A Comprehensive Guide to the Districts of Uganda: Understanding the Administrative Landscape
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Districts of Uganda: Understanding the Administrative Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Districts of Uganda: Understanding the Administrative Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Districts of Uganda: Understanding the Administrative Landscape
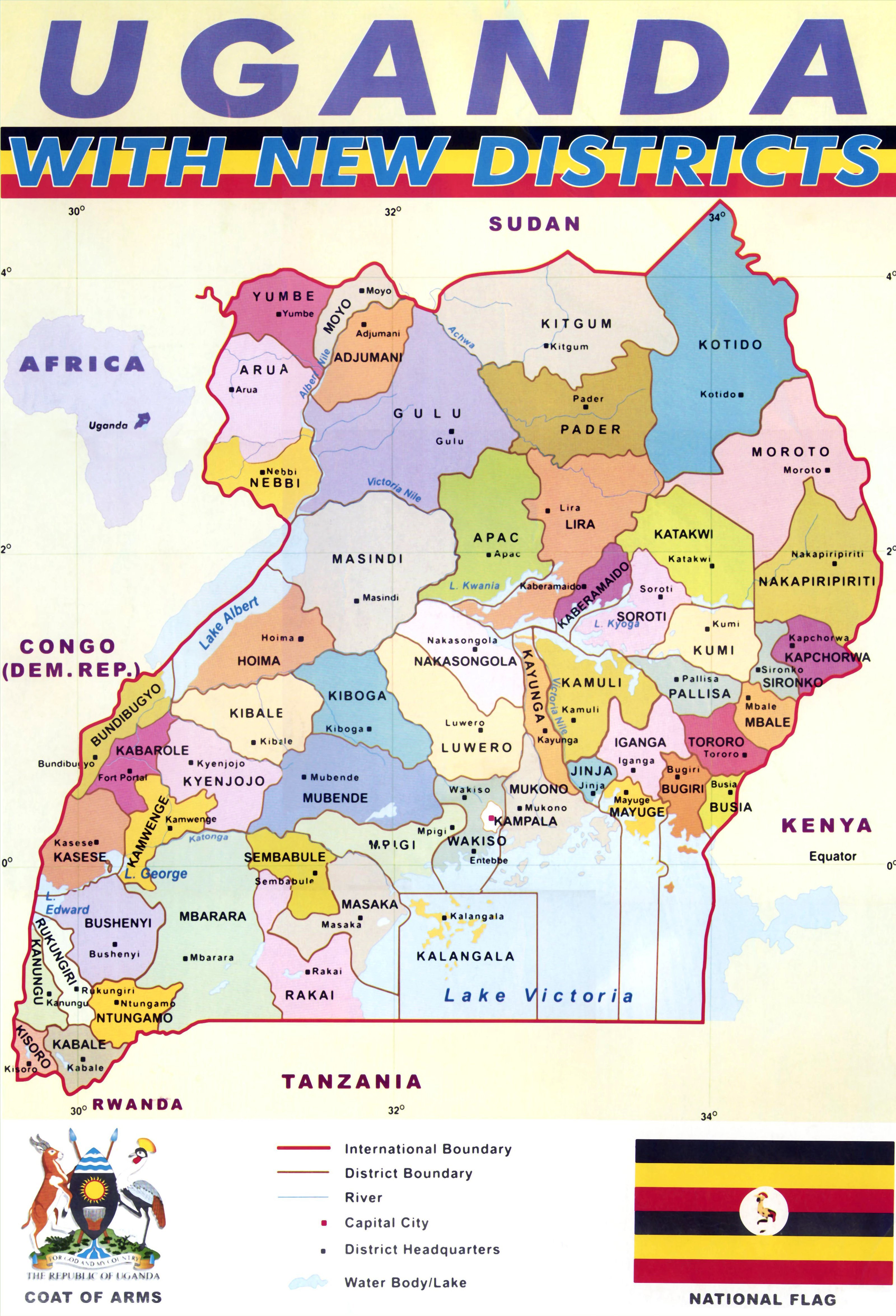
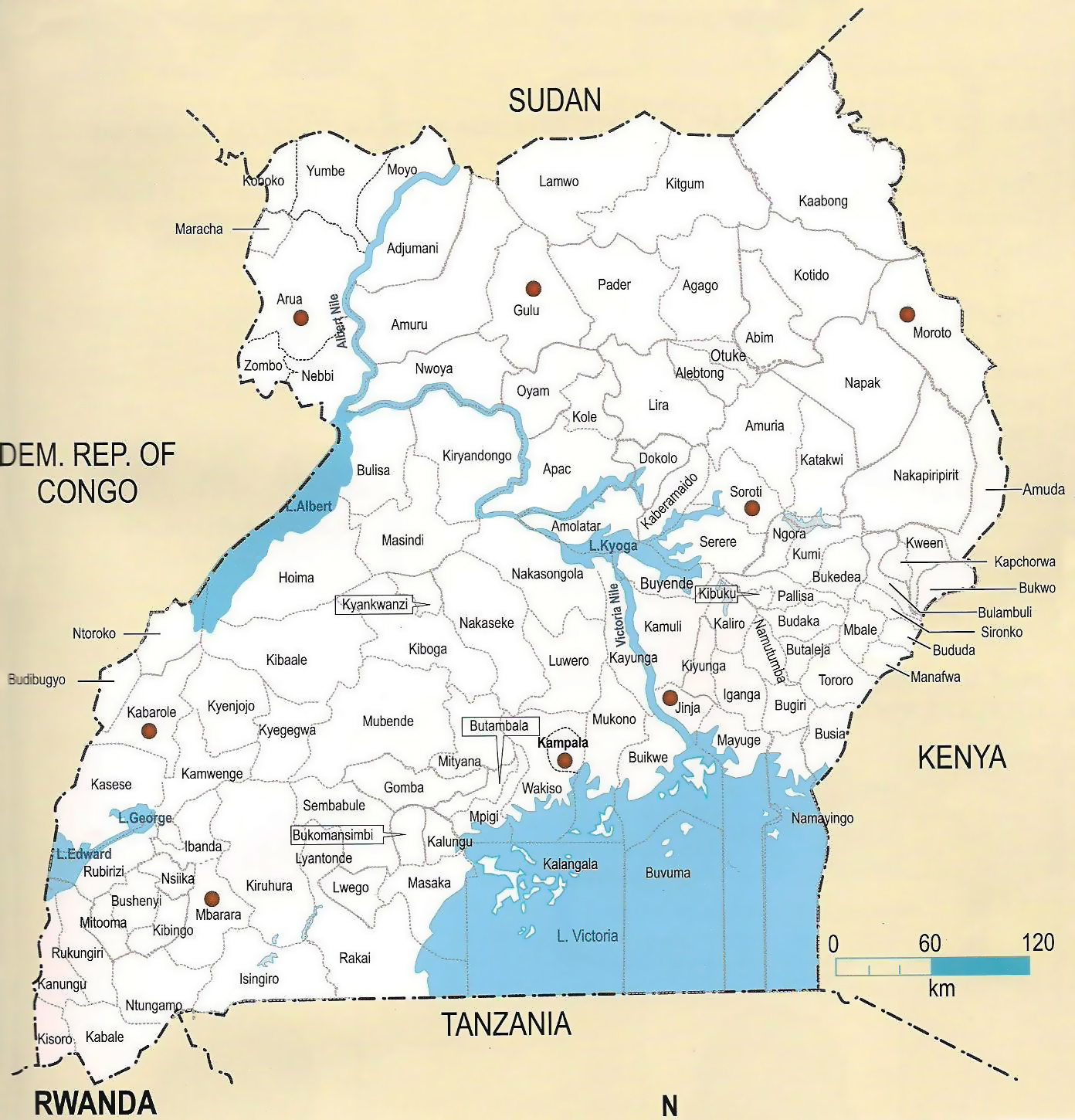
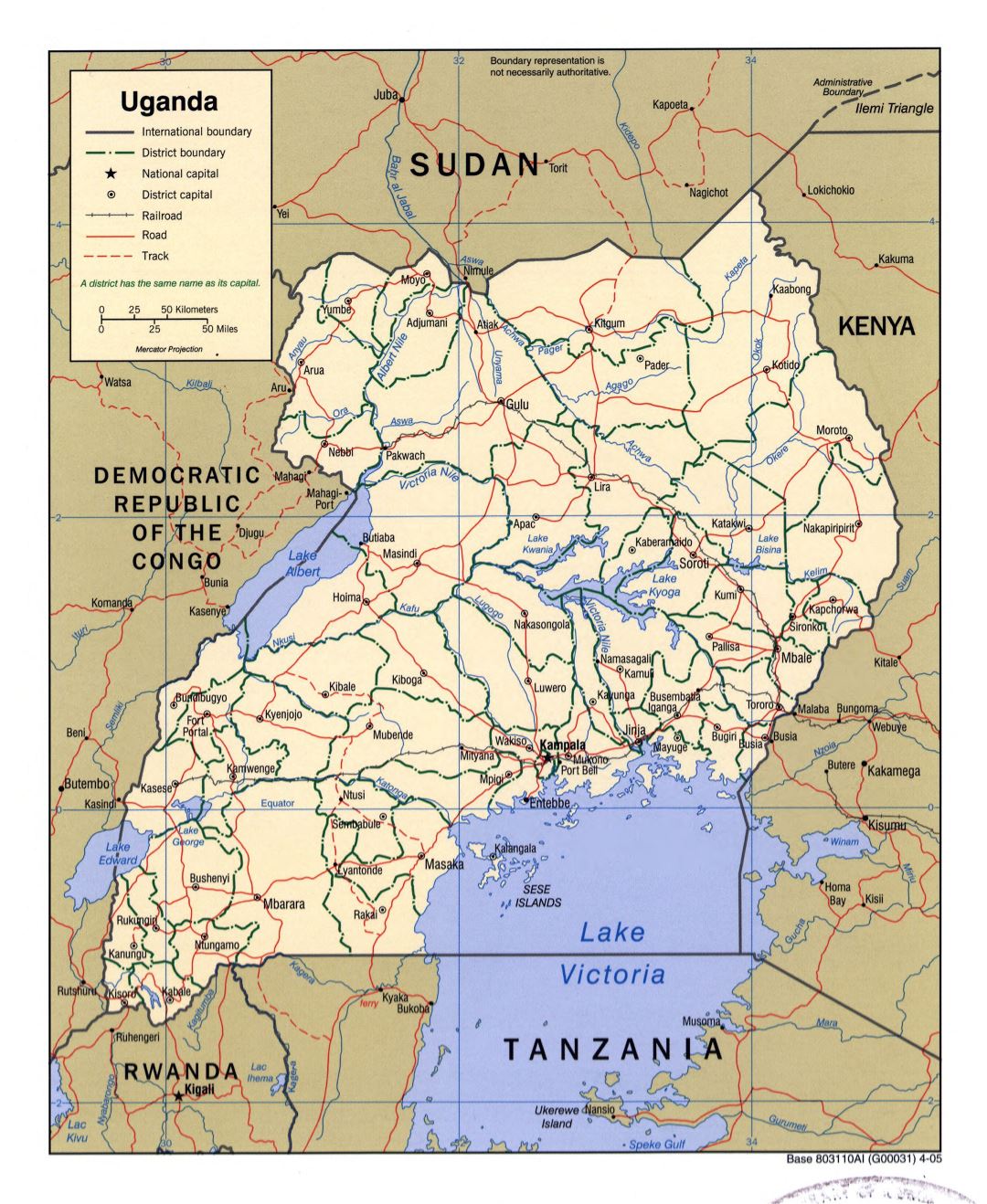
Uganda, a vibrant East African nation, is characterized by its diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and a dynamic administrative structure. At the heart of this structure lies the district, a crucial unit of governance and development. This article delves into the intricacies of Uganda’s district map, providing a comprehensive understanding of its evolution, importance, and practical applications.
A Historical Perspective: From Provinces to Districts
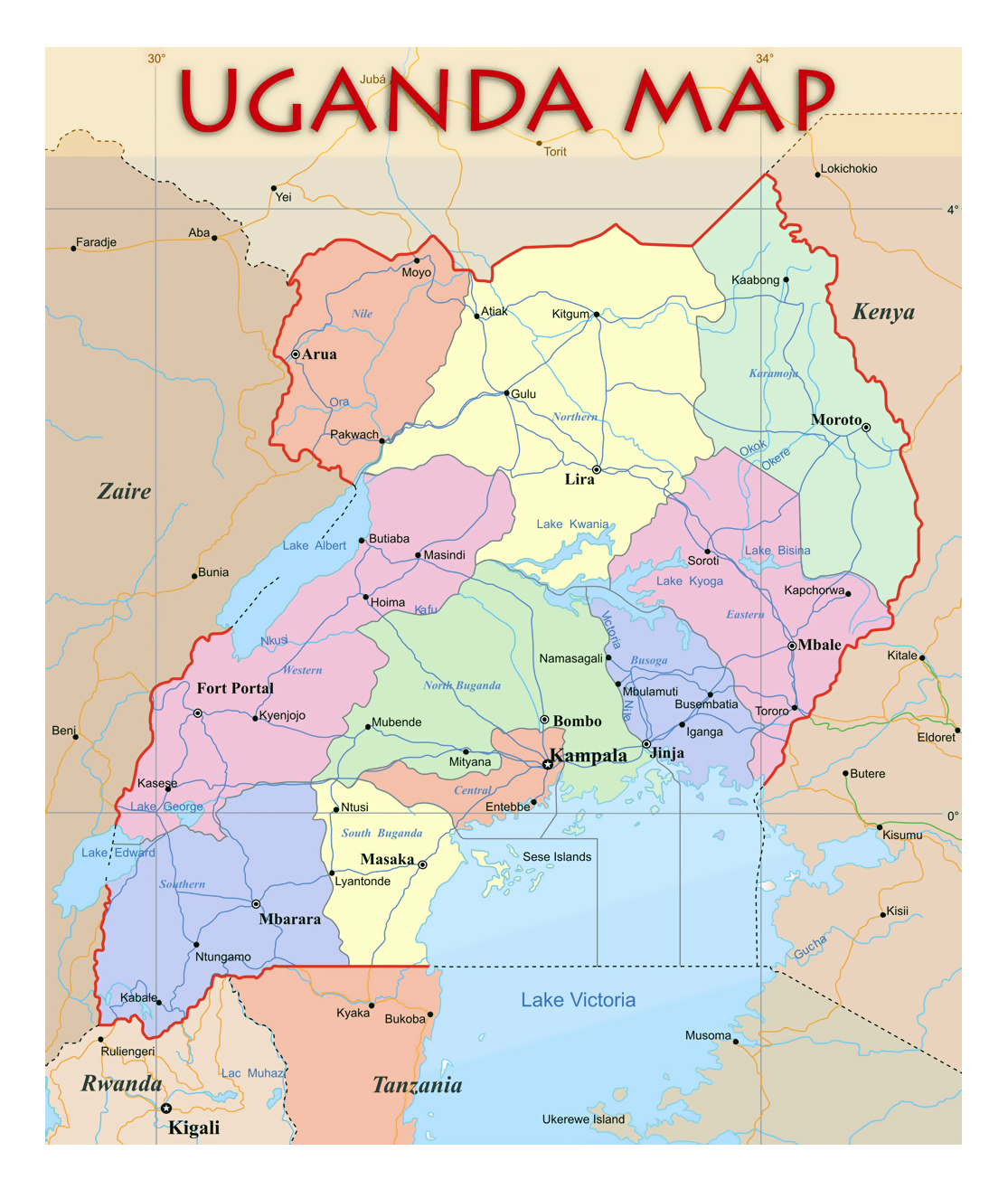
The current district map of Uganda is a product of a long historical evolution. Prior to 1966, the country was divided into four provinces: Buganda, Eastern, Northern, and Western. Each province was further subdivided into districts, with the number and boundaries of these districts evolving over time.
The 1966 Constitution abolished the provinces, creating a centralized system of governance. The districts continued to exist, but their role and responsibilities were redefined. In 1995, the new Constitution introduced a decentralized system of governance, further enhancing the significance of districts.
The District Map: A Vital Tool for Governance and Development
The district map of Uganda is a vital tool for understanding the country’s administrative landscape. It provides a clear visual representation of the geographical divisions and their corresponding administrative structures. Each district possesses its own unique characteristics, including:
- Population: Districts vary significantly in terms of population density, ranging from densely populated urban areas to sparsely populated rural regions.
- Geography: The diverse landscape of Uganda is reflected in the district map, with districts encompassing mountains, valleys, lakes, and plains.
- Economy: Districts exhibit distinct economic activities, from agriculture and tourism to mining and manufacturing.
- Culture: Uganda’s rich cultural tapestry is evident in the district map, with each district possessing its own traditions, languages, and customs.
Understanding the District Structure
Each district is headed by a District Local Government (DLG), which is responsible for delivering essential services to the local population. The DLG is composed of elected officials, including:
- District Chairperson: The political head of the district, responsible for overall leadership and coordination.
- District Council: A legislative body responsible for enacting local laws and policies.
- District Executive Committee (DEC): Responsible for implementing the decisions of the District Council.
The Importance of the District Map: Why it Matters
The district map of Uganda serves several crucial purposes:
- Decentralized Governance: The district map facilitates the implementation of Uganda’s decentralized governance system, empowering local communities to participate in decision-making processes.
- Development Planning: Districts are the primary units for development planning, enabling targeted interventions based on local needs and priorities.
- Resource Allocation: The district map assists in the efficient allocation of resources, ensuring that funds are directed to areas where they are most needed.
- Service Delivery: Districts play a vital role in the delivery of essential services, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
- Conflict Resolution: The district map helps to facilitate conflict resolution by providing a framework for addressing local grievances and promoting peacebuilding efforts.
The Evolution of the District Map: A Dynamic Landscape
Uganda’s district map is not static but has undergone significant transformations over the years. The creation of new districts and the adjustment of district boundaries are driven by several factors:
- Population Growth: As Uganda’s population continues to grow, the need for more efficient service delivery necessitates the creation of new districts.
- Political Considerations: The creation of new districts can also be influenced by political factors, such as the desire to enhance representation and promote local development.
- Economic Development: The emergence of new economic hubs can lead to the creation of new districts to cater to the needs of these growing areas.
Current District Structure: A Detailed Look
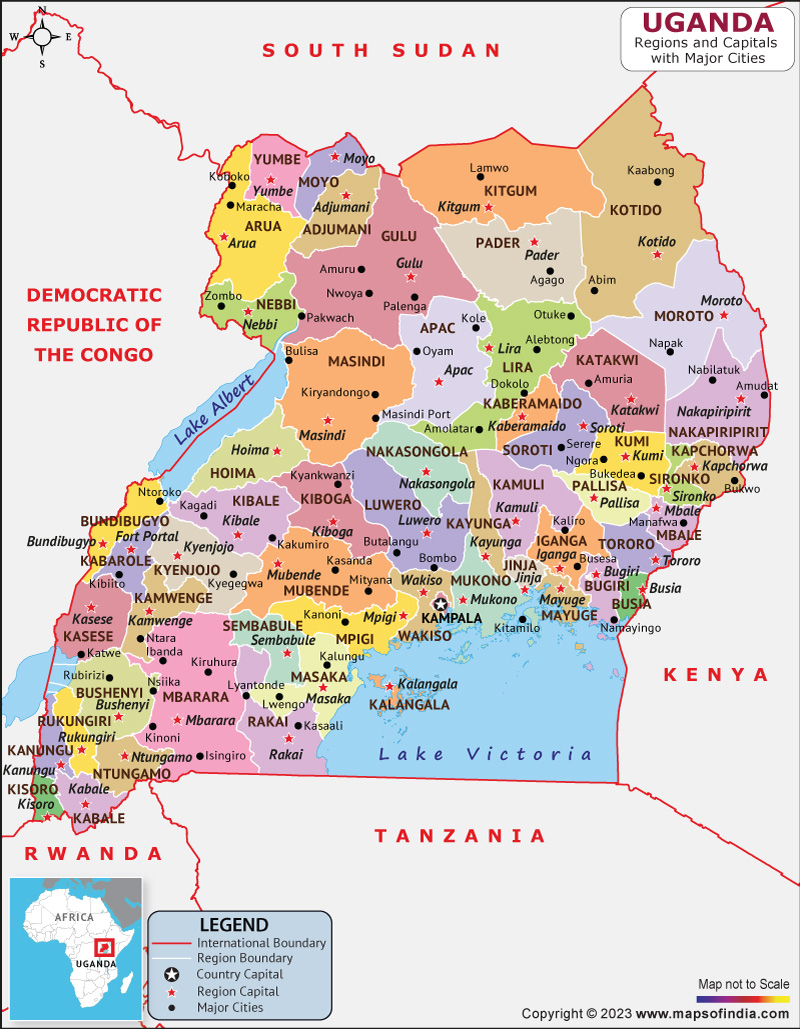
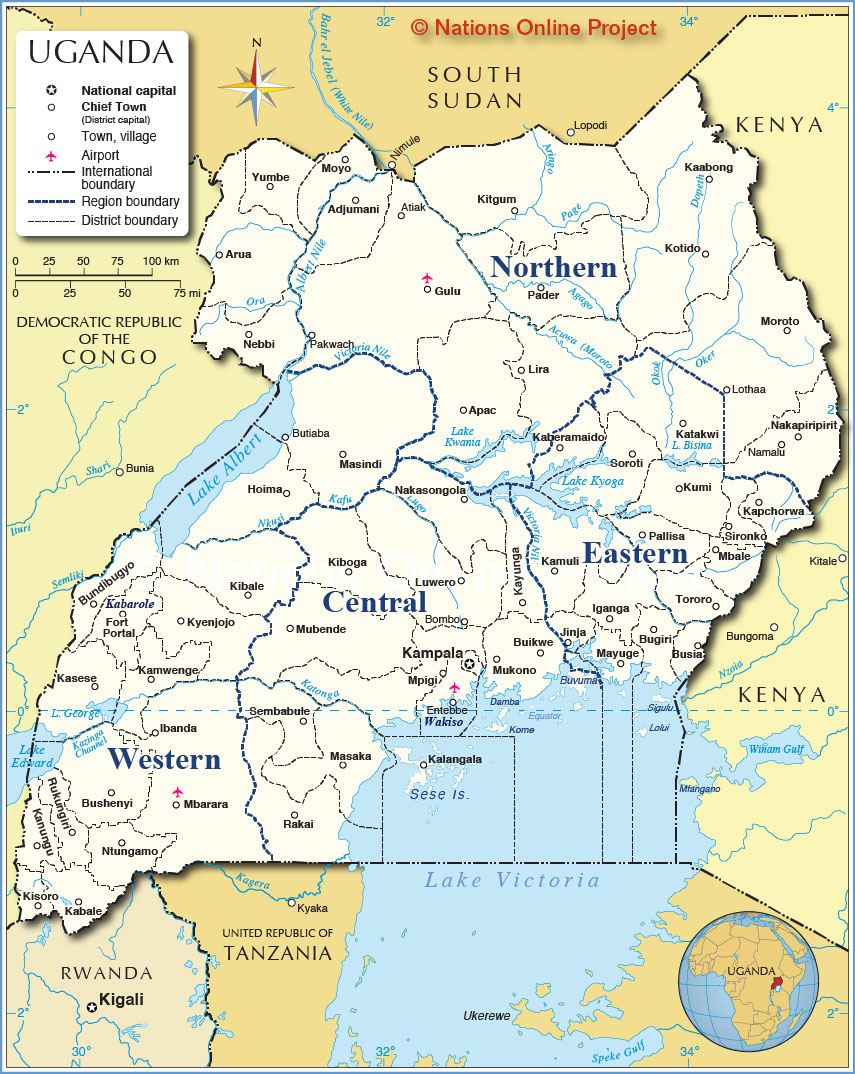
As of 2023, Uganda is divided into 146 districts, further categorized into four administrative regions:
- Central Region: This region encompasses the capital city, Kampala, and surrounding areas.
- Eastern Region: This region is characterized by its fertile agricultural lands and vibrant cultural traditions.
- Northern Region: This region is known for its diverse wildlife and natural beauty.
- Western Region: This region is home to the Rwenzori Mountains and the Queen Elizabeth National Park.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: How many districts are there in Uganda?
A: As of 2023, there are 146 districts in Uganda.
Q: What is the purpose of districts in Uganda?
A: Districts are the primary units of local governance in Uganda, responsible for delivering essential services, promoting development, and facilitating community participation in decision-making.
Q: How are districts created in Uganda?
A: The creation of new districts is typically initiated by a proposal from the local community, followed by a process of consultation and approval by the central government.
Q: What are the benefits of a decentralized governance system?
A: Decentralization empowers local communities, enhances service delivery, promotes economic development, and fosters greater political participation.
Q: What are the challenges facing Uganda’s district system?
A: Challenges include inadequate funding, lack of capacity, corruption, and political interference.
Tips for Navigating the District Map
- Use online resources: Websites like the Uganda Bureau of Statistics and the Ministry of Local Government provide comprehensive information on district boundaries, population data, and other relevant details.
- Consult local authorities: Local government offices can offer insights into specific districts, including their unique characteristics and development priorities.
- Explore district websites: Many districts have their own websites, providing information on local services, projects, and contact details.
Conclusion: A Vital Framework for Development
The district map of Uganda is a vital tool for understanding the country’s administrative landscape and its diverse socio-economic realities. It is a reflection of the country’s commitment to decentralized governance, promoting local development, and empowering communities. As Uganda continues to evolve, the district map will remain a crucial framework for shaping the country’s future, ensuring that development efforts are tailored to the unique needs and aspirations of each district.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Districts of Uganda: Understanding the Administrative Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!