Decoding the Weather: Understanding Weather Map Lines and Their Significance
Related Articles: Decoding the Weather: Understanding Weather Map Lines and Their Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Decoding the Weather: Understanding Weather Map Lines and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Decoding the Weather: Understanding Weather Map Lines and Their Significance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Decoding the Weather: Understanding Weather Map Lines and Their Significance
- 3.1 Isobars: Lines of Equal Pressure
- 3.2 Isotherms: Lines of Equal Temperature
- 3.3 Fronts: Boundaries of Air Masses
- 3.4 Interpreting Weather Maps: A Comprehensive Approach
- 3.5 FAQs About Weather Map Lines
- 3.6 Tips for Using Weather Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Importance of Weather Map Lines
- 4 Closure
Decoding the Weather: Understanding Weather Map Lines and Their Significance
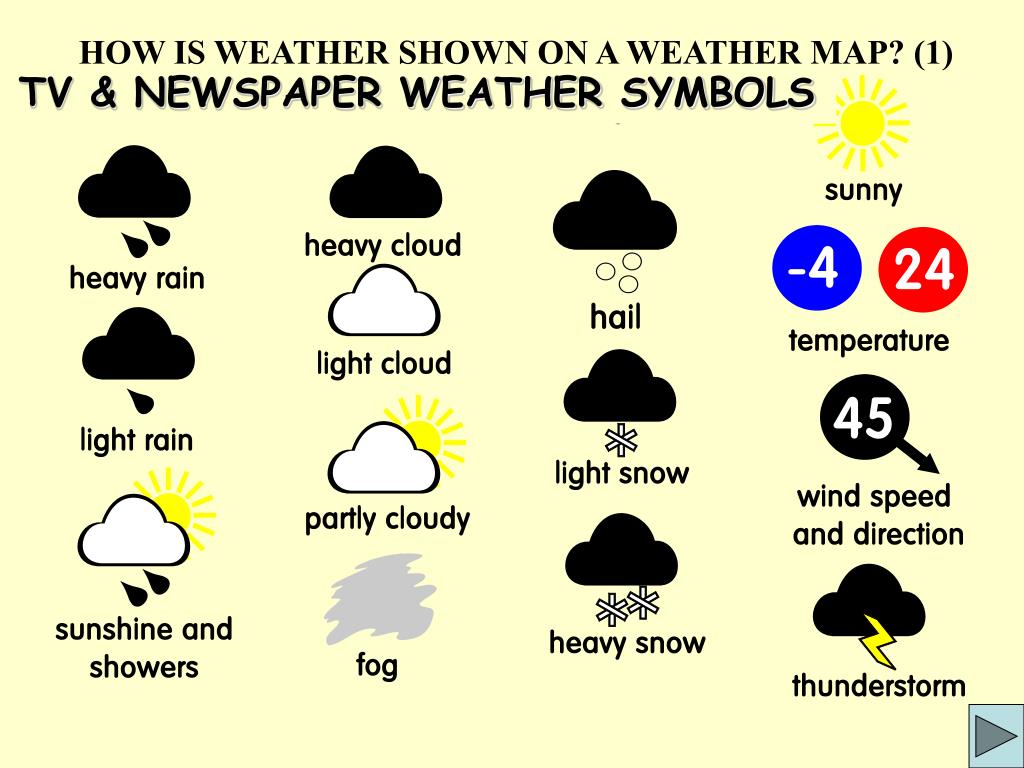
Weather maps, those intricate diagrams often seen in news reports and weather apps, are more than just a collection of lines and symbols. These lines, known as isobars, isotherms, and fronts, are the visual language of meteorologists, revealing crucial information about atmospheric conditions and predicting future weather patterns. Understanding these lines and their significance is key to comprehending the complex dynamics of the atmosphere and making informed decisions about our daily lives.
Isobars: Lines of Equal Pressure
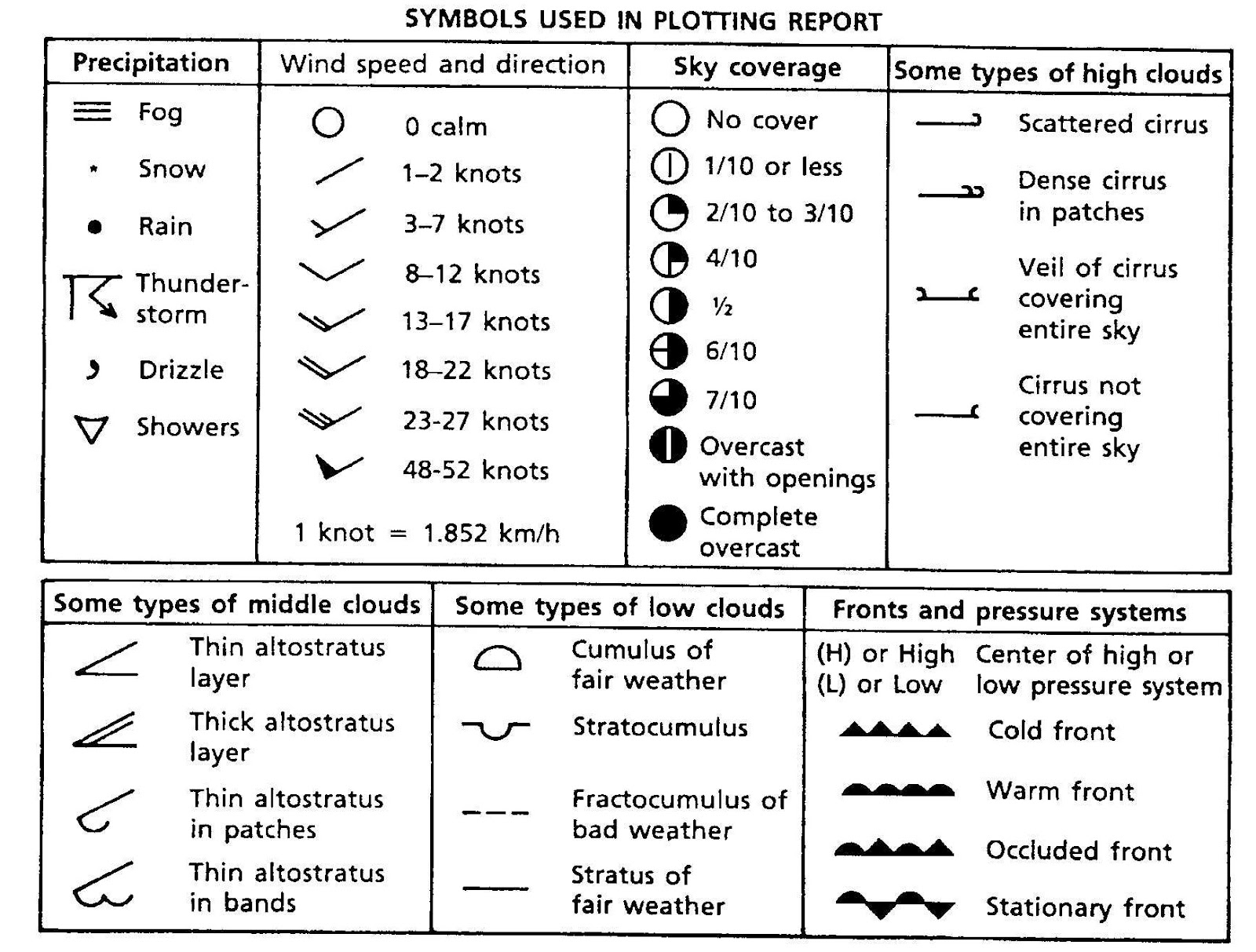
Isobars are lines drawn on weather maps connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. These lines are essential for understanding the movement of air, as air tends to flow from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. The closer the isobars are to each other, the steeper the pressure gradient, indicating a stronger wind. Conversely, widely spaced isobars suggest a gentle pressure gradient and lighter winds.
Importance of Isobars:
- Wind Prediction: Isobars are fundamental for forecasting wind speed and direction. The closer the isobars, the stronger the wind.
- Weather System Identification: Isobars help identify weather systems like high-pressure systems (anticyclones) and low-pressure systems (cyclones). High-pressure systems are associated with clear skies and calm weather, while low-pressure systems bring clouds, precipitation, and potentially stormy conditions.
- Understanding Air Movement: Isobars provide a visual representation of the flow of air, enabling meteorologists to understand how air masses move and interact, leading to various weather phenomena.
Isotherms: Lines of Equal Temperature
Isotherms are lines drawn on weather maps connecting points of equal temperature. These lines provide a snapshot of the temperature distribution across a geographical area, highlighting temperature gradients and revealing the influence of factors like latitude, altitude, and proximity to water bodies.
Importance of Isotherms:
- Temperature Distribution: Isotherms offer a visual representation of temperature variations across a region, allowing for a clear understanding of temperature gradients.
- Identifying Temperature Inversions: Isotherms can reveal temperature inversions, where warmer air sits above cooler air, creating stable atmospheric conditions that can trap pollutants and contribute to smog formation.
- Understanding Climate Patterns: Isotherms play a crucial role in understanding regional climate patterns, identifying areas with similar temperatures and highlighting the influence of geographical features on temperature distribution.
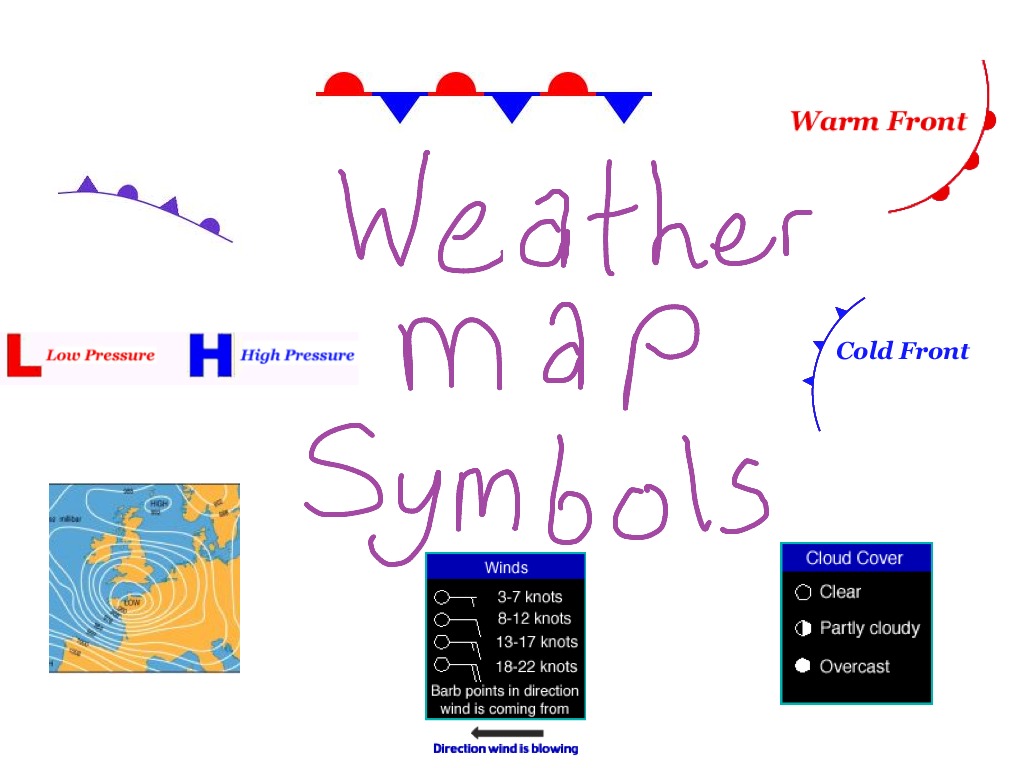
Fronts: Boundaries of Air Masses
Fronts are boundaries between different air masses, characterized by significant changes in temperature, humidity, and wind direction. These boundaries are represented on weather maps by lines with specific symbols, indicating the type of front and its movement.
Types of Fronts:
- Cold Front: A cold front occurs when a colder air mass displaces a warmer air mass. Cold fronts are associated with strong winds, heavy precipitation, and rapid temperature drops.
- Warm Front: A warm front occurs when a warmer air mass displaces a colder air mass. Warm fronts are associated with light to moderate precipitation, rising temperatures, and cloud formation.
- Stationary Front: A stationary front occurs when two air masses meet but neither is strong enough to displace the other. Stationary fronts can bring prolonged periods of precipitation and cloud cover.
- Occluded Front: An occluded front occurs when a cold front overtakes a warm front, lifting the warmer air mass off the ground. Occluded fronts are associated with complex weather patterns, including heavy precipitation and strong winds.
Importance of Fronts:
- Weather Prediction: Fronts are crucial for predicting short-term weather changes, as they bring abrupt shifts in temperature, precipitation, and wind conditions.
- Severe Weather Potential: Fronts, especially cold fronts, can trigger severe weather events like thunderstorms, tornadoes, and heavy snowstorms.
- Understanding Weather Systems: Fronts are fundamental to understanding the dynamics of weather systems, as they represent the boundaries where air masses interact and create the conditions for various weather phenomena.
Interpreting Weather Maps: A Comprehensive Approach
Reading weather maps effectively requires a holistic understanding of the interplay between isobars, isotherms, and fronts. By analyzing the position, orientation, and density of these lines, meteorologists can gain valuable insights into the current state of the atmosphere and predict future weather developments.
Key Considerations:
- Isobar Density: Closely spaced isobars indicate strong winds, while widely spaced isobars suggest lighter winds.
- Isotherm Orientation: Isotherms can reveal temperature gradients and identify temperature inversions.
- Front Location and Movement: Fronts indicate boundaries between air masses and predict shifts in temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns.
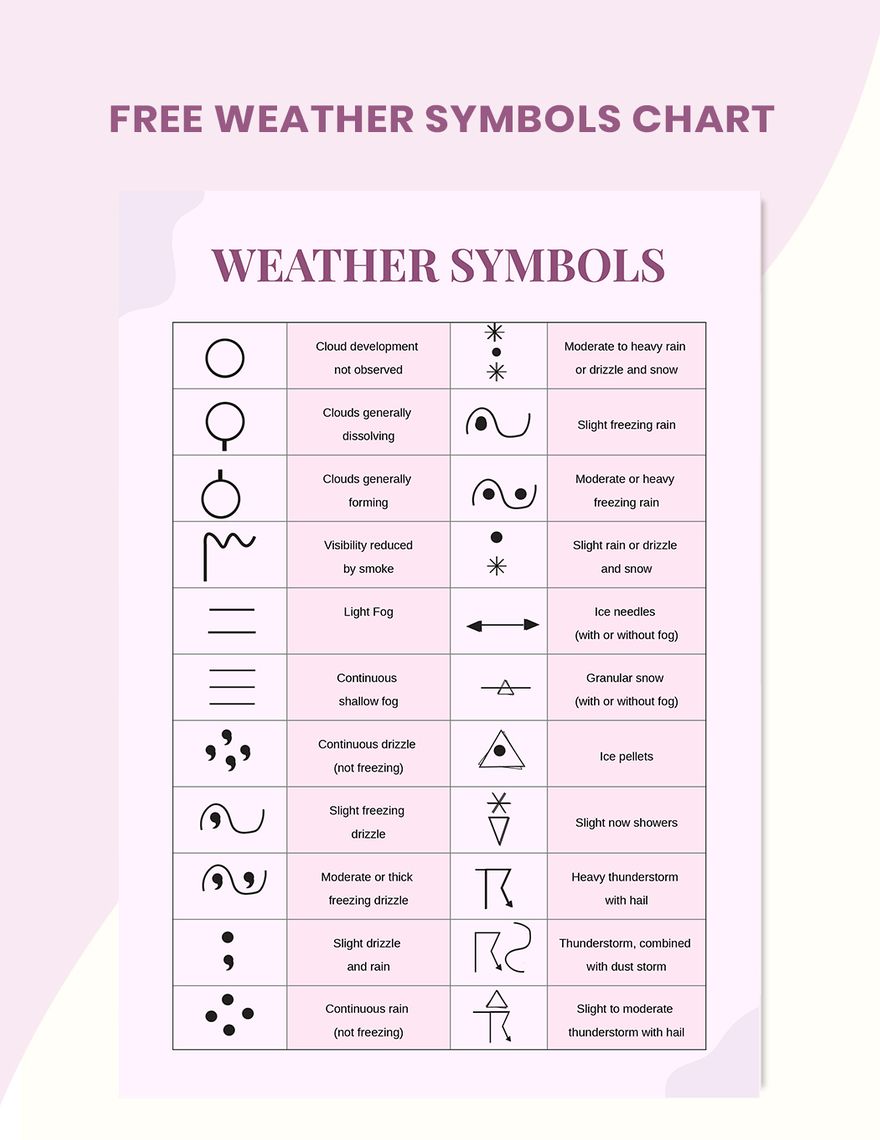
- Symbol Interpretation: Weather map symbols represent various weather phenomena like precipitation, cloud cover, and wind direction.
Benefits of Understanding Weather Maps:
- Informed Decision Making: Weather maps provide valuable information for individuals and organizations to make informed decisions about daily activities, travel plans, and outdoor events.
- Safety and Preparedness: Understanding weather maps helps individuals and communities prepare for potential severe weather events, mitigating risks and ensuring safety.
- Environmental Awareness: Weather maps provide insights into the complex dynamics of the atmosphere, fostering environmental awareness and understanding the interconnectedness of weather patterns and climate change.
FAQs About Weather Map Lines
1. What is the difference between an isobar and an isotherm?
Isobars are lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure, while isotherms connect points of equal temperature. Isobars are crucial for understanding wind patterns and weather systems, while isotherms reveal temperature gradients and identify temperature inversions.
2. How do I determine the direction of wind from a weather map?
Wind blows from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. On a weather map, the wind direction is generally perpendicular to the isobars, with the wind blowing from the high-pressure side to the low-pressure side.
3. What are the different types of fronts, and what weather conditions do they bring?
There are four main types of fronts: cold fronts, warm fronts, stationary fronts, and occluded fronts. Each front brings distinct weather conditions, including changes in temperature, precipitation, and wind direction.
4. How can I use weather map lines to predict potential severe weather events?
Fronts, particularly cold fronts, can trigger severe weather events like thunderstorms, tornadoes, and heavy snowstorms. By monitoring the movement and interaction of fronts, meteorologists can identify areas at risk of severe weather and issue warnings accordingly.
5. How can I improve my ability to interpret weather maps?
To improve your understanding of weather maps, familiarize yourself with the symbols used, practice interpreting isobars, isotherms, and fronts, and consult weather reports and forecasts to correlate map data with actual weather conditions.
Tips for Using Weather Maps Effectively
- Familiarize yourself with symbols: Learn the symbols used on weather maps to represent various weather phenomena, including precipitation, cloud cover, wind direction, and temperature.
- Focus on isobars, isotherms, and fronts: Pay attention to the position, orientation, and density of these lines to understand wind patterns, temperature gradients, and weather system movement.
- Consult weather reports and forecasts: Correlate map data with actual weather conditions by checking weather reports and forecasts for additional information and context.
- Practice interpreting maps: Regularly review weather maps and practice interpreting the information they convey to enhance your understanding and improve your ability to predict weather changes.
- Utilize online resources: Explore online weather websites and apps that provide interactive weather maps, animations, and detailed explanations of weather phenomena.
Conclusion: The Importance of Weather Map Lines
Weather map lines, including isobars, isotherms, and fronts, are essential tools for meteorologists and the general public alike. They provide a visual representation of atmospheric conditions, allowing for informed decisions about daily activities, travel plans, and preparedness for potential severe weather events. By understanding the significance of these lines and the information they convey, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex dynamics of the atmosphere and make informed choices to ensure safety and well-being.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding the Weather: Understanding Weather Map Lines and Their Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!