A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Germany in 1900
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Germany in 1900
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Germany in 1900. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Germany in 1900
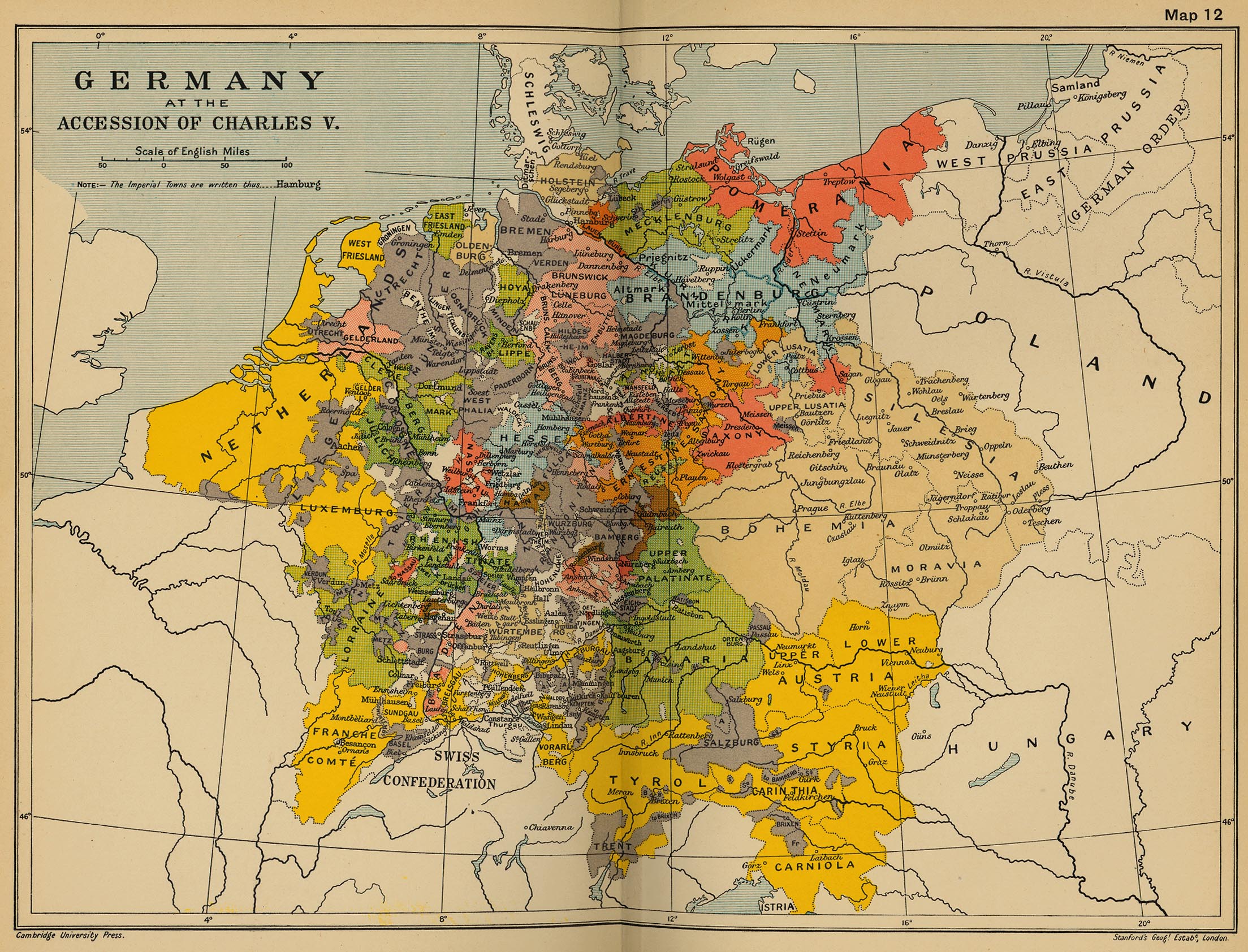
The year 1900 marks a pivotal point in German history, a time of burgeoning industrialization, burgeoning national pride, and a burgeoning sense of power on the world stage. This era is reflected in the map of Germany in 1900, a complex tapestry of political boundaries, ethnicities, and economic forces that shaped the nation’s destiny.
The Political Landscape: A Mosaic of Kingdoms and States
The map of Germany in 1900 presents a fragmented picture, far removed from the unified nation we know today. The German Empire, established in 1871, was a patchwork of 26 kingdoms, grand duchies, duchies, principalities, and free cities. These entities, each with its own unique history, traditions, and political structures, were bound together by a shared language, culture, and a powerful sense of national identity.
The Importance of the Map:
Understanding the map of Germany in 1900 provides a vital lens through which to analyze the nation’s political, social, and economic development. This historical snapshot reveals:
- The Legacy of German Unification: The map highlights the recent unification of the German states under the Prussian leadership, demonstrating the power dynamics and regional differences that continued to shape the nation.
- The Rise of Prussia: The map clearly illustrates the dominance of Prussia, both in terms of size and influence. Its vast territories and strategic location were crucial to the unification process and subsequent rise of the German Empire.
- The Power of the Bundesrat: The map underscores the importance of the Bundesrat, the council of representatives from the individual states, in shaping national policy. This decentralized structure, while fostering a sense of regional autonomy, also presented challenges to the centralized authority of the Kaiser.
- The Impact of Colonialism: The map also reflects Germany’s expanding colonial ambitions. By 1900, Germany had established colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific, signifying its growing global influence and contributing to the tensions that would lead to World War I.
A Deeper Dive into the Map: Key Territories and Their Significance
- Prussia: The largest and most influential state, Prussia dominated the German Empire. Its vast territories, including the strategically important provinces of Brandenburg, Pomerania, and Silesia, fueled its economic and military power.
- Bavaria: A powerful kingdom in southern Germany, Bavaria retained a significant degree of autonomy and often challenged Prussian dominance. Its rich cultural heritage and strong sense of regional identity contributed to a complex relationship with the rest of Germany.
- Saxony: Located in eastern Germany, Saxony was a major industrial center, renowned for its textile production and mining industries. Its economic prosperity and cultural achievements made it a prominent player in the German Empire.
- Württemberg: Situated in southwestern Germany, Württemberg was a significant industrial and agricultural region. Its strong sense of independence and its commitment to social welfare programs contributed to its distinctive character.
- Alsace-Lorraine: This region, annexed from France in 1871, was a constant source of tension between Germany and France. Its strategic location and mixed ethnicities fueled nationalist sentiments on both sides of the border.
The Ethnic Mosaic: A Diverse Nation
The map of Germany in 1900 also reveals a diverse ethnic landscape. While German was the dominant language, pockets of other ethnicities, including Polish, Danish, and French, existed within the borders of the empire. This ethnic diversity, while enriching German culture, also contributed to political tensions and nationalist aspirations.
Economic Development: The Rise of Industry
The map of Germany in 1900 reflects the nation’s rapid industrialization. Major industrial centers, such as Essen, Dortmund, and Leipzig, dotted the map, showcasing the growth of heavy industries like coal mining, steel production, and textiles. This economic boom transformed German society, leading to urbanization, social change, and the emergence of a powerful industrial working class.
The Map as a Catalyst for Change
The map of Germany in 1900 is not merely a static representation of a historical moment. It serves as a springboard for understanding the forces that shaped the nation’s future. The political fragmentation, ethnic diversity, and economic dynamism depicted on the map contributed to the social and political tensions that culminated in the First World War.
FAQs about the Map of Germany in 1900
-
What was the status of the German Empire in 1900?
The German Empire, established in 1871, was a federation of 26 states with a powerful Prussian leadership. -
What were the major economic centers of Germany in 1900?
Major industrial centers like Essen, Dortmund, and Leipzig thrived on coal mining, steel production, and textiles. -
What were the main ethnicities present in Germany in 1900?
While German was the dominant language, pockets of Polish, Danish, and French communities existed within the empire. -
How did the map of Germany in 1900 influence the country’s future?
The political fragmentation, ethnic diversity, and economic dynamism depicted on the map contributed to the tensions that led to the First World War.
Tips for Studying the Map of Germany in 1900
- Pay attention to the scale: The map’s scale provides a crucial understanding of the relative size and importance of different states and regions.
- Analyze the boundaries: The map’s political boundaries reveal the intricate political structure of the German Empire, highlighting the power dynamics and regional differences.
- Examine the major cities: The location of major cities provides insights into the economic and cultural centers of the German Empire.
- Consider the context: Remember that the map is a snapshot of a specific moment in time and reflects the historical events and forces that shaped the German Empire.
Conclusion
The map of Germany in 1900 is more than just a geographical representation. It is a powerful tool for understanding the complex forces that shaped the nation’s destiny. The political fragmentation, ethnic diversity, and economic dynamism depicted on the map provide a rich context for analyzing the social, political, and economic transformations that occurred in Germany during this pivotal era. By studying the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the challenges and opportunities that faced Germany at the dawn of the 20th century, a period that would forever alter the course of world history.
![German Empire Population Density 1900 [1500x1090] Cartography map](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/23/af/2a/23af2a675384fd0cedf06077bab5a18f.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Map of Germany in 1900. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!