Navigating the Asian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the Asian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Asian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Asian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude
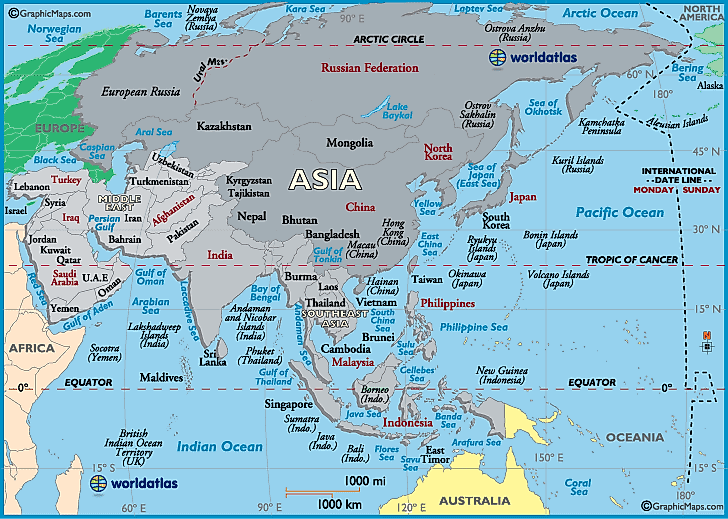
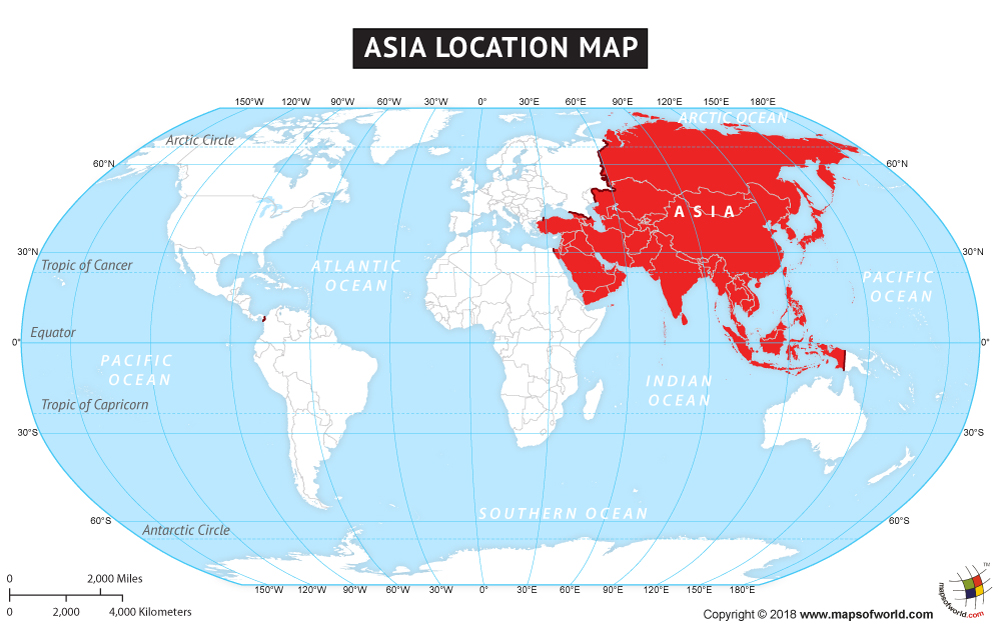
Asia, the world’s largest and most populous continent, encompasses a vast expanse of land stretching from the eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea to the Pacific Ocean. Understanding the geographical coordinates of this diverse region – latitude and longitude – is crucial for navigating its varied landscapes, diverse cultures, and complex geopolitical landscape.
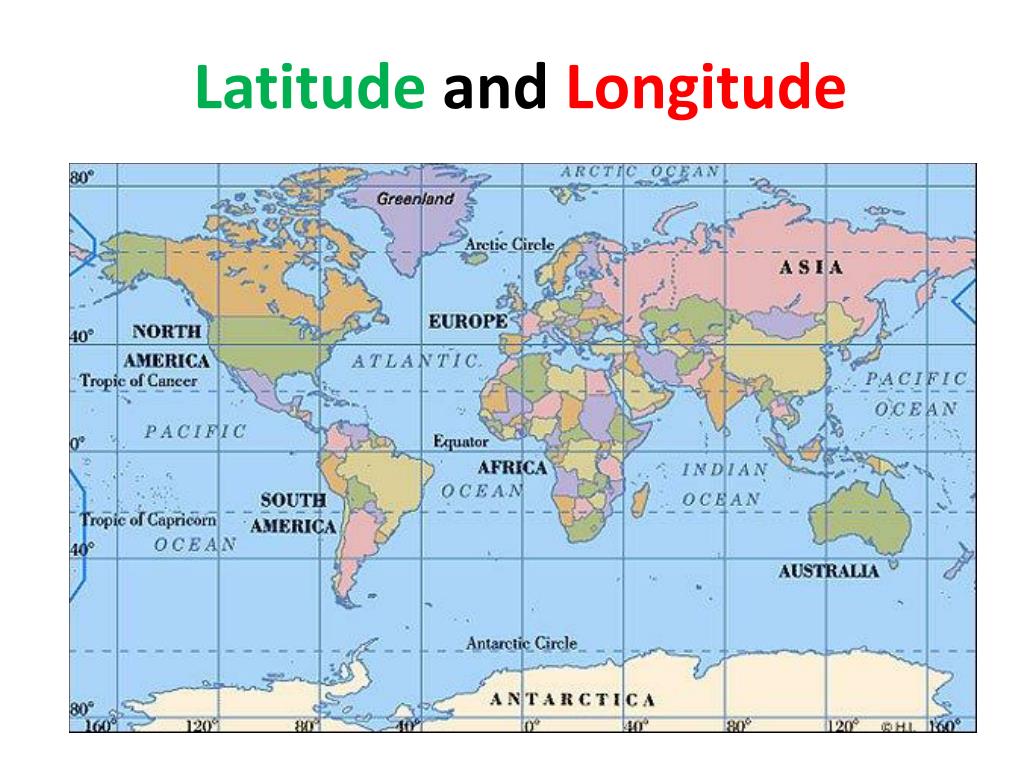
Latitude and Longitude: The Foundation of Geographic Location
Latitude and longitude form the foundation of a global grid system, enabling precise location identification on Earth’s surface. Latitude lines run horizontally around the globe, parallel to the equator, measuring distance north or south of the equator. Longitude lines run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, measuring distance east or west of the prime meridian.
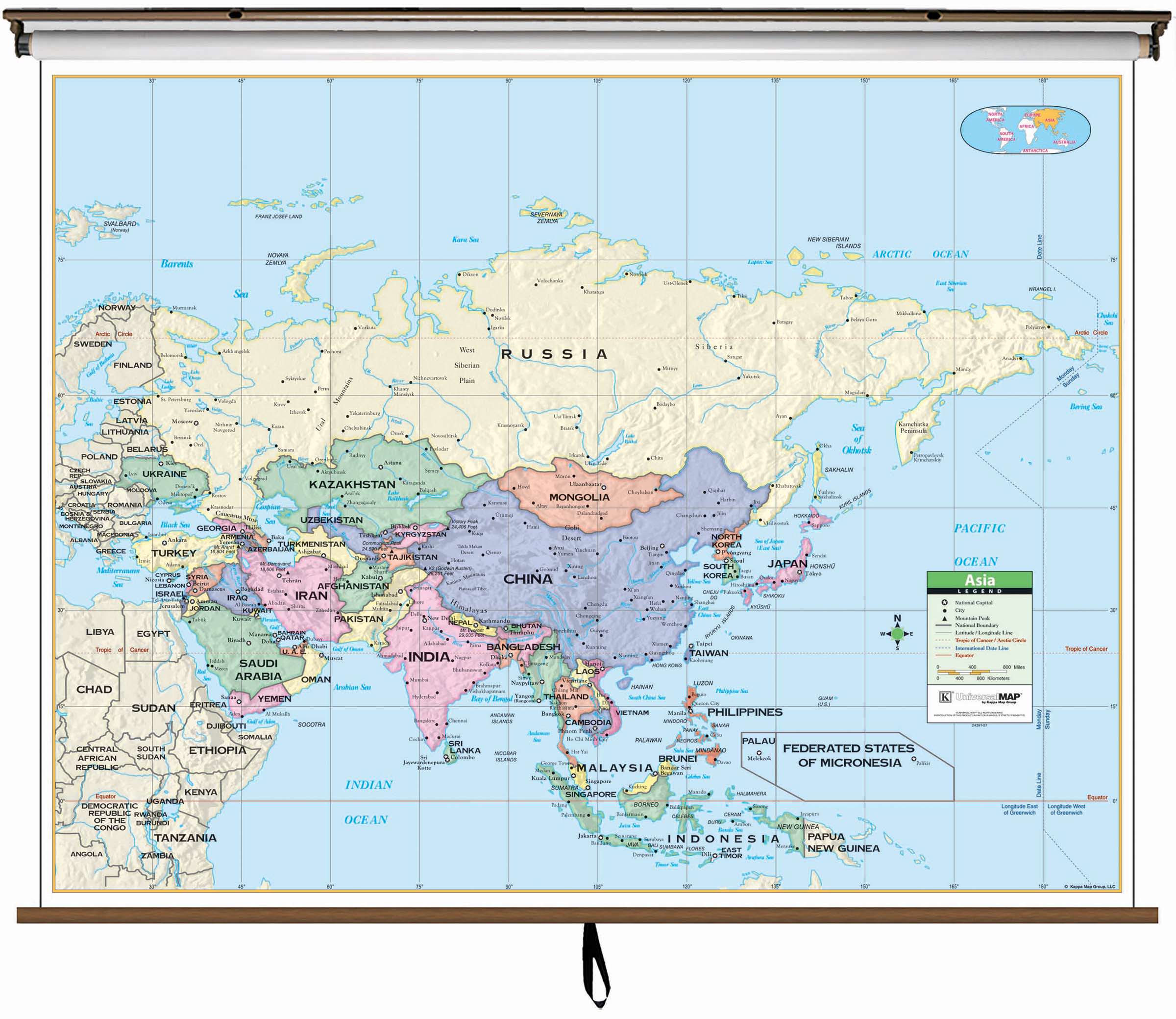
Asia’s Geographic Coordinates: A Detailed Exploration
Asia’s geographic coordinates reveal a fascinating array of landscapes, climates, and cultural influences.
- Northernmost Point: The northernmost point of Asia is Cape Chelyuskin in Russia, located at approximately 77° 43′ N, 104° 18′ E.
- Southernmost Point: The southernmost point of Asia is the southern tip of the Indonesian island of Roti, located at approximately 11° 07′ S, 123° 26′ E.
- Easternmost Point: The easternmost point of Asia is Cape Dezhnev in Russia, located at approximately 66° 05′ N, 169° 40′ W.
- Westernmost Point: The westernmost point of Asia is the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, located at approximately 12° 40′ N, 43° 19′ E.
Understanding Asia’s Geographic Diversity Through Latitude and Longitude
Latitude and longitude reveal the remarkable diversity of Asia’s terrain, climate, and human settlements.
- High Latitude Regions: The northernmost regions of Asia, including Siberia and parts of Mongolia, fall within high latitudes. These areas experience extremely cold winters and short, cool summers due to their distance from the equator.
- Mid-Latitude Regions: The majority of Asia falls within the mid-latitude range, experiencing a wide variety of climates. This region encompasses diverse landscapes, from the fertile plains of China and India to the mountainous terrain of the Himalayas.
- Low Latitude Regions: Southeast Asia and parts of South Asia fall within low latitudes, characterized by tropical climates with high temperatures and abundant rainfall. These regions are home to lush rainforests, dense mangrove swamps, and vibrant coral reefs.
The Significance of Latitude and Longitude in Asia
Understanding Asia’s latitude and longitude is critical for various reasons:
- Navigation and Travel: Latitude and longitude are essential for navigation, particularly for air and sea travel. They allow for precise location identification, facilitating efficient route planning and safe travel.
- Climate and Weather Prediction: Latitude plays a significant role in determining climate patterns. The distance from the equator dictates the amount of solar radiation received, influencing temperature and precipitation levels. This information is crucial for weather forecasting and agricultural planning.
- Resource Management: Latitude and longitude help identify areas with specific resources, such as fertile land, mineral deposits, and water sources. This information is vital for resource management, economic development, and environmental protection.
- Geopolitical Understanding: Latitude and longitude provide insights into the geopolitical landscape of Asia. They reveal the proximity of countries, their access to key waterways, and their strategic locations. This understanding is crucial for diplomacy, security, and conflict resolution.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude in Asia
1. What is the importance of the equator in relation to Asia?
The equator is a significant line of latitude that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is a key reference point for understanding climate patterns, as regions closer to the equator experience higher temperatures and more consistent weather patterns.
2. How does longitude influence time zones in Asia?
Longitude determines time zones. As the Earth rotates on its axis, different regions experience sunrise and sunset at different times. Time zones are based on longitude, with each zone representing approximately 15 degrees of longitude. Asia has multiple time zones, reflecting its vast east-west expanse.
3. How can I use latitude and longitude to locate specific places in Asia?
Latitude and longitude coordinates can be used to pinpoint specific locations on maps, using online mapping tools or GPS devices. These coordinates provide precise information about a location’s position relative to the equator and the prime meridian.
4. What are the benefits of using latitude and longitude for geographical research in Asia?
Latitude and longitude provide a standardized and precise system for describing locations, enabling accurate data collection and analysis. They facilitate the study of spatial patterns, resource distribution, population density, and other geographical phenomena.
5. How can I learn more about the geographic coordinates of specific countries or regions in Asia?
Numerous online resources, including mapping websites, encyclopedias, and scientific databases, provide detailed information about the latitude and longitude of specific locations in Asia. These resources can be valuable tools for students, researchers, and anyone interested in exploring the region’s geography.
Tips for Using Latitude and Longitude in Asia
- Use Online Mapping Tools: Utilize online mapping websites like Google Maps, Bing Maps, or OpenStreetMap to visualize latitude and longitude coordinates. These tools allow you to explore specific locations and their surrounding areas, providing valuable geographical insights.
- Learn to Read Latitude and Longitude Coordinates: Familiarize yourself with the format of latitude and longitude coordinates, which typically involve degrees, minutes, and seconds. This knowledge will help you interpret and understand geographical data.
- Consider the Impact of Latitude on Climate: When studying Asia, consider how latitude influences climate patterns. Regions closer to the equator experience warmer temperatures and more consistent weather, while regions further north or south experience colder temperatures and more seasonal variation.
- Explore the Relationship between Latitude and Longitude: Remember that latitude and longitude work together to define a precise location on Earth’s surface. Understanding the interplay between these coordinates is crucial for comprehending geographical relationships and spatial patterns.
- Utilize Latitude and Longitude for Travel Planning: When planning travel to Asia, use latitude and longitude coordinates to find specific destinations, map out routes, and estimate travel times. This information can enhance your travel experience and ensure a smooth journey.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude are fundamental tools for understanding Asia’s vast and diverse landscape. They provide a precise system for locating places, analyzing geographic patterns, and navigating the continent’s complex geopolitical landscape. By leveraging these coordinates, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships between geography, climate, culture, and human activity in Asia, fostering a more informed and nuanced understanding of this dynamic region.
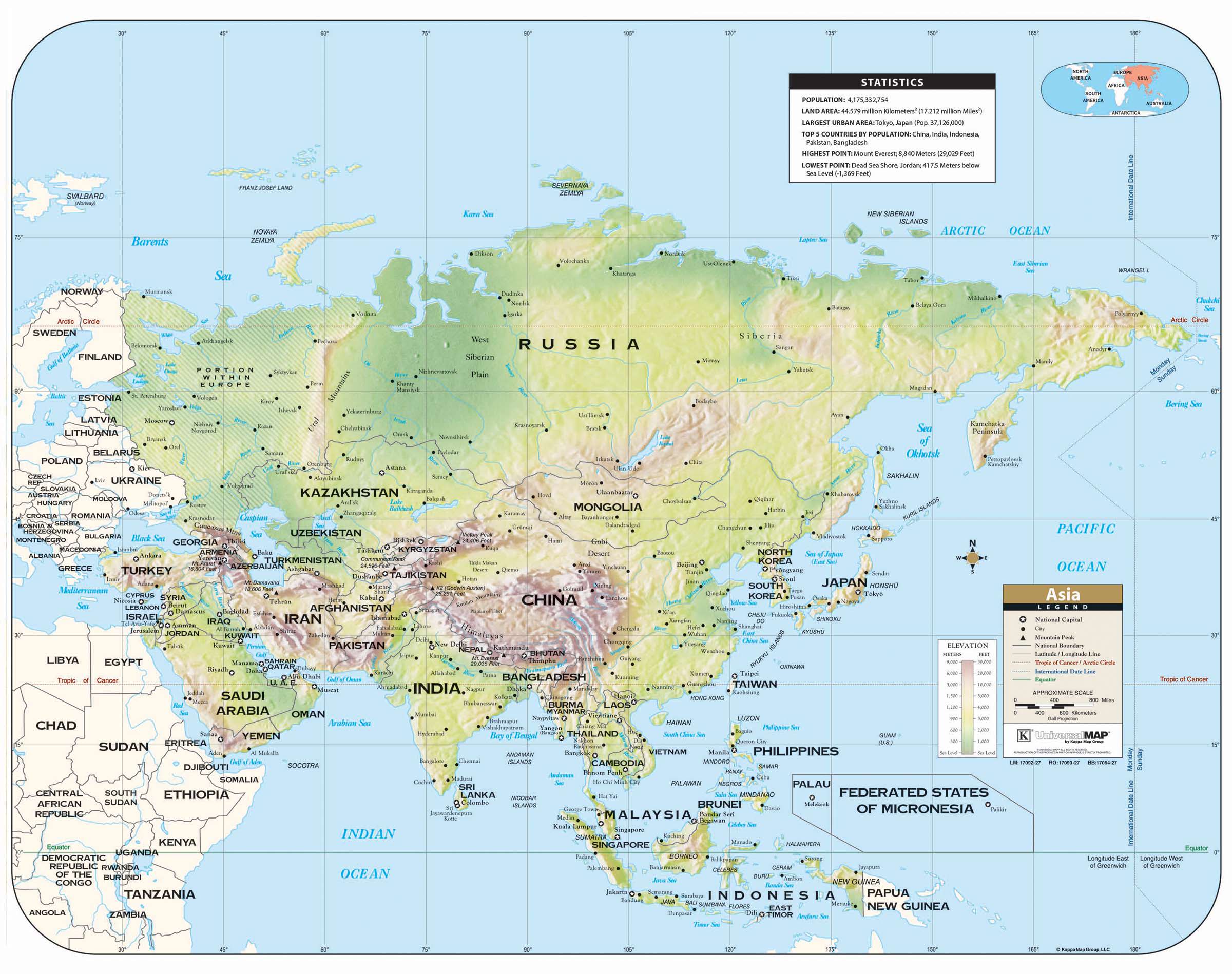
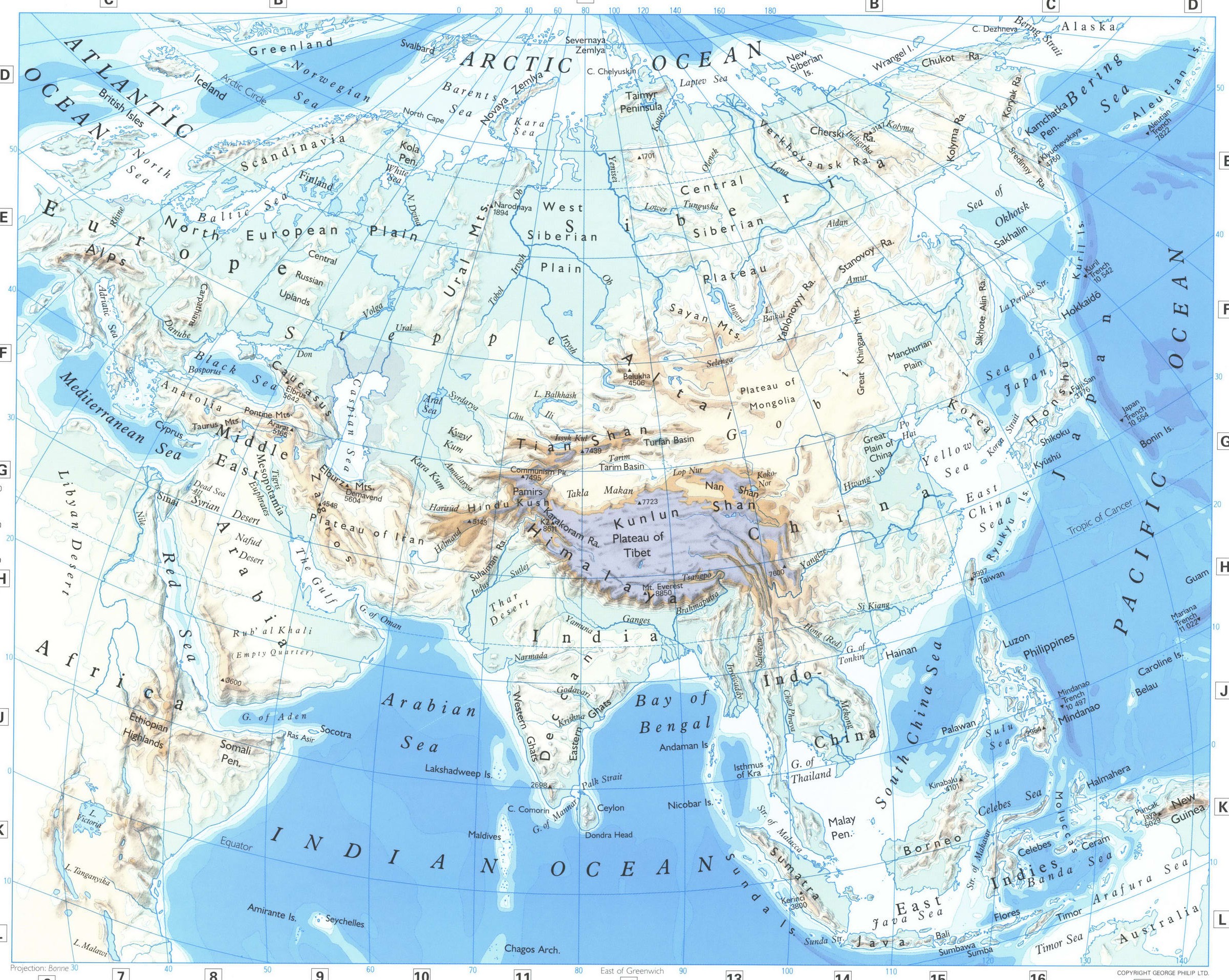

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Asian Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!