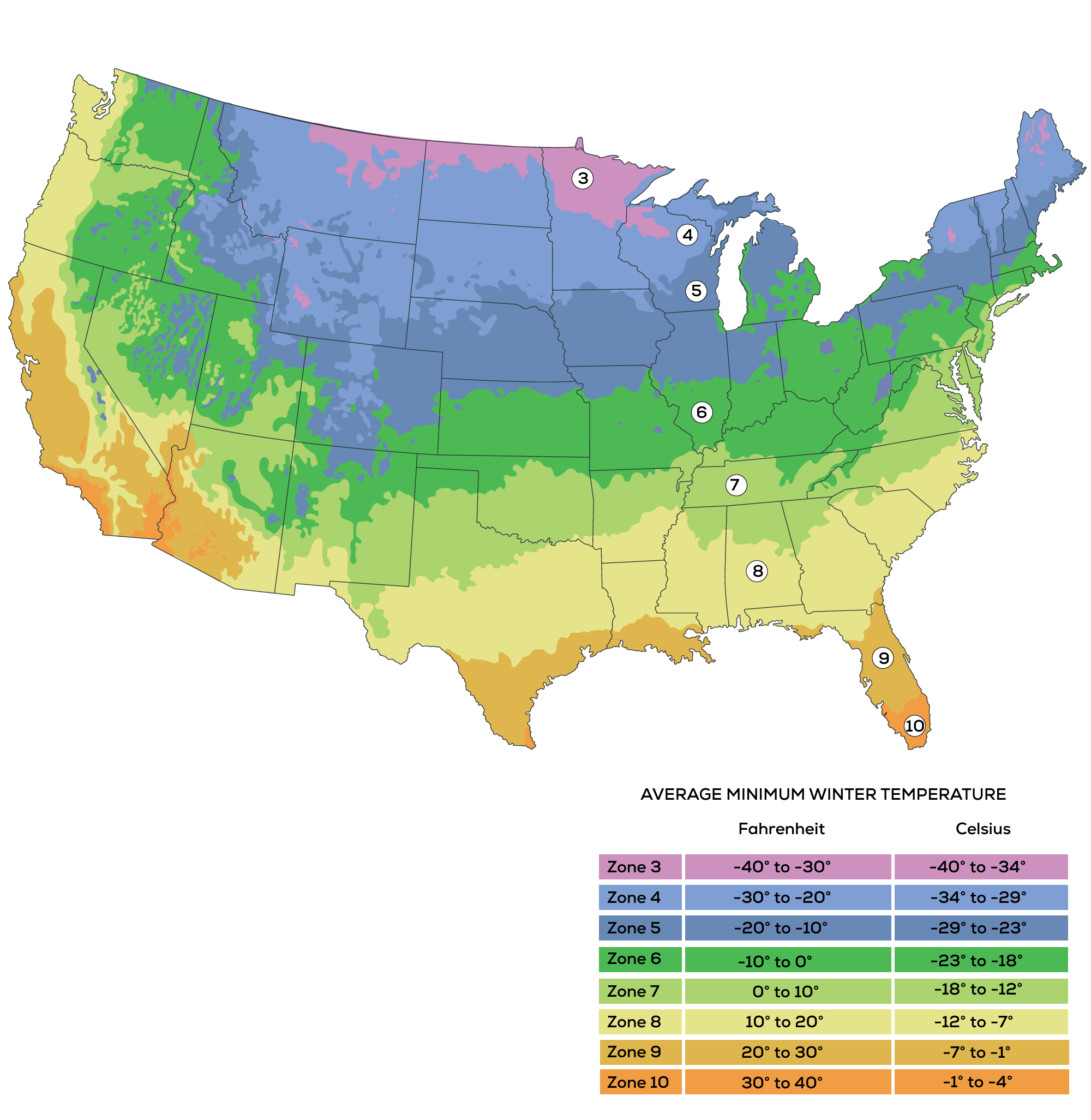
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides the United States into 11 zones, each representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit range of average minimum winter temperatures. Zone 1, the coldest, encompasses areas with average minimum winter temperatures below -60 degrees Fahrenheit, while Zone 11, the warmest, experiences average minimum winter temperatures above 40 degrees Fahrenheit.
Key Features of the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map:
- Geographic Precision: The map delineates zones based on historical temperature data, providing a geographically accurate representation of climate conditions across the United States.
- Temperature-Based Classification: The zones are defined by the average minimum winter temperature, a crucial factor for plant survival during cold periods.
- Plant Selection Guidance: The map serves as a guide for selecting plants that can withstand the specific winter temperatures of a particular region.
- Regional Variations: The map acknowledges the diverse climate patterns across the country, allowing for targeted plant selection based on regional variations.
- Decadal Updates: The USDA regularly updates the map to reflect changes in climate patterns and ensure accuracy.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Nuances of Plant Hardiness Zones
While the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a valuable framework for plant selection, it’s essential to consider additional factors that influence plant survival:
- Microclimates: Variations in elevation, proximity to bodies of water, and local topography can create microclimates within a specific zone, impacting the actual minimum winter temperature.
- Site Conditions: Factors such as soil type, drainage, and exposure to wind can influence plant hardiness, even within the same zone.
- Plant Species Variations: Different plant species within the same hardiness zone may exhibit varying tolerances to cold temperatures.
- Climate Change: As climate change alters temperature patterns, the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map may require adjustments in the future.
Utilizing the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Practical Guide for Success
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as a foundational tool for informed plant selection and successful gardening practices. Here’s how to utilize this valuable resource effectively:
- Locate Your Zone: Determine your specific hardiness zone by using the online USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map or consulting a printed version.
- Consult Plant Labels: When purchasing plants, look for the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone range listed on the label, ensuring compatibility with your region’s climate.
- Consider Microclimates: Evaluate your specific site conditions, such as elevation and proximity to water, to understand potential microclimate variations.
- Research Plant Species: Explore plant species within your hardiness zone, considering their specific cold tolerance and other factors.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of updates to the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, as climate change may necessitate adjustments in plant selection.
The Importance of the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map: Fostering Sustainable Agriculture
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map plays a critical role in supporting sustainable agricultural practices by:
- Optimizing Plant Selection: By recommending plants suited to specific climates, the map helps minimize plant losses due to unsuitable conditions.
- Reducing Water Consumption: Selecting drought-tolerant plants appropriate for the region reduces the need for excessive irrigation, promoting water conservation.
- Minimizing Pesticide Use: By choosing plants adapted to local conditions, the map contributes to reducing the reliance on pesticides to combat pests and diseases.
- Enhancing Biodiversity: The map encourages the cultivation of diverse plant species, promoting biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
1. What is the purpose of the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map?
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides information about the average minimum winter temperatures in different regions of the United States, guiding plant selection for successful growth.
2. How often is the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map updated?
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is updated every decade to reflect changes in climate patterns and ensure accuracy.
3. What is the difference between a hardiness zone and a growing zone?
A hardiness zone refers to the average minimum winter temperature, while a growing zone indicates the length of the growing season.
4. Can I grow plants outside of my hardiness zone?
While it’s possible to grow plants outside their designated hardiness zone, it requires careful planning and consideration of microclimates and plant species variations.
5. How does climate change affect the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map?
Climate change is altering temperature patterns, potentially leading to shifts in hardiness zones. The USDA is actively monitoring these changes to ensure the map remains accurate.
Tips for Utilizing the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
- Consult Local Garden Centers: Seek advice from local garden centers for plant recommendations tailored to your specific region and microclimate.
- Experiment with Plants: Try different plant species within your hardiness zone to discover which ones thrive best in your local conditions.
- Protect Plants During Extreme Weather: Take steps to protect plants during extreme weather events, such as cold snaps or heat waves, even within their designated hardiness zone.
- Consider Plant Maturity: Remember that young plants may be more susceptible to cold temperatures than mature plants.
- Stay Informed About Local Weather Patterns: Monitor local weather forecasts and adjust gardening practices accordingly.
Conclusion: The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map – A Powerful Tool for Sustainable Agriculture
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable resource for anyone involved in agriculture, from home gardeners to professional farmers. By understanding the average minimum winter temperatures in different regions, individuals can select plants suited to their specific climate, fostering successful growth and contributing to sustainable agricultural practices. The map empowers informed decision-making, promotes biodiversity, and encourages water conservation, ultimately contributing to the health and resilience of our agricultural landscapes. As climate change continues to alter temperature patterns, the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map will remain an indispensable tool for navigating the evolving landscape of American agriculture.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of American Agriculture: Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!